1 22 polytope
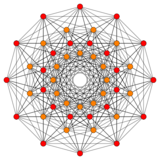 122 |
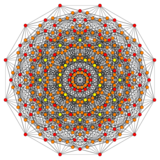 Rectified 122 |
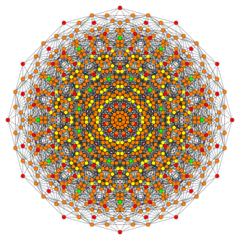 Birectified 122 |
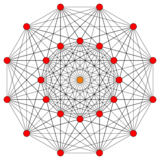 221 |
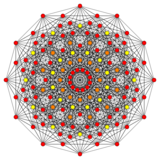 Rectified 221 | |
| orthogonal projections in E6 Coxeter plane | ||
|---|---|---|
In 6-dimensional geometry, the 122 polytope is a uniform polytope, constructed from the E6 group. It was first published in E. L. Elte's 1912 listing of semiregular polytopes, named as V72 (for its 72 vertices).[1]
Its Coxeter symbol is 122, describing its bifurcating Coxeter-Dynkin diagram, with a single ring on the end of the 1-node sequence. There are two rectifications of the 122, constructed by positions points on the elements of 122. The rectified 122 is constructed by points at the mid-edges of the 122. The birectified 122 is constructed by points at the triangle face centers of the 122.
These polytopes are from a family of 39 convex uniform polytopes in 6-dimensions, made of uniform polytope facets and vertex figures, defined by all permutations of rings in this Coxeter-Dynkin diagram: ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() .
.
122 polytope
| 122 polytope | |
|---|---|
| Type | Uniform 6-polytope |
| Family | 1k2 polytope |
| Schläfli symbol | {3,32,2} |
| Coxeter symbol | 122 |
| Coxeter-Dynkin diagram | |
| 5-faces | 54: 27 121 27 121 |
| 4-faces | 702: 270 111 432 120 |
| Cells | 2160: 1080 110 1080 {3,3} |
| Faces | 2160 {3} |
| Edges | 720 |
| Vertices | 72 |
| Vertex figure | Birectified 5-simplex: 022 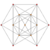
|
| Petrie polygon | Dodecagon |
| Coxeter group | E6, 3,32,2, order 103680 |
| Properties | convex, isotopic |
The 122 polytope contains 72 vertices, and 54 5-demicubic facets. It has a birectified 5-simplex vertex figure. Its 72 vertices represent the root vectors of the simple Lie group E6.
Alternate names
- Pentacontatetra-peton (Acronym Mo) - 54-facetted polypeton (Jonathan Bowers)[2]
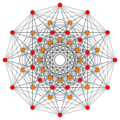
Images
| E6 [12] |
D5 [8] |
D4 / A2 [6] | |
|---|---|---|---|
 (1,2) |
 (1,3) |
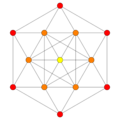 (1,9,12) | |
| B6 [12/2] |
A5 [6] |
A4 [[5]] = [10] |
A3 / D3 [4] |
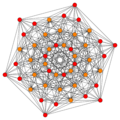 (1,2) |
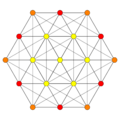 (2,3,6) |
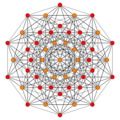 (1,2) |
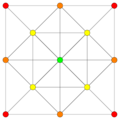 (1,6,8,12) |
Construction
It is created by a Wythoff construction upon a set of 6 hyperplane mirrors in 6-dimensional space.
The facet information can be extracted from its Coxeter-Dynkin diagram, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() .
.
Removing the node on either of 2-length branches leaves the 5-demicube, 131, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() .
.
The vertex figure is determined by removing the ringed node and ringing the neighboring node. This makes the birectified 5-simplex, 022, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() .
.
