Chemistry:Quizartinib
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
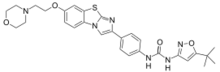
| Preferred IUPAC name
N-(5-tert-Butyl-1,2-oxazol-3-yl)-N′-(4-{7-[2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethoxy]imidazo[2,1-b][1,3]benzothiazol-2-yl}phenyl)urea | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C29H32N6O4S | |
| Molar mass | 560.67 g·mol−1 |
| Pharmacology | |
| 1=ATC code }} | L01EX11 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| License data |
|
| Drug class | Receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor |
| Identifiers | |
| PDB ligand | |
Quizartinib, sold under the brand name Vanflyta, is an anti-cancer medication used for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia.[2]
It is a small molecule receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Its molecular target is FLT3, also known as CD135 which is a proto-oncogene.[5]
FLT3 mutations are among the most common mutations in acute myeloid leukemia due to internal tandem duplication of FLT3, and the presence of this mutation is a marker of adverse outcome.[6]
It was approved for medical use in Japan in October 2019,[7] in the United States in July 2023,[2] and the European Union in November 2023.[3]
Quizartinib was originally developed by Ambit Biosciences, which was acquired by Daiichi Sankyo in 2014. Daiichi Sankyo is the current manufacturer of quizartinib.
Medical uses
Quizartinib is indicated, in combination with standard cytarabine and anthracycline induction and cytarabine consolidation, and as maintenance monotherapy following consolidation chemotherapy, for the treatment of newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia with FLT3 internal tandem duplication (ITD)-positive.[2][3]
Adverse effects
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) label includes a boxed warning noting QT prolongation, torsades de pointes, and cardiac arrest.[2]
Mechanism of action
Quizartinib selectively inhibits class III receptor tyrosine kinases, including FMS-related tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3/STK1), colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R/FMS), stem cell factor receptor (SCFR/KIT), and platelet derived growth factor receptors (PDGFRs).[8]
Mutations cause constant activation of the FLT3 pathway resulting in inhibition of ligand-independent leukemic cell proliferation and apoptosis.[8]
History
Efficacy of quizartinib with chemotherapy was evaluated in QuANTUM-First (NCT02668653), a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of 539 participants with newly diagnosed FLT3 internal tandem duplication positive acute myeloid leukemia.[2] FLT3 internal tandem duplication status was determined prospectively with a clinical trial assay and verified retrospectively with the companion diagnostic LeukoStrat CDx FLT3 Mutation Assay.[2] Participants were randomized (1:1) to receive quizartinib (n=268) or placebo (n=271) with induction and consolidation therapy and as maintenance monotherapy according to the initial assignment.[2] There was no re-randomization at the initiation of post-consolidation therapy.[2] Participants who proceeded to hematopoietic stem cell transplantation initiated maintenance therapy after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation recovery.[2]
The main efficacy outcome measure was overall survival, measured from randomization date until death by any cause.[2] The primary analysis was conducted after a minimum follow-up of 24 months after the last patient was randomized.[2] The trial demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in overall survival for the quizartinib arm [hazard ratio (HR) 0.78; 95% CI: 0.62, 0.98; 2‑sided p=0.0324].[2] The CR rate in the quizartinib arm was 55% (95% CI: 48.7, 60.9) with a median duration of 38.6 months (95% CI: 21.9, NE), and the CR rate in those receiving placebo was 55% (95% CI: 49.2, 61.4) with a median duration of 12.4 months (95% CI: 8.8, 22.7).[2]
The FDA granted the application for quizartinib priority review, fast track, and orphan drug designations.[2]
Clinical trials
It reported good results in 2012, from a phase II clinical trial for refractory acute myeloid leukemia - in participants who went on to have a stem cell transplant.[9][unreliable medical source?]
(As of July 2023), it has completed seventeen clinical trials, and another eleven are active.[10]
Society and culture
Legal status
The application for quizartinib was denied in the European Union in 2019.[11]
In September 2023, the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use of the European Medicines Agency adopted a positive opinion, recommending the granting of a marketing authorization for the medicinal product Vanflyta, intended for the treatment of acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) that is FLT3-ITD positive.[3] The applicant for this medicinal product is Daiichi Sankyo Europe GmbH.[3]
Quizartinib was approved for medical use in Japan in October 2019,[7] in the United States in July 2023,[2] and the European Union in November 2023.[3][4]
Brand names
Quizartinib is the international nonproprietary name.[12]
Quizartinib is sold under the brand name Vanflyta.[1][3]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Vanflyta- quizartinib tablet, film coated". 26 July 2023. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=29cdbcfe-497d-4e78-bb7b-2d4acafe8e86.
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 2.12 2.13 2.14 2.15 "FDA approves quizartinib for newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 20 July 2023. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-approvals-and-databases/fda-approves-quizartinib-newly-diagnosed-acute-myeloid-leukemia. Retrieved 21 July 2023.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 "Vanflyta EPAR". 21 November 2023. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/vanflyta-0. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Vanflyta Product information". 7 November 2023. https://ec.europa.eu/health/documents/community-register/html/h1768.htm.
- ↑ "Identification of N-(5-tert-Butyl-isoxazol-3-yl)-N'-{4-[7-(2-morpholin-4-yl-ethoxy)imidazo[2,1-b][1,3]benzothiazol-2-yl]phenyl}urea dihydrochloride (AC220), a uniquely potent, selective, and efficacious FMS-like tyrosine kinase-3 (FLT3) inhibitor". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 52 (23): 7808–7816. December 2009. doi:10.1021/jm9007533. PMID 19754199.
- ↑ "Internal tandem duplications of the FLT3 gene are present in leukemia stem cells". Blood 106 (2): 673–80. July 2005. doi:10.1182/blood-2004-05-1902. PMID 15797998.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "Daiichi Sankyo Launches FLT3 Inhibitor Vanflyta in Japan for the Treatment of Patients with Relapsed/Refractory FLT3-ITD AML" (Press release). Archived from the original on 10 August 2023. Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 "Quizartinib (AC220) is a potent second generation class III tyrosine kinase inhibitor that displays a distinct inhibition profile against mutant-FLT3, -PDGFRA and -KIT isoforms". Molecular Cancer 12: 19. March 2013. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-12-19. PMID 23497317.
- ↑ "Drug Tames Refractory AML. ASH Dec 2012". 9 December 2012. http://www.medpagetoday.com/MeetingCoverage/ASHHematology/36351.
- ↑ "Quizartinib studies". https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?term=quizartinib&Search=Search.
- ↑ "Vanflyta". 6 January 2020. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/vanflyta.
- ↑ "International nonproprietary names for pharmaceutical substances (INN): recommended INN: list 66". WHO Drug Information 25 (3). 2011.
Further reading
- "Quizartinib plus chemotherapy in newly diagnosed patients with FLT3-internal-tandem-duplication-positive acute myeloid leukaemia (QuANTUM-First): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial". Lancet 401 (10388): 1571–1583. May 2023. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00464-6. PMID 37116523.
External links
- Clinical trial number NCT02668653 for "Quizartinib With Standard of Care Chemotherapy and as Continuation Therapy in Patients With Newly Diagnosed FLT3-ITD (+) Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) (QuANTUM-First)" at ClinicalTrials.gov
 |

