Astronomy:List of quadrangles on Mars
From HandWiki
The surface of Mars has been divided into 30 quadrangles by the United States Geological Survey, so named because their borders lie along lines of latitude and longitude and so maps appear rectangular. Martian quadrangles are named after local features[1][2] and are numbered with the prefix "MC" for "Mars Chart".[3] West longitude is used.
| Name[7] | Number[7] | Area[7] |
|---|---|---|
| Mare Boreum (North Pole) | MC-01 | Latitude 65° to 90°, Longitude 0° to 360° |
| Diacria | MC-02 | Latitude 30° to 65°, Longitude 120° to 180° |
| Arcadia | MC-03 | Latitude 30° to 65°, Longitude 60° to 120° |
| Mare Acidalium[8] | MC-04 | Latitude 30° to 65°, Longitude 0° to 60° |
| Ismenius Lacus | MC-05 | Latitude 30° to 65°, Longitude 300° to 360° |
| Casius[9] | MC-06 | Latitude 30° to 65°, Longitude 240° to 300° |
| Cebrenia | MC-07 | Latitude 30° to 65°, Longitude 180° to 240° |
| Amazonis | MC-08 | Latitude 0° to 30°, Longitude 135° to 180° |
| Tharsis | MC-09 | Latitude 0° to 30°, Longitude 90° to 135° |
| Lunae Palus | MC-10 | Latitude 0° to 30°, Longitude 45° to 90° |
| Oxia Palus | MC-11 | Latitude 0° to 30°, Longitude 0° to 45° |
| Arabia[10] | MC-12 | Latitude 0° to 30°, Longitude 315° to 360° |
| Syrtis Major[11] | MC-13 | Latitude 0° to 30°, Longitude 270° to 315° |
| Amenthes | MC-14 | Latitude 0° to 30°, Longitude 225° to 270° |
| Elysium | MC-15 | Latitude 0° to 30°, Longitude 180° to 225° |
| Memnonia | MC-16 | Latitude -30° to 0°, Longitude 135° to 180° |
| Phoenicis Lacus | MC-17 | Latitude -30° to 0°, Longitude 90° to 135° |
| Coprates | MC-18 | Latitude -30° to 0°, Longitude 45° to 90° |
| Margaritifer Sinus | MC-19 | Latitude -30° to 0°, Longitude 0° to 45° |
| Sinus Sabaeus | MC-20 | Latitude -30° to 0°, Longitude 315° to 360° |
| Iapygia | MC-21 | Latitude -30° to 0°, Longitude 270° to 315° |
| Mare Tyrrhenum | MC-22 | Latitude -30° to 0°, Longitude 225° to 270° |
| Aeolis | MC-23 | Latitude -30° to 0°, Longitude 180° to 225° |
| Phaethontis | MC-24 | Latitude -65° to -30°, Longitude 120° to 180° |
| Thaumasia | MC-25 | Latitude -65° to -30°, Longitude 60° to 120° |
| Argyre | MC-26 | Latitude -65° to -30°, Longitude 0° to 60° |
| Noachis[12] | MC-27 | Latitude -65° to -30°, Longitude 300° to 360° |
| Hellas | MC-28 | Latitude -65° to -30°, Longitude 240° to 300° |
| Eridania | MC-29 | Latitude -65° to -30°, Longitude 180° to 240° |
| Mare Australe (South Pole) | MC-30 | Latitude -90° to -65°, Longitude 0° to 360° |
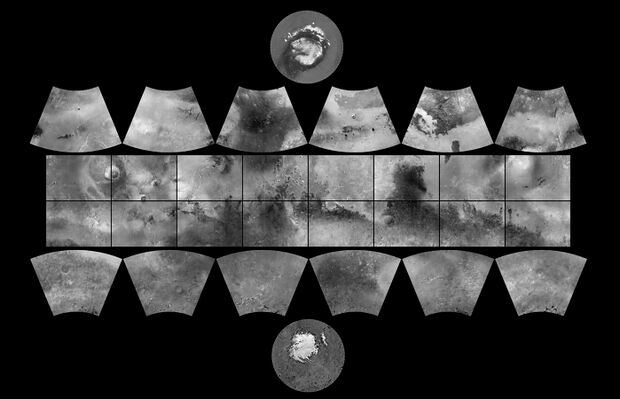
Relationship of quadrangles to each other:
References
- ↑ Morton, Oliver (2002). Mapping Mars: Science, Imagination, and the Birth of a World. New York: Picador USA. pp. 98. ISBN 0-312-24551-3.
- ↑ Online Atlas of Mars
- ↑ Catalog Page for PIA03467
- ↑ Morton, Oliver (2002). Mapping Mars: Science, Imagination, and the Birth of a World. New York: Picador USA. p. 98. ISBN 0-312-24551-3.
- ↑ "Online Atlas of Mars". http://ralphaeschliman.com/id30.htm. Retrieved December 16, 2012.
- ↑ "PIA03467: The MGS MOC Wide Angle Map of Mars". NASA / Jet Propulsion Laboratory. February 16, 2002. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA03467. Retrieved December 16, 2012.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 USGS Astrogeology: Planetary Map Listing
- ↑ USGS Astrogeology: Planetary Map Listing
- ↑ Geology of Mars Quadrangle MC-6 (Casius)
- ↑ Geologic Summary of the Mars Quadrangle MC-12 (Arabia)
- ↑ USGS Astrogeology: Planetary Map Listing
- ↑ Geology of the Noachis Quadrangle, Mars
External links
- Mars - Geologic Map (USGS, 2014) (original / crop / full / video (00:56)).