Seen in a configuration matrix, the element counts can be derived by mirror removal and ratios of Coxeter group orders.[3]
| E6 | k-face | fk | f0 | f1 | f2 | f3 | f4 | f5 | k-figure | notes | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A5 | ( ) | f0 | 72 | 20 | 90 | 60 | 60 | 15 | 15 | 30 | 6 | 6 | r{3,3,3} | E6/A5 = 72*6!/6! = 72 | |
| A2A2A1 | { } | f1 | 2 | 720 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 3 | 3 | 9 | 3 | 3 | {3}×{3} | E6/A2A2A1 = 72*6!/3!/3!/2 = 720 | |
| A2A1A1 | {3} | f2 | 3 | 3 | 2160 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 2 | s{2,4} | E6/A2A1A1 = 72*6!/3!/2/2 = 2160 | |
| A3A1 | {3,3} | f3 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 1080 | * | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | { }∨( ) | E6/A3A1 = 72*6!/4!/2 = 1080 | |
| 4 | 6 | 4 | * | 1080 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| A4A1 | {3,3,3} | f4 | 5 | 10 | 10 | 5 | 0 | 216 | * | * | 2 | 0 | { } | E6/A4A1 = 72*6!/5!/2 = 216 | |
| 5 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 5 | * | 216 | * | 0 | 2 | ||||||
| D4 | h{4,3,3} | 8 | 24 | 32 | 8 | 8 | * | * | 270 | 1 | 1 | E6/D4 = 72*6!/8/4! = 270 | |||
| D5 | h{4,3,3,3} | f5 | 16 | 80 | 160 | 80 | 40 | 16 | 0 | 10 | 27 | * | ( ) | E6/D5 = 72*6!/16/5! = 27 | |
| 16 | 80 | 160 | 40 | 80 | 0 | 16 | 10 | * | 27 | ||||||
Related complex polyhedron
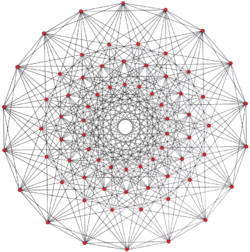
The regular complex polyhedron 3{3}3{4}2, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() , in has a real representation as the 122 polytope in 4-dimensional space. It has 72 vertices, 216 3-edges, and 54 3{3}3 faces. Its complex reflection group is 3[3]3[4]2, order 1296. It has a half-symmetry quasiregular construction as
, in has a real representation as the 122 polytope in 4-dimensional space. It has 72 vertices, 216 3-edges, and 54 3{3}3 faces. Its complex reflection group is 3[3]3[4]2, order 1296. It has a half-symmetry quasiregular construction as ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() , as a rectification of the Hessian polyhedron,
, as a rectification of the Hessian polyhedron, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() .[4]
.[4]
Related polytopes and honeycomb
Along with the semiregular polytope, 221, it is also one of a family of 39 convex uniform polytopes in 6-dimensions, made of uniform polytope facets and vertex figures, defined by all permutations of rings in this Coxeter-Dynkin diagram: ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() .
.
Geometric folding
The 122 is related to the 24-cell by a geometric folding E6 → F4 of Coxeter-Dynkin diagrams, E6 corresponding to 122 in 6 dimensions, F4 to the 24-cell in 4 dimensions. This can be seen in the Coxeter plane projections. The 24 vertices of the 24-cell are projected in the same two rings as seen in the 122.
| E6/F4 Coxeter planes | |
|---|---|
 122 |
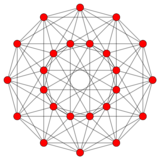 24-cell |
| D4/B4 Coxeter planes | |
 122 |
 24-cell |
Tessellations
This polytope is the vertex figure for a uniform tessellation of 6-dimensional space, 222, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() .
.
