Divisor

In mathematics, a divisor of an integer [math]\displaystyle{ n, }[/math] also called a factor of [math]\displaystyle{ n, }[/math] is an integer [math]\displaystyle{ m }[/math] that may be multiplied by some integer to produce [math]\displaystyle{ n. }[/math][1] In this case, one also says that [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] is a multiple of [math]\displaystyle{ m. }[/math] An integer [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] is divisible or evenly divisible by another integer [math]\displaystyle{ m }[/math] if [math]\displaystyle{ m }[/math] is a divisor of [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math]; this implies dividing [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] by [math]\displaystyle{ m }[/math] leaves no remainder.
Definition
An integer [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] is divisible by a nonzero integer [math]\displaystyle{ m }[/math] if there exists an integer [math]\displaystyle{ k }[/math] such that [math]\displaystyle{ n=km. }[/math] This is written as
- [math]\displaystyle{ m\mid n. }[/math]
This may be read as that [math]\displaystyle{ m }[/math] divides [math]\displaystyle{ n, }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ m }[/math] is a divisor of [math]\displaystyle{ n, }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ m }[/math] is a factor of [math]\displaystyle{ n, }[/math] or [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] is a multiple of [math]\displaystyle{ m. }[/math] If [math]\displaystyle{ m }[/math] does not divide [math]\displaystyle{ n, }[/math] then the notation is [math]\displaystyle{ m\not\mid n. }[/math][2][3]
There are two conventions, distinguished by whether [math]\displaystyle{ m }[/math] is permitted to be zero:
- With the convention without an additional constraint on [math]\displaystyle{ m, }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ m \mid 0 }[/math] for every integer [math]\displaystyle{ m. }[/math][2][3]
- With the convention that [math]\displaystyle{ m }[/math] be nonzero, [math]\displaystyle{ m \mid 0 }[/math] for every nonzero integer [math]\displaystyle{ m. }[/math][4][5]
General
Divisors can be negative as well as positive, although often the term is restricted to positive divisors. For example, there are six divisors of 4; they are 1, 2, 4, −1, −2, and −4, but only the positive ones (1, 2, and 4) would usually be mentioned.
1 and −1 divide (are divisors of) every integer. Every integer (and its negation) is a divisor of itself. Integers divisible by 2 are called even, and integers not divisible by 2 are called odd.
1, −1, [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ -n }[/math] are known as the trivial divisors of [math]\displaystyle{ n. }[/math] A divisor of [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] that is not a trivial divisor is known as a non-trivial divisor (or strict divisor[6]). A nonzero integer with at least one non-trivial divisor is known as a composite number, while the units −1 and 1 and prime numbers have no non-trivial divisors.
There are divisibility rules that allow one to recognize certain divisors of a number from the number's digits.
Examples

- 7 is a divisor of 42 because [math]\displaystyle{ 7\times 6=42, }[/math] so we can say [math]\displaystyle{ 7\mid 42. }[/math] It can also be said that 42 is divisible by 7, 42 is a multiple of 7, 7 divides 42, or 7 is a factor of 42.
- The non-trivial divisors of 6 are 2, −2, 3, −3.
- The positive divisors of 42 are 1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 14, 21, 42.
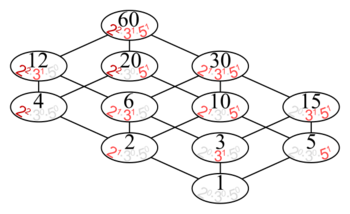
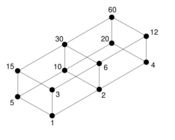
- The set of all positive divisors of 60, [math]\displaystyle{ A=\{1,2,3,4,5,6,10,12,15,20,30,60\}, }[/math] partially ordered by divisibility, has the Hasse diagram:
Further notions and facts
There are some elementary rules:
- If [math]\displaystyle{ a \mid b }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ b \mid c, }[/math] then [math]\displaystyle{ a \mid c, }[/math] i.e. divisibility is a transitive relation.
- If [math]\displaystyle{ a \mid b }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ b \mid a, }[/math] then [math]\displaystyle{ a = b }[/math] or [math]\displaystyle{ a = -b. }[/math]
- If [math]\displaystyle{ a \mid b }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ a \mid c, }[/math] then [math]\displaystyle{ a \mid (b + c) }[/math] holds, as does [math]\displaystyle{ a \mid (b - c). }[/math][lower-alpha 1] However, if [math]\displaystyle{ a \mid b }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ c \mid b, }[/math] then [math]\displaystyle{ (a + c) \mid b }[/math] does not always hold (e.g. [math]\displaystyle{ 2\mid6 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ 3 \mid 6 }[/math] but 5 does not divide 6).
If [math]\displaystyle{ a \mid bc, }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \gcd(a, b) = 1, }[/math] then [math]\displaystyle{ a \mid c. }[/math][lower-alpha 2] This is called Euclid's lemma.
If [math]\displaystyle{ p }[/math] is a prime number and [math]\displaystyle{ p \mid ab }[/math] then [math]\displaystyle{ p \mid a }[/math] or [math]\displaystyle{ p \mid b. }[/math]
A positive divisor of [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] that is different from [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] is called a proper divisor or an aliquot part of [math]\displaystyle{ n. }[/math] A number that does not evenly divide [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] but leaves a remainder is sometimes called an aliquant part of [math]\displaystyle{ n. }[/math]
An integer [math]\displaystyle{ n \gt 1 }[/math] whose only proper divisor is 1 is called a prime number. Equivalently, a prime number is a positive integer that has exactly two positive factors: 1 and itself.
Any positive divisor of [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] is a product of prime divisors of [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] raised to some power. This is a consequence of the fundamental theorem of arithmetic.
