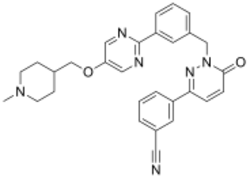
Chemistry:Tepotinib
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Tepmetko |
| Other names | EMD-1214063 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C29H28N6O2 |
| Molar mass | 492.583 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Tepotinib, sold under the brand name Tepmetko, is an anti-cancer medication used for the treatment of adults with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).[4][5][7]
The most common side effects include edema (build-up of fluid), nausea (feeling sick), low albumin level in the blood, diarrhea, and increase in creatinine level in the blood (a sign of kidney problems).[6]
Tepotinib first received marketing approval in Japan, in March 2020, as a "line-agnostic" drug, meaning it is approved both for treatment-naive patients and for those in whom previous attempts at treatment have failed.[8] US approval followed in February 2021. It is the second therapy approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat non-small cell lung cancer with these particular mutations, after capmatinib.[9]
Medical uses
Tepotinib is indicated for the treatment of adults with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose tumors have a mutation that leads to MET exon 14 skipping.[4][5]
Adverse effects
The most common side effects seen in clinical trials were edema, fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, muscle aches, and shortness of breath. Like capmatinib, tepotinib can also cause interstitial lung disease and liver damage, and is toxic to a developing fetus.[5] The most common treatment-related adverse effect in a 2021 study were peripheral edema (54.1%), nausea (20.0%), diarrhea (19.6%), blood creatinine increased (17.6%), and hypoalbuminemia (14.5%), which were 'mostly mild or moderate'.[10]
Society and culture
Legal status
On 16 December 2021, the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) of the European Medicines Agency (EMA) adopted a positive opinion, recommending the granting of a marketing authorization for the medicinal product Tepmetko, intended for the treatment of patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harboring alterations leading to mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor gene exon 14 (METex14) skipping.[11] The applicant for this medicinal product is Merck Europe B.V.[11] Tepotinib (Tepmetko) was approved for medical use in the European Union in February 2022.[6][12]
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted the application for tepotinib orphan drug designation.[13]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Tepmetko APMDS". 27 January 2022. https://www.tga.gov.au/resources/auspmd/tepmetko.
- ↑ "Updates to the Prescribing Medicines in Pregnancy database". 21 December 2022. https://www.tga.gov.au/resources/resource/guidance/updates-prescribing-medicines-pregnancy-database.
- ↑ "Summary Basis of Decision (SBD) for Tepmetko". 23 October 2014. https://hpr-rps.hres.ca/reg-content/summary-basis-decision-detailTwo.php?linkID=SBD00554&lang=en.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 "Tepmetko- tepotinib hydrochloride tablet". https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=80a0f1b9-071a-47f5-9e67-32d638a669dc.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 "FDA grants accelerated approval to tepotinib for metastatic non-small cell lung cancer". 3 February 2021. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-approvals-and-databases/fda-grants-accelerated-approval-tepotinib-metastatic-non-small-cell-lung-cancer.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 "Tepmetko EPAR". 14 December 2021. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/tepmetko. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "FDA Approves Tepmetko as the First and Only Once-daily Oral MET Inhibitor for Patients with Metastatic NSCLC with METex14 Skipping Alterations". EMD Serono (Press release). 3 February 2021. Archived from the original on 4 February 2021. Retrieved 3 February 2021.
- ↑ "Tepmetko (Tepotinib) Approved in Japan for Advanced NSCLC with METex14 Skipping Alterations" (Press release). Merck KGaA. 25 March 2020. Retrieved 3 February 2021.
- ↑ "FDA Approval Summary: Capmatinib and Tepotinib for the Treatment of Metastatic NSCLC Harboring MET Exon 14 Skipping Mutations or Alterations". Clinical Cancer Research 28 (2): 249–254. January 2022. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-1566. PMID 34344795.
- ↑ "O13-4 Tepotinib safety in MET exon 14 (METex14) skipping NSCLC: Updated results from the VISION trial". Annals of Oncology 32: S291. July 2021. doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2021.05.541. ISSN 0923-7534.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 "Tepmetko: Pending EC decision". 17 December 2021. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/summaries-opinion/tepmetko. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- ↑ "Tepmetko Product information". https://ec.europa.eu/health/documents/community-register/html/h1596.htm.
- ↑ (PDF) Advancing Health Through Innovation: New Drug Therapy Approvals 2021 (Report). 13 May 2022. https://www.fda.gov/media/155227/download. Retrieved 22 January 2023.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
Further reading
- "Tepotinib in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with MET Exon 14 Skipping Mutations". The New England Journal of Medicine 383 (10): 931–943. September 2020. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2004407. PMID 32469185.
External links
- "Tepotinib". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://druginfo.nlm.nih.gov/drugportal/name/tepotinib.
- "Tepotinib hydrochloride". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://druginfo.nlm.nih.gov/drugportal/name/tepotinib_hydrochloride.
- "Tepotinib hydrochloride". NCI Drug Dictionary. National Cancer Institute. https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-drug.
- Clinical trial number NCT02864992 for "Tepotinib Phase II in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Harboring MET Alterations (VISION)" at ClinicalTrials.gov
 |

