Astronomy:List of objects at Lagrangian points
This is a list of known objects which occupy, have occupied, or are planned to occupy any of the five Lagrangian points of two-body systems in space.
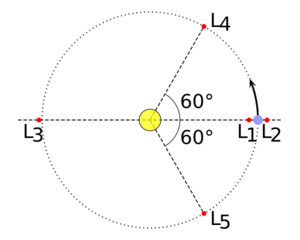
Sun–Earth Lagrangian points
L1
L1 is the Lagrangian point located approximately 1.5 million km from Earth towards the Sun.
Past probes
- International Cometary Explorer, formerly the International Sun–Earth Explorer 3 (ISEE-3), diverted out of L1 in 1983 for a comet rendezvous mission. Currently in heliocentric orbit.
- NASA's Genesis probe collected solar wind samples at L1 from December 3, 2001 to April 1, 2004, when it returned the sample capsule to Earth. It returned briefly in late 2004 before being pushed into heliocentric orbit in early 2005.
- LISA Pathfinder
Present probes

DSCOVR · Earth · Moon
- The Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO)
- The Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE)
- WIND (spacecraft) (At L1 since 2004)
- The Deep Space Climate Observatory (DSCOVR), designed to image the sunlit earth in 10 wavelengths (EPIC) and monitor total reflected radiation (NISTAR)
Planned probes
- Aditya-L1
- Kuafu
- Lagrange mission (ESA). One spacecraft in L1 and one in L5.
L2
L2 is the Lagrangian point located approximately 1.5 million km from Earth in the direction opposite the Sun.
Past probes

WMAP · Earth
- NASA's Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) observed the cosmic microwave background from 2001 until 2010. It was moved to a heliocentric orbit to avoid posing a hazard to future missions.
- NASA's WIND from November 2003 to April 2004. The spacecraft then went to Earth orbit, before heading to L1.
- The ESA Herschel Space Observatory exhausted its supply of liquid helium and was moved from the Lagrangian point in June 2013.
- At the end of its mission ESA's Planck spacecraft was put into a heliocentric orbit and passivated to prevent it from endangering any future missions.
- CNSA's Chang'e 2[1] from August 2011 to April 2012. Chang'e 2 was then placed onto a heliocentric orbit that took it past the near-Earth asteroid 4179 Toutatis.
Present probes
- The ESA Gaia probe
- The joint Russian-German high-energy astrophysics observatory Spektr-RG
Planned probes
- The ESA Euclid mission, to better understand dark energy and dark matter by accurately measuring the acceleration of the universe.
- The joint NASA, ESA and CSA James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), formerly known as the Next Generation Space Telescope (NGST)
- The ESA PLATO mission, which will find and characterize rocky exoplanets.
- The JAXA LiteBIRD mission.
- The NASA Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope (WFIRST)
- The ESA ARIEL mission, which will observe the atmospheres of exoplanets.
- The ESA Advanced Telescope for High ENergy Astrophysics (ATHENA)
- The NASA Advanced Technology Large-Aperture Space Telescope, which would replace the Hubble Space Telescope and possibly the JWST.
Cancelled probes
- The ESA Eddington mission
- The NASA Terrestrial Planet Finder mission (may be placed in an Earth-trailing orbit instead)
L3
L3 is the Sun–Earth Lagrangian point located on the side of the Sun opposite Earth, slightly outside the Earth's orbit.
- There are no known objects in this orbital location.
L4
L4 is the Sun–Earth Lagrangian point located close to the Earth's orbit 60° ahead of Earth.
- Asteroid 2010 TK7 is the first discovered "tadpole" orbit companion to Earth, orbiting L4 with a mean distance of about one astronomical unit.
- STEREO A (Solar TErrestrial RElations Observatory – Ahead) made its closest pass to L4 in September 2009, on its orbit around the Sun, slightly faster than Earth.[2]
- OSIRIS-REx passed near the L4 point and performed a survey for asteroids between 9 and 20 February 2017.
L5
L5 is the Sun–Earth Lagrangian point located close to the Earth's orbit 60° behind Earth.
- Asteroid (419624) 2010 SO16, in a horseshoe companion orbit with Earth, is currently proximal to L5 but at a high inclination.
