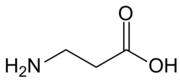
Chemistry:Β-Alanine
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
β-Alanine
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
3-Aminopropanoic acid | |
| Other names
3-Aminopropionic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties[1][2] | |
| C3H7NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 89.093 g/mol |
| Appearance | white bipyramidal crystals |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 1.437 g/cm3 (19 °C) |
| Melting point | 207 °C (405 °F; 480 K) (decomposes) |
| 54.5 g/100 mL | |
| Solubility | soluble in methanol. Insoluble in diethyl ether, acetone |
| log P | -3.05 |
| Acidity (pKa) |
|
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Irritant |
| Safety data sheet | [1] |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
1000 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
β-Alanine (or beta-alanine) is a naturally occurring beta amino acid, which is an amino acid in which the amino group is attached to the β-carbon (i.e. the carbon two carbon atoms away from the carboxylate group) instead of the more usual α-carbon for alanine (α-alanine). The IUPAC name for β-alanine is 3-aminopropanoic acid. Unlike its counterpart α-alanine, β-alanine has no stereocenter.
Biosynthesis and industrial route
In terms of its biosynthesis, it is formed by the degradation of dihydrouracil and carnosine. β-Alanine ethyl ester is the ethyl ester which hydrolyses within the body to form β-alanine.[3] It is produced industrially by the reaction of ammonia with β-propiolactone.[4]
Sources for β-alanine includes pyrimidine catabolism of cytosine and uracil.
Biochemical function
β-Alanine residues are rare. It is a component of the peptides carnosine and anserine and also of pantothenic acid (vitamin B5), which itself is a component of coenzyme A. β-alanine is metabolized into acetic acid.
Precursor of carnosine
β-Alanine is the rate-limiting precursor of carnosine, which is to say carnosine levels are limited by the amount of available β-alanine, not histidine.[5] Supplementation with β-alanine has been shown to increase the concentration of carnosine in muscles, decrease fatigue in athletes, and increase total muscular work done.[6][7] Simply supplementing with carnosine is not as effective as supplementing with β-alanine alone since carnosine, when taken orally, is broken down during digestion to its components, histidine and β-alanine. Hence, by weight, only about 40% of the dose is available as β-alanine.[5]

Because β-alanine dipeptides are not incorporated into proteins, they can be stored at relatively high concentrations. Occurring at 17–25 mmol/kg (dry muscle),[8] carnosine (β-alanyl-L-histidine) is an important intramuscular buffer, constituting 10-20% of the total buffering capacity in type I and II muscle fibres. In carnosine, the pKa of the imidazolium group is 6.83, which is ideal for buffering.[9]
Receptors
Even though much weaker than glycine (and, thus, with a debated role as a physiological transmitter), β-alanine is an agonist next in activity to the cognate ligand glycine itself, for strychnine-sensitive inhibitory glycine receptors (GlyRs) (the agonist order: glycine ≫ β-alanine > taurine ≫ alanine, L-serine > proline).[10]
β-alanine has five known receptor sites, including GABA-A, GABA-C a co-agonist site (with glycine) on NMDA receptors, the aforementioned GlyR site, and blockade of GAT protein-mediated glial GABA uptake, making it a putative "small molecule neurotransmitter."[11]
Athletic performance enhancement
There is evidence that β-alanine supplementation can increase exercise and cognitive performance,[12][13][14][15] for some sporting modalities,[16] and exercises within a 0.5–10 min time frame.[17] β-alanine is converted within muscle cells into carnosine, which acts as a buffer for the lactic acid produced during high-intensity exercises, and helps delay the onset of neuromuscular fatigue.[14][18]
Ingestion of β-alanine can cause paraesthesia, reported as a tingling sensation, in a dose-dependent fashion.[15] Aside from this, no important adverse effect of β-alanine has been reported, however, there is also no information on the effects of its long-term usage or its safety in combination with other supplements, and caution on its use has been advised.[12][13] Furthermore, many studies have failed to test for the purity of the supplements used and check for the presence of banned substances.[14]
Metabolism
β-Alanine can undergo a transamination reaction with pyruvate to form malonate-semialdehyde and L-alanine. The malonate semialdehyde can then be converted into malonate via malonate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase. Malonate is then converted into malonyl-CoA and enter fatty acid biosynthesis.[19]
Alternatively, β-alanine can be diverted into pantothenic acid and coenzyme A biosynthesis.[19]
References
- ↑ An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals (11th ed.), Merck, 1989, ISBN 091191028X, 196.
