Chemistry:Potassium trispyrazolylborate
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Potassium tri(1H-pyrazol-1-yl)boranuide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H10BKN6 | |
| Molar mass | 252.13 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 188 to 189 °C (370 to 372 °F; 461 to 462 K)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
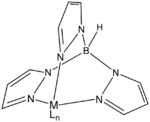
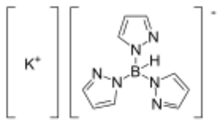
Potassium trispyrazolylborate, commonly abbreviated KTp, is the potassium salt with the formula :KHB(C
3N
2H
3)
3. This salt is the source of the trispyrazolylborate ligand.[1]
KTp is a white crystalline solid that is soluble in polar solvents, alcohols, and water. The synthesis of KTp involves potassium borohydride and pyrazole without a solvent.[2]
- KBH
4 + 3 C
3N
2H
4 → KHB(C
3N
2H
3)
3 + 3 H
2
The tris(pyrazolyl)borate forms octahedral coordination compounds with the formula M[Tp]2 with first row transition metals. KTp also forms 1:1 complexes, for example it can be converted to K[TpMo(CO)3];
- KTp + Mo(CO)
6→K[TpMo(CO)
3] + 3 CO
When K[TpMo(CO)3] is treated with butyl nitrite it yields the neutral orange complex TpMo(CO)2NO.[3]
- K[TpMo(CO)3]+ BuONO→TpMo(CO)2NO+CO+KOBu
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Trofimenko, Swiatoslaw (1967). "Boron-pyrazole chemistry. II. Poly(1-pyrazolyl)-borates". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 89 (13): 3170–3177. doi:10.1021/ja00989a017.
- ↑ Trofimenko, Swiatoslaw (1970). "Poly(1‐pyrazolyl)borates, Their Transition‐Metal Complexes, and Pyrazaboles". Inorganic Syntheses. 12. pp. 99–109. doi:10.1002/9780470132432.ch18. ISBN 9780470132432.
- ↑ Trofimenko, Swiatoslaw (1999). Scorpionates: Polypyrazolylborate Ligands and Their Coordination Chemistry.. World Scientific Publishing Company. ISBN 978-1860941726.
 |