Chemistry:Ivosidenib
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˌaɪvoʊˈsɪdənɪb/ EYE-voh-SID-ə-nib |
| Trade names | Tibsovo |
| Other names | AG-120 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a618042 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Antineoplastic agent |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
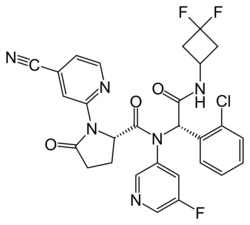
| Formula | C28H22ClF3N6O3 |
| Molar mass | 582.97 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
Ivosidenib, sold under the brand name Tibsovo, is an anti-cancer medication for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and cholangiocarcinoma.[3] It is a small molecule inhibitor of isocitrate dehydrogenase-1 (IDH1), which is mutated in several forms of cancer. Ivosidenib is an isocitrate dehydrogenase-1 inhibitor that works by decreasing abnormal production of the oncometabolite 2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG), leading to differentiation of malignant cells.[7]
Ivosidenib was approved for medical use in the United States in July 2018,[7][8][9][10] and in the European Union in May 2023.[5][11] The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) considers it to be a first-in-class medication.[12]
Medical uses
Ivosidenib is indicated for people with acute myeloid leukemia and locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma.[3][13][14]
Adverse effects
In ivosidenib-treated patients, reported adverse effects have been febrile neutropenia, alanine aminotransferase increased, aspartate aminotransferase increased, colitis, hypertension, maculopapular rash. However, Ivosidenib was taken in conjunction with standard AML induction treatment, and side effects can not be directly related to the drug.[15]
History
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) awarded orphan drug designations for acute myeloid leukemia and for cholangiocarcinoma.[16][17][18][19]
Society and culture
Legal status
On 23 February 2023, the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) of the European Medicines Agency (EMA) adopted a positive opinion, recommending the granting of a marketing authorization for the medicinal product Tibsovo, intended for the treatment of adults with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia and for the treatment of adults with locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma.[20] The applicant for this medicinal product is Les Laboratoires Servier.[20] Tibsovo was approved for medical use in the European Union in May 2023.[5]
Research
In tumors from people diagnosed with glioma, acute myeloid leukemia (AML), cholangiocarcinoma, and chondrosarcoma, somatic mutations in the conserved active site of isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) 1 and 2 are observed. With these new mutations, these enzymes exhibit new, neomorphic behavior, which results in the reduction of α-ketoglutarate to the oncometabolite R-2-hydroxyglutarate. The new molecule competitively inhibits α-ketoglutarate–dependent enzymes, ultimately leading to epigenetic alterations and impaired hematopoietic differentiation. Mutations in the IDH1 enzyme mutations occur in approximately 6 to 10% of the patients with AML, and IDH2 mutations occur in approximately 9 to 13% of those with AML, with unknown statistics on other conditions listed.[21]
The drug is also believed to be a slow-binding inhibitor of the IDH1-WT homodimer. Ivosidenib showed uncompetitive inhibition to the NADP cofactor, showing a hyperbolic curve for the rate constant of inhibition relative to concentration. Ivosidenib also showed no time-dependence in IC50 between 1 and 16 hours of incubation for either homodimer.[22]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Tibsovo". 19 April 2023. https://www.tga.gov.au/resources/auspmd/tibsovo.
- ↑ "Tibsovo (Servier Laboratories (Aust) Pty Ltd)". 26 April 2023. https://www.tga.gov.au/resources/prescription-medicines-registrations/tibsovo-servier-laboratories-aust-pty-ltd.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "Tibsovo- ivosidenib tablet, film coated". 24 April 2019. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=5b6d8ae8-bac8-4e1b-b1b4-7f9665e62de5.
- ↑ "Tibsovo- ivosidenib tablet, film coated". 9 June 2022. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=65d254c0-67ad-42c4-b972-ad463b755b2d.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 "Tibsovo EPAR". 12 May 2023. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/tibsovo-0.
- ↑ "Tibsovo". 8 May 2023. https://ec.europa.eu/health/documents/community-register/html/h1728.htm.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "FDA approves first targeted treatment for patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia who have a certain genetic mutation". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 20 July 2018. Archived from the original on 11 December 2019. Retrieved 18 December 2019.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ "Drug Trials Snapshots: Tibsovo". 2 August 2018. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-approvals-and-databases/drug-trials-snapshots-tibsovo.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ "FDA approves ivosidenib for relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia". 23 January 2019. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-ivosidenib-relapsed-or-refractory-acute-myeloid-leukemia.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ "Drug Approval Package: Tibsovo (ivosidenib)". https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2018/211192Orig1s000TOC.cfm.
- ↑ "Tibsovo". 8 May 2023. https://ec.europa.eu/health/documents/community-register/html/h1728.htm.
- ↑ (PDF) New Drug Therapy Approvals 2018 (Report). January 2019. https://www.fda.gov/media/120357/download. Retrieved 16 September 2020.
- ↑ "FDA approves ivosidenib as first-line treatment for AML with IDH1 mutation". 3 May 2019. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-ivosidenib-first-line-treatment-aml-idh1-mutation.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ "FDA approves ivosidenib for advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma". 26 August 2021. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-ivosidenib-advanced-or-metastatic-cholangiocarcinoma.
- ↑ "Ivosidenib or Enasidenib Combined with Standard Induction Chemotherapy Is Well Tolerated and Active in Patients with Newly Diagnosed AML with an IDH1 or IDH2 Mutation: Initial Results from a Phase 1 Trial". Blood 130 (Suppl 1): 726. 7 December 2017. doi:10.1182/blood.V130.Suppl_1.726.726. http://www.bloodjournal.org/content/130/Suppl_1/726. Retrieved 12 April 2019.
- ↑ "Tibsovo Orphan Drug Designation and Approval". https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/opdlisting/oopd/detailedIndex.cfm?cfgridkey=481515.
- ↑ "Ivosidenib Orphan Drug Designation and Approval". https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/opdlisting/oopd/detailedIndex.cfm?cfgridkey=562216.
- ↑ "Ivosidenib Orphan Drug Designations and Approvals". https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/opdlisting/oopd/detailedIndex.cfm?cfgridkey=739720.
- ↑ "Ivosidenib Orphan Drug Designations and Approvals". https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/opdlisting/oopd/detailedIndex.cfm?cfgridkey=637718.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 "Tibsovo: Pending EC decision". 24 February 2023. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/summaries-opinion/tibsovo. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- ↑ "Durable Remissions with Ivosidenib in IDH1-Mutated Relapsed or Refractory AML". The New England Journal of Medicine 378 (25): 2386–2398. June 2018. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1716984. PMID 29860938.
- ↑ "Discovery of AG-120 (Ivosidenib): A First-in-Class Mutant IDH1 Inhibitor for the Treatment of IDH1 Mutant Cancers". ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters 9 (4): 300–305. April 2018. doi:10.1021/acsmedchemlett.7b00421. PMID 29670690.
External links
- Clinical trial number NCT02074839 for "Study of Orally Administered AG-120 in Subjects With Advanced Hematologic Malignancies With an IDH1 Mutation" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- Clinical trial number NCT02989857 for "Study of AG-120 in Previously Treated Advanced Cholangiocarcinoma With IDH1 Mutations (ClarIDHy) (ClarIDHy)" at ClinicalTrials.gov
 |