Rectified 122 polytope
| Rectified 122 | |
|---|---|
| Type | Uniform 6-polytope |
| Schläfli symbol | 2r{3,3,32,1} r{3,32,2} |
| Coxeter symbol | 0221 |
| Coxeter-Dynkin diagram | or |
| 5-faces | 126 |
| 4-faces | 1566 |
| Cells | 6480 |
| Faces | 6480 |
| Edges | 6480 |
| Vertices | 720 |
| Vertex figure | 3-3 duoprism prism |
| Petrie polygon | Dodecagon |
| Coxeter group | E6, 3,32,2, order 103680 |
| Properties | convex |
The rectified 122 polytope (also called 0221) can tessellate 6-dimensional space as the Voronoi cell of the E6* honeycomb lattice (dual of E6 lattice).[5]
Alternate names
- Birectified 221 polytope
- Rectified pentacontatetrapeton (acronym Ram) - rectified 54-facetted polypeton (Jonathan Bowers)[6]
Images
Vertices are colored by their multiplicity in this projection, in progressive order: red, orange, yellow.
| E6 [12] |
D5 [8] |
D4 / A2 [6] |
B6 [12/2] |
|---|---|---|---|

|
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination | 
|
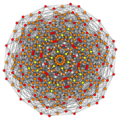
|
| A5 [6] |
A4 [5] |
A3 / D3 [4] | |
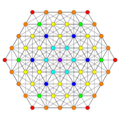
|

|
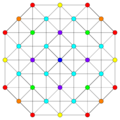
|
Construction
Its construction is based on the E6 group and information can be extracted from the ringed Coxeter-Dynkin diagram representing this polytope: ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() .
.
Removing the ring on the short branch leaves the birectified 5-simplex, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() .
.
Removing the ring on the either 2-length branch leaves the birectified 5-orthoplex in its alternated form: t2(211), ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() .
.
The vertex figure is determined by removing the ringed node and ringing the neighboring ring. This makes 3-3 duoprism prism, {3}×{3}×{}, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() .
.
Seen in a configuration matrix, the element counts can be derived by mirror removal and ratios of Coxeter group orders.[7][8]
| E6 | k-face | fk | f0 | f1 | f2 | f3 | f4 | f5 | k-figure | notes | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A2A2A1 | ( ) | f0 | 720 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 9 | 6 | 18 | 9 | 6 | 9 | 6 | 3 | 6 | 9 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | {3}×{3}×{ } | E6/A2A2A1 = 72*6!/3!/3!/2 = 720 | |
| A1A1A1 | { } | f1 | 2 | 6480 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | { }∨{ }∨( ) | E6/A1A1A1 = 72*6!/2/2/2 = 6480 | |
| A2A1 | {3} | f2 | 3 | 3 | 4320 | * | * | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | Sphenoid | E6/A2A1 = 72*6!/3!/2 = 4320 | |
| 3 | 3 | * | 4320 | * | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| A2A1A1 | 3 | 3 | * | * | 2160 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | { }∨{ } | E6/A2A1A1 = 72*6!/3!/2/2 = 2160 | |||
| A2A1 | {3,3} | f3 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 1080 | * | * | * | * | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | { }∨( ) | E6/A2A1 = 72*6!/3!/2 = 1080 | |
| A3 | r{3,3} | 6 | 12 | 4 | 4 | 0 | * | 2160 | * | * | * | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | {3} | E6/A3 = 72*6!/4! = 2160 | ||
| A3A1 | 6 | 12 | 4 | 0 | 4 | * | * | 1080 | * | * | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | { }∨( ) | E6/A3A1 = 72*6!/4!/2 = 1080 | |||