- ↑ Weast, Robert C., ed (1981). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (62nd ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. p. C-83. ISBN 0-8493-0462-8..
- ↑ Wright, Margaret Robson (1969). "Arrhenius parameters for the acid hydrolysis of esters in aqueous solution. Part I. Glycine ethyl ester, β-alanine ethyl ester, acetylcholine, and methylbetaine methyl ester". Journal of the Chemical Society B: Physical Organic: 707–710. doi:10.1039/J29690000707.
- ↑ Miltenberger, Karlheinz (2005). "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a13_507.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "Beta-Alanine Supplementation For Exercise Performance". http://pharmacistanswers.com/beta-alanine-supplementation-for-exercise-performance.html.
- ↑ "Beta-alanine supplementation augments muscle carnosine content and attenuates fatigue during repeated isokinetic contraction bouts in trained sprinters". J Appl Physiol 103 (5): 1736–43. August 9, 2007. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00397.2007. PMID 17690198.
- ↑ "Influence of beta-alanine supplementation on skeletal muscle carnosine concentrations and high intensity cycling capacity". Amino Acids 32 (2): 225–33. 2007. doi:10.1007/s00726-006-0364-4. PMID 16868650.
- ↑ Mannion, AF; Jakeman, PM; Dunnett, M; Harris, RC; Willan, PLT (1992). "Carnosine and anserine concentrations in the quadriceps femoris muscle of healthy humans". Eur. J. Appl. Physiol 64 (1): 47–50. doi:10.1007/BF00376439. PMID 1735411.
- ↑ Bate-Smith, EC (1938). "The buffering of muscle in rigor: protein, phosphate and carnosine". Journal of Physiology 92 (3): 336–343. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.1938.sp003605. PMID 16994977.
- ↑ Encyclopedia of Life Sciences Amino Acid Neurotransmitters. Jeremy M Henley, 2001 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. doi:10.1038/npg.els.0000010, Article Online Posting Date: April 19, 2001
- ↑ "Beta-alanine as a small molecule neurotransmitter". Neurochem Int 57 (3): 177–88. October 2010. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2010.06.001. PMID 20540981.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 "The effects of beta-alanine supplementation on performance: a systematic review of the literature". Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 24 (1): 14–27. 2014. doi:10.1123/ijsnem.2013-0007. PMID 23918656.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 "β-Alanine supplementation and military performance". Amino Acids 47 (12): 2463–74. 2015. doi:10.1007/s00726-015-2051-9. PMID 26206727.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 Hobson, R. M.; Saunders, B.; Ball, G.; Harris, R. C.; Sale, C. (9 December 2016). "Effects of β-alanine supplementation on exercise performance: a meta-analysis". Amino Acids 43 (1): 25–37. doi:10.1007/s00726-011-1200-z. ISSN 0939-4451. PMID 22270875.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 "International society of sports nutrition position stand: Beta-Alanine". J Int Soc Sports Nutr 12: 30. 2015. doi:10.1186/s12970-015-0090-y. PMID 26175657.
- ↑ Brisola, Gabriel M P; Zagatto, Alessandro M (2019). "Ergogenic Effects of β-Alanine Supplementation on Different Sports Modalities: Strong Evidence or Only Incipient Findings?". The Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research 33 (1): 253–282. doi:10.1519/JSC.0000000000002925. PMID 30431532.
- ↑ Bryan Saunders; Kirsty Elliott-Sale; Guilherme G Artioli1; Paul A Swinton; Eimear Dolan; Hamilton Roschel; Craig Sale; Bruno Gualano (2017). "β-alanine supplementation to improve exercise capacity and performance: a systematic review and meta-analysis FREE". British Journal of Sports Medicine 51 (8): 658–669. doi:10.1136/bjsports-2016-096396. PMID 27797728.
- ↑ Guilherme Giannini Artioli; Bruno Gualano; Abbie Smith; Jeffrey Stout; Antonio Herbert Lancha Jr. (June 2010). "Role of beta-alanine supplementation on muscle carnosine and exercise performance". Med Sci Sports Exerc 42 (6): 1162–73. doi:10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181c74e38. PMID 20479615.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 "KEGG PATHWAY: beta-Alanine metabolism - Reference pathway". http://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/show_pathway?scale=1.0&query=1.2.1.15&map=map00410&scale=&auto_image=&show_description=hide&multi_query=.
External links
 |