A number [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] is said to be perfect if it equals the sum of its proper divisors, deficient if the sum of its proper divisors is less than [math]\displaystyle{ n, }[/math] and abundant if this sum exceeds [math]\displaystyle{ n. }[/math]
The total number of positive divisors of [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] is a multiplicative function [math]\displaystyle{ d(n), }[/math] meaning that when two numbers [math]\displaystyle{ m }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] are relatively prime, then [math]\displaystyle{ d(mn)=d(m)\times d(n). }[/math] For instance, [math]\displaystyle{ d(42) = 8 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 = d(2) \times d(3) \times d(7) }[/math]; the eight divisors of 42 are 1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 14, 21 and 42. However, the number of positive divisors is not a totally multiplicative function: if the two numbers [math]\displaystyle{ m }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] share a common divisor, then it might not be true that [math]\displaystyle{ d(mn)=d(m)\times d(n). }[/math] The sum of the positive divisors of [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] is another multiplicative function [math]\displaystyle{ \sigma (n) }[/math] (e.g. [math]\displaystyle{ \sigma (42) = 96 = 3 \times 4 \times 8 = \sigma (2) \times \sigma (3) \times \sigma (7) = 1+2+3+6+7+14+21+42 }[/math]). Both of these functions are examples of divisor functions.
If the prime factorization of [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] is given by
- [math]\displaystyle{ n = p_1^{\nu_1} \, p_2^{\nu_2} \cdots p_k^{\nu_k} }[/math]
then the number of positive divisors of [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] is
- [math]\displaystyle{ d(n) = (\nu_1 + 1) (\nu_2 + 1) \cdots (\nu_k + 1), }[/math]
and each of the divisors has the form
- [math]\displaystyle{ p_1^{\mu_1} \, p_2^{\mu_2} \cdots p_k^{\mu_k} }[/math]
where [math]\displaystyle{ 0 \le \mu_i \le \nu_i }[/math] for each [math]\displaystyle{ 1 \le i \le k. }[/math]
For every natural [math]\displaystyle{ n, }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ d(n) \lt 2 \sqrt{n}. }[/math]
Also,[7]
- [math]\displaystyle{ d(1)+d(2)+ \cdots +d(n) = n \ln n + (2 \gamma -1) n + O(\sqrt{n}), }[/math]
where [math]\displaystyle{ \gamma }[/math] is Euler–Mascheroni constant. One interpretation of this result is that a randomly chosen positive integer n has an average number of divisors of about [math]\displaystyle{ \ln n. }[/math] However, this is a result from the contributions of numbers with "abnormally many" divisors.
In abstract algebra
Ring theory
Division lattice
In definitions that allow the divisor to be 0, the relation of divisibility turns the set [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbb{N} }[/math] of non-negative integers into a partially ordered set that is a complete distributive lattice. The largest element of this lattice is 0 and the smallest is 1. The meet operation ∧ is given by the greatest common divisor and the join operation ∨ by the least common multiple. This lattice is isomorphic to the dual of the lattice of subgroups of the infinite cyclic group Z.
See also
- Arithmetic functions
- Euclidean algorithm
- Fraction (mathematics)
- Integer factorization
- Table of divisors – A table of prime and non-prime divisors for 1–1000
- Table of prime factors – A table of prime factors for 1–1000
- Unitary divisor
Notes
- ↑ [math]\displaystyle{ a \mid b,\, a \mid c }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ \Rightarrow \exists j\colon ja=b,\, \exists k\colon ka=c }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ \Rightarrow \exists j,k\colon (j+k)a=b+c }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ \Rightarrow a \mid (b+c). }[/math] Similarly, [math]\displaystyle{ a \mid b,\, a \mid c }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ \Rightarrow \exists j\colon ja=b,\, \exists k\colon ka=c }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ \Rightarrow \exists j,k\colon (j-k)a=b-c }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ \Rightarrow a \mid (b-c). }[/math]
- ↑ [math]\displaystyle{ \gcd }[/math] refers to the greatest common divisor.
Citations
- ↑ Tanton 2005, p. 185
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Hardy & Wright 1960, p. 1
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Niven, Zuckerman & Montgomery 1991, p. 4
- ↑ Sims 1984, p. 42
- ↑ Durbin (2009), p. 57, Chapter III Section 10
- ↑ "FoCaLiZe and Dedukti to the Rescue for Proof Interoperability by Raphael Cauderlier and Catherine Dubois". https://perso.crans.org/cauderlier/org/ITP17_draft.pdf.
- ↑ Hardy & Wright 1960, p. 264, Theorem 320
References
- Durbin, John R. (2009). Modern Algebra: An Introduction (6th ed.). New York: Wiley. ISBN 978-0470-38443-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=dnDJDwAAQBAJ.
- Unsolved Problems in Number Theory (3rd ed.), Springer Verlag, 2004, ISBN 0-387-20860-7; section B
- An Introduction to the Theory of Numbers (4th ed.). Oxford University Press. 1960. https://archive.org/details/introductiontoth00hard.
- Herstein, I. N. (1986), Abstract Algebra, New York: Macmillan Publishing Company, ISBN 0-02-353820-1
- An Introduction to the Theory of Numbers (5th ed.). John Wiley & Sons. 1991. ISBN 0-471-62546-9.
- Øystein Ore, Number Theory and its History, McGraw–Hill, NY, 1944 (and Dover reprints).
- Sims, Charles C. (1984), Abstract Algebra: A Computational Approach, New York: John Wiley & Sons, ISBN 0-471-09846-9
- Tanton, James (2005). Encyclopedia of mathematics. New York: Facts on File. ISBN 0-8160-5124-0. OCLC 56057904. https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/56057904.
 |