| {3,3} | 4 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 0 | * | * | * | 1080 | * | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | |||||
| r{3,3} | 6 | 12 | 0 | 4 | 4 | * | * | * | * | 1080 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | |||||
| A4 | r{3,3,3} | f4 | 10 | 30 | 20 | 10 | 0 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 432 | * | * | * | * | 1 | 1 | 0 | { } | E6/A4 = 72*6!/5! = 432 | |
| A4A1 | 10 | 30 | 20 | 0 | 10 | 5 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | * | 216 | * | * | * | 0 | 2 | 0 | E6/A4A1 = 72*6!/5!/2 = 216 | ||||
| A4 | 10 | 30 | 10 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 5 | 0 | * | * | 432 | * | * | 1 | 0 | 1 | E6/A4 = 72*6!/5! = 432 | ||||
| D4 | {3,4,3} | 24 | 96 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 0 | 8 | 8 | 0 | 8 | * | * | * | 270 | * | 0 | 1 | 1 | E6/D4 = 72*6!/8/4! = 270 | |||
| A4A1 | r{3,3,3} | 10 | 30 | 0 | 20 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 5 | * | * | * | * | 216 | 0 | 0 | 2 | E6/A4A1 = 72*6!/5!/2 = 216 | |||
| A5 | 2r{3,3,3,3} | f5 | 20 | 90 | 60 | 60 | 0 | 15 | 30 | 0 | 15 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 72 | * | * | ( ) | E6/A5 = 72*6!/6! = 72 | |
| D5 | 2r{4,3,3,3} | 80 | 480 | 320 | 160 | 160 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 0 | 40 | 16 | 16 | 0 | 10 | 0 | * | 27 | * | E6/D5 = 72*6!/16/5! = 27 | |||
| 80 | 480 | 160 | 320 | 160 | 0 | 80 | 40 | 80 | 80 | 0 | 0 | 16 | 10 | 16 | * | * | 27 | ||||||
Truncated 122 polytope
| Truncated 122 | |
|---|---|
| Type | Uniform 6-polytope |
| Schläfli symbol | t{3,32,2} |
| Coxeter symbol | t(122) |
| Coxeter-Dynkin diagram | or |
| 5-faces | 72+27+27 |
| 4-faces | 32+216+432+270+216 |
| Cells | 1080+2160+1080+1080+1080 |
| Faces | 4320+4320+2160 |
| Edges | 6480+720 |
| Vertices | 1440 |
| Vertex figure | ( )v{3}x{3} |
| Petrie polygon | Dodecagon |
| Coxeter group | E6, 3,32,2, order 103680 |
| Properties | convex |
Alternate names
- Truncated 122 polytope
Construction
Its construction is based on the E6 group and information can be extracted from the ringed Coxeter-Dynkin diagram representing this polytope: ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() .
.
Images
Vertices are colored by their multiplicity in this projection, in progressive order: red, orange, yellow.
| E6 [12] |
D5 [8] |
D4 / A2 [6] |
B6 [12/2] |
|---|---|---|---|

|

|
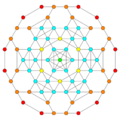
|

|
| A5 [6] |
A4 [5] |
A3 / D3 [4] | |
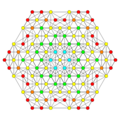
|

|
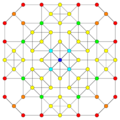
|
Birectified 122 polytope
| Birectified 122 polytope | |
|---|---|
| Type | Uniform 6-polytope |
| Schläfli symbol | 2r{3,32,2} |
| Coxeter symbol | 2r(122) |
| Coxeter-Dynkin diagram | or |
| 5-faces | 126 |
| 4-faces | 2286 |
| Cells | 10800 |
| Faces | 19440 |
| Edges | 12960 |
| Vertices | 2160 |
| Vertex figure | |
| Coxeter group | E6, 3,32,2, order 103680 |
| Properties | convex |
Alternate names
- Bicantellated 221
- Birectified pentacontitetrapeton (barm) (Jonathan Bowers)[9]
Images
Vertices are colored by their multiplicity in this projection, in progressive order: red, orange, yellow.
