Biology:Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase
| Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
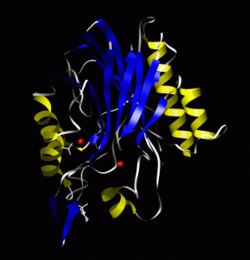 Crystal structure of sphingomyelinase from Bacillus cereus.[1] | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 3.1.4.12 | ||||||||
| CAS number | 9031-54-3 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
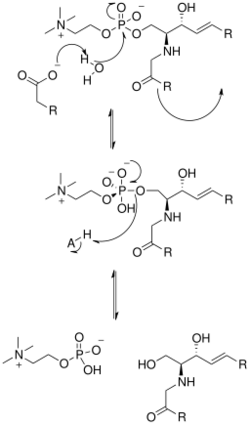
Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase (EC 3.1.4.12, also known as neutral sphingomyelinase, sphingomyelinase, or SMase; systematic name sphingomyelin cholinephosphohydrolase) is a hydrolase enzyme that is involved in sphingolipid metabolism reactions. SMase is a member of the DNase I superfamily of enzymes and is responsible for breaking sphingomyelin (SM) down into phosphocholine and ceramide. The activation of SMase has been suggested as a major route for the production of ceramide in response to cellular stresses.[2]
Sphingomyelinase family
Five types of SMase have been identified. These are classified according to their cation dependence and pH optima of action and are:
- Lysosomal acid SMase
- Secreted zinc-dependent acid SMase
- Magnesium-dependent neutral SMase
- Magnesium-independent neutral SMase
- Alkaline SMase
Of these, the lysosomal acidic SMase and the magnesium-dependent neutral SMase are considered major candidates for the production of ceramide in the cellular response to stress.
Neutral sphingomyelinase
Neutral sphingomyelinase (N-SMase) activity was first described in fibroblasts from patients with Niemann-Pick disease – a lysosomal storage disease characterized by deficiencies in acid SMase.[3] Subsequent study found that this enzyme was the product of a distinct gene, had an optimum pH of 7.4, was dependent on Mg2+ ions for activity, and was particularly enriched in brain.[4] However, a more recent study in bovine brain suggested the existence of multiple N-SMase isoforms with different biochemical and chromatographical properties.[5]
A major breakthrough came in the mid-1980s with the cloning of the first N-SMases from Bacillus cereus and Staphylococcus aureus.[6][7] Using the sequences of these bacterial sphingomyelinases in homology searches ultimately led to the identification of the yeast N-SMases ISC1 in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae[8] and the mammalian N-SMase enzymes, nSMase1 and nSMase2.[9][10] The identity between mammalian, yeast and bacterial SMases is very low - being approximately 20% between nSMase2 and the B. cereus SMase. However, an alignment of the sequences (see figure) indicate a number of conserved residues throughout the family, particularly in the catalytic region of the enzymes.[11] This has led to the suggestion of a common catalytic mechanism for the N-SMase family.
A third N-SMase protein – termed nSMase3 – was cloned and characterized in 2006.[12] nSMase3 bears little sequence similarity to either nSMase1 or nSMase2. However, there appears to be a high degree of evolutionary conservation from lower to higher organisms, suggesting that it may comprise a unique and distinct N-SMase. The high expression of nSMase3 in heart and skeletal muscle also suggests potential roles in heart function.[13]
Active site
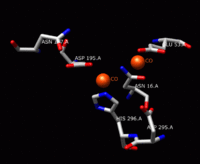
The solving of the crystal structure of the neutral sphingomyelinase from Listeria ivanovii and Bacillus cereus has allowed a fuller understanding of their enzymatic site. The active site of the B. cereus SMase comprises the residues Asn-16, Glu-53, Asp-195, Asn-197, and His-296. Of these, the residues Glu-53, Asp-195, and His-296 are known to be essential for activity. The relative catalytic activities of SMase when metal ions are bound to the active site have been studied for divalent metal ions Co2+, Mn2+, Mg2+, Ca2+, and Sr2+. Of these five metal ions, Co2+, Mn2+, and Mg2+ bound to the active site result in high catalytic activity of SMase. Ca2+ and Sr2+ bound to the active site exhibit much lower catalytic activity of SMase. When one Mg2+ ion or two Co2+ ions bind to the active site, double hexa-coordinated geometry results with two octahedral bi-pyramids for Co2+ and one octahedral bi-pyramid for Mg2+. When one Ca2+ ion binds to the active site, a hepta-coordinated geometry results. Therefore, the difference in catalytic activity for metal ions is predicted to be due to geometrical differences. Of Co2+ and Mg2+, SMase has better reactivity when two Co2+ ions are bound to SMase; when these Co2+ ions are bound, Glu-53 and His-296 each bind one divalent metal cation. These cations are surrounded by bridged water molecules and function as Lewis acids.[1]
Mechanism
