Chemistry:5-Methyluridine
From HandWiki
Short description: One of the five major nucleosides in nucleic acids
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
5-Methyluridine
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
1-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-Dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-5-methylpyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione | |
| Other names
Ribothymidine, Ribosylthymine; Thymine riboside, m5U
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H14N2O6 | |
| Molar mass | 258.23 g/mol |
| Density | 1,6 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | 184[2] °C (363 °F; 457 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
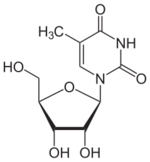
The chemical compound 5-methyluridine (symbol m⁵U or m5U), also called ribothymidine (rT)[footnote 1], is a pyrimidine nucleoside. It is the ribonucleoside counterpart to the deoxyribonucleoside thymidine, which lacks a hydroxyl group at the 2' position. 5-Methyluridine contains a thymine base joined to a ribose pentose sugar.[3] It is a white solid.
m5U is one of the most common modifications made to cellular RNA. It almost universallly occurs in position 54 (part of the T arm) of eukaryotic and bacterial tRNA, serving to stabilize the molecule. The same "T-loop" motif occurs in many other forms of noncoding RNA such as tmRNA and rRNA. Loss of the tRNA modification does not usually produce a different, less fit, phenotype.[4]
See also
Footnotes
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs named{{{1}}}
References
- ↑ "5-Methyluridine". http://www.chemspider.com/Chemical-Structure.29788257.html?rid=646f071c-9da8-46a6-be4c-b7497c5c9f0c&page_num=0.
- ↑ William M. Haynes (2016). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (97th ed.). Boca Raton: CRC Press. p. 3-400. ISBN 978-1-4987-5429-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=VVezDAAAQBAJ.
- ↑ Shobbir Hussain (2019). "Catalytic crosslinking-based methods for enzyme-specified profiling of RNAribonucleotide modifications". Methods 156: 60–65. doi:10.1016/j.ymeth.2018.10.003. PMID 30308313. https://researchportal.bath.ac.uk/en/publications/5a05dcf5-c4df-4344-bc70-7877c5ef08bf.
- ↑ Powell, CA; Minczuk, M (April 2020). "TRMT2B is responsible for both tRNA and rRNA m(5)U-methylation in human mitochondria.". RNA Biology 17 (4): 451–462. doi:10.1080/15476286.2020.1712544. PMID 31948311.
 |