- STEREO B (Solar TErrestrial RElations Observatory – Behind) made its closest pass to L5 in October 2009, on its orbit around the Sun, slightly slower than Earth.[2]
- The Spitzer Space Telescope is in an Earth-trailing heliocentric orbit drifting away c. 0.1 AU per year. In c. 2013–15 it has passed L5 in its orbit.
- Hayabusa2 passed near L5 during the spring of 2017, and imaged the surrounding area to search for Earth trojans in 18 April 2018.[3]
Proposed
- Lagrange mission (ESA). One spacecraft in L5 and one in L1.
Earth–Moon Lagrangian points
L2
- ARTEMIS
- Chang'e 5-T1
- Queqiao relay satellite
L4 and L5
- Kordylewski clouds[4]
- future location of TDRS-style communication satellites to support L2 satellite
Past probes
- Hiten was the first spacecraft to demonstrate a low energy trajectory, passing by L4 and L5 to achieve lunar orbit at a very low fuel expense, compared to usual orbital techniques. Hiten did not find any conclusive increase in dust density at Lagrange points.[5]
Proposed objects
- Exploration Gateway Platform
- In his 1976 book The High Frontier: Human Colonies in Space Dr. Gerard O'Neill proposed the establishment of gigantic Space Islands in L5. The inhabitants of the L5 Society should convert lunar material to huge solar power satellites. Many works of fiction, most notably the Gundam series, involve colonies at these locations.
Sun–Venus Lagrangian points
L4
Sun–Mars Lagrangian points
Asteroids in the L4 and L5 Sun–Mars Lagrangian points are sometimes called Mars trojans, with a lower-case t, as "Trojan asteroid" was originally defined as a term for Lagrangian asteroids of Jupiter. They may also be called Mars Lagrangian asteroids.
L4
L5
- 5261 Eureka
- (101429) 1998 VF31
- (311999) 2007 NS2
- (385250) 2001 DH47, 2001 FG24, 2001 FR127 (not confirmed as true Lagrangian asteroids)
Source: Minor Planet Center [1]
Sun–Jupiter Lagrangian points
Asteroids in the L4 and L5 Sun–Jupiter Lagrangian points are known as Jupiter Trojan asteroids or simply Trojan asteroids.
L4
- Trojan asteroids, Greek camp
L5
- Trojan asteroids, Trojan camp
Saturn–Tethys Lagrangian points
L4
L5
Saturn–Dione Lagrangian points
L4
L5
- Polydeuces, follows a "tadpole" orbit around L5
Sun–Uranus Lagrangian points
L3
- 83982 Crantor, follows a "horseshoe" orbit around L3
L4
Sun–Neptune Lagrangian points
Minor planets in the L4 and L5 Sun–Neptune Lagrangian points are called Neptune trojans, with a lower-case t, as "Trojan asteroid" was originally defined as a term for Lagrangian asteroids of Jupiter.
L4
L5
Source: Minor Planet Center [2]
See also
- Lagrangian point (especially section on spacecraft and missions)
- Trojan points
- Trojan asteroid
- Trojan moon
- Trojan planet
Footnotes
- ↑ "China's Moon orbiter Chang'e-2 travels 1.5 km into outer space". The Economic Times. 2011-08-30. http://articles.economictimes.indiatimes.com/2011-08-30/news/29945291_1_chang-e-2-china-s-moon-moon-landing. Retrieved 2011-08-31.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 NASA - Join STEREO and Explore Gravitational "Parking Lots" That May Hold Secret of Moon's Origin
- ↑ "太陽−地球系のL5点付近の観測の結果について" (in Japanese). JAXA. 23 August 2017. http://www.hayabusa2.jaxa.jp/topics/20170823/.
- ↑ Slíz-Balogh, Judith; Barta, András; Horváth, Gábor (11 November 2018). "Celestial mechanics and polarization optics of the Kordylewski dust cloud in the Earth–Moon Lagrange point L5 – I. Three-dimensional celestial mechanical modelling of dust cloud formation". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 480 (4): 5550–5559. doi:10.1093/mnras/sty2049.
- ↑ "Hiten", NSSDC.GSFC.NASA.gov.
- ↑ The first known Uranian Trojan and the frequency of temporary giant-planet co-orbitals: Mike Alexandersen, Brett Gladman, Sarah Greenstreet, J.J. Kavelaars, Jean-Marc Petit