| E6 [12] |
D5 [8] |
D4 / A2 [6] |
B6 [12/2] |
|---|---|---|---|
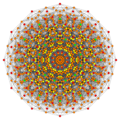
|
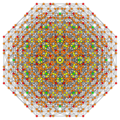
|
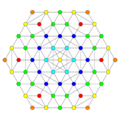
|
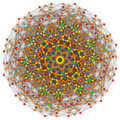
|
| A5 [6] |
A4 [5] |
A3 / D3 [4] | |
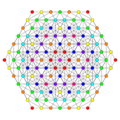
|
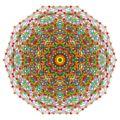
|
|
Trirectified 122 polytope
| Trirectified 122 polytope | |
|---|---|
| Type | Uniform 6-polytope |
| Schläfli symbol | 3r{3,32,2} |
| Coxeter symbol | 3r(122) |
| Coxeter-Dynkin diagram | or |
| 5-faces | 558 |
| 4-faces | 4608 |
| Cells | 8640 |
| Faces | 6480 |
| Edges | 2160 |
| Vertices | 270 |
| Vertex figure | |
| Coxeter group | E6, 3,32,2, order 103680 |
| Properties | convex |
Alternate names
- Tricantellated 221
- Trirectified pentacontitetrapeton (trim or cacam) (Jonathan Bowers)[10]
See also
- List of E6 polytopes
Notes
- ↑ Elte, 1912
- ↑ Klitzing, (o3o3o3o3o *c3x - mo)
- ↑ Coxeter, Regular Polytopes, 11.8 Gossett figures in six, seven, and eight dimensions, p. 202-203
- ↑ Coxeter, H. S. M., Regular Complex Polytopes, second edition, Cambridge University Press, (1991). p.30 and p.47
- ↑ The Voronoi Cells of the E6* and E7* Lattices , Edward Pervin
- ↑ Klitzing, (o3o3x3o3o *c3o - ram)
- ↑ Coxeter, Regular Polytopes, 11.8 Gossett figures in six, seven, and eight dimensions, p. 202-203
- ↑ Klitzing, Richard. "6D convex uniform polypeta o3o3x3o3o *c3o - ram". https://bendwavy.org/klitzing/dimensions/polypeta.htm.
- ↑ Klitzing, (o3x3o3x3o *c3o - barm)
- ↑ Klitzing, (x3o3o3o3x *c3o - cacam
References
- Elte, E. L. (1912), The Semiregular Polytopes of the Hyperspaces, Groningen: University of Groningen
- H. S. M. Coxeter, Regular Polytopes, 3rd Edition, Dover New York, 1973
- Kaleidoscopes: Selected Writings of H.S.M. Coxeter, edited by F. Arthur Sherk, Peter McMullen, Anthony C. Thompson, Asia Ivic Weiss, Wiley-Interscience Publication, 1995, ISBN 978-0-471-01003-6 [1]
- (Paper 24) H.S.M. Coxeter, Regular and Semi-Regular Polytopes III, [Math. Zeit. 200 (1988) 3-45] See p334 (figure 3.6a) by Peter mcMullen: (12-gonal node-edge graph of 122)
- Klitzing, Richard. "6D uniform polytopes (polypeta)". https://bendwavy.org/klitzing/dimensions/polypeta.htm. o3o3o3o3o *c3x - mo, o3o3x3o3o *c3o - ram, o3x3o3x3o *c3o - barm
Fundamental convex regular and uniform polytopes in dimensions 2–10
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Family | An | Bn | I2(p) / Dn | E6 / E7 / E8 / F4 / G2 | Hn | |||||||
| Regular polygon | Triangle | Square | p-gon | Hexagon | Pentagon | |||||||
| Uniform polyhedron | Tetrahedron | Octahedron • Cube | Demicube | Dodecahedron • Icosahedron | ||||||||
| Uniform 4-polytope | 5-cell | 16-cell • Tesseract | Demitesseract | 24-cell | 120-cell • 600-cell | |||||||
| Uniform 5-polytope | 5-simplex | 5-orthoplex • 5-cube | 5-demicube | |||||||||
| Uniform 6-polytope | 6-simplex | 6-orthoplex • 6-cube | 6-demicube | 122 • 221 | ||||||||
| Uniform 7-polytope | 7-simplex | 7-orthoplex • 7-cube | 7-demicube | 132 • 231 • 321 | ||||||||
| Uniform 8-polytope | 8-simplex | 8-orthoplex • 8-cube | 8-demicube | 142 • 241 • 421 | ||||||||
| Uniform 9-polytope | 9-simplex | 9-orthoplex • 9-cube | 9-demicube | |||||||||
| Uniform 10-polytope | 10-simplex | 10-orthoplex • 10-cube | 10-demicube | |||||||||
| Uniform n-polytope | n-simplex | n-orthoplex • n-cube | n-demicube | 1k2 • 2k1 • k21 | n-pentagonal polytope | |||||||
| Topics: Polytope families • Regular polytope • List of regular polytopes and compounds | ||||||||||||
 |