The solving of the crystal structure of the neutral sphingomyelinase from Listeria ivanovii and Bacillus cereus has also shed light on their catalytic mechanisms. The active site of SMase contains Glu and His residues that are each bound to one or two divalent metal cations, usually Co2+, Mg2+, or Ca2+ for optimum performance. These two cations assist in catalysis by recruiting SM to the active site of SMase. The divalent cation bound to the Glu residue interacts with the amido-oxygen and ester-oxygen between C1 and the phosphate group of SM; an Asn residue and the divalent metal cation bound to the His residue bind to the oxygen atoms of the phosphate group of SM. This stabilizes the phosphate group's negative charge. The metal cation bound to the His residue and Asp and Asn side chains lower the pKa value of one of the bridged water molecules, thus activating a water molecule. This water molecule then acts as a nucleophile and attacks the phosphate group of SM, creating a pentavalent phosphorus atom whose negative charge is stabilized by the divalent metal cations. The phosphate then reforms its tetrahedral conformation and results in the products ceramide and phosphocholine.[1] In 2016 a model based on crystal structure of mammalian acid sphingomyelinase study was proposed whereby ASMase exists in equilibrium between open and closed forms of the saposin domain. In the absence of membranes, closed ASMasesap decoupled from ASMasecat would predominate and render the enzyme inactive. In the presence of anionic membranes, open ASMasesap becomes prevalent, docks onto the membrane surface and concomitantly forms an interface with the catalytic domain activating it for sphingomyelin hydrolysis.[14]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 PDB: 2ddt; "Structural basis of the sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase activity in neutral sphingomyelinase from Bacillus cereus". J. Biol. Chem. 281 (23): 16157–67. June 2006. doi:10.1074/jbc.M601089200. PMID 16595670.
- ↑ "The Ceramide-centric universe of lipid-mediated cell regulation: stress encounters of the lipid kind". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (29): 25847–50. July 2002. doi:10.1074/jbc.R200008200. PMID 12011103.
- ↑ "Sphingomyelinase in normal human spleens and in spleens from subjects with Niemann-Pick disease". J. Lipid Res. 8 (3): 202–9. May 1967. doi:10.1016/S0022-2275(20)40138-5. PMID 4962590.
- ↑ "Sphingomyelinase activity at pH 7.4 in human brain and a comparison to activity at pH 5.0". J. Lipid Res. 17 (5): 506–15. September 1976. doi:10.1016/S0022-2275(20)41749-3. PMID 9463.
- ↑ "Identification of multiple forms of membrane-associated neutral sphingomyelinase in bovine brain". J. Neurochem. 75 (3): 1004–14. September 2000. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2000.0751004.x. PMID 10936181.
- ↑ "Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus of the beta-lysin determinant from Staphylococcus aureus: evidence that bacteriophage conversion of beta-lysin activity is caused by insertional inactivation of the beta-lysin determinant". Microb. Pathog. 1 (6): 549–64. December 1986. doi:10.1016/0882-4010(86)90040-9. PMID 3334158.
- ↑ "Nucleotide sequence and expression in Escherichia coli of the gene coding for sphingomyelinase of Bacillus cereus". Eur. J. Biochem. 175 (2): 213–20. August 1988. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14186.x. PMID 2841128.
- ↑ "Identification of ISC1 (YER019w) as inositol phosphosphingolipid phospholipase C in Saccharomyces cerevisiae". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (50): 39793–8. December 2000. doi:10.1074/jbc.M007721200. PMID 11006294.
- ↑ "Cloned mammalian neutral sphingomyelinase: functions in sphingolipid signaling?". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95 (7): 3638–43. March 1998. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.7.3638. PMID 9520418. Bibcode: 1998PNAS...95.3638T.
- ↑ "Characterization and subcellular localization of murine and human magnesium-dependent neutral sphingomyelinase". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (8): 5710–7. February 2000. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.8.5710. PMID 10681556.
- ↑ "The extended family of neutral sphingomyelinases". Biochemistry 45 (38): 11247–56. September 2006. doi:10.1021/bi061307z. PMID 16981685.
- ↑ Krut, Oleg; Wiegmann, Katja; Kashkar, Hamid; Yazdanpanah, Benjamin; Krönke, Martin (2006-05-12). "Novel tumor necrosis factor-responsive mammalian neutral sphingomyelinase-3 is a C-tail-anchored protein". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 281 (19): 13784–13793. doi:10.1074/jbc.M511306200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 16517606.
- ↑ "Novel tumor necrosis factor-responsive mammalian neutral sphingomyelinase-3 is a C-tail-anchored protein". J. Biol. Chem. 281 (19): 13784–93. May 2006. doi:10.1074/jbc.M511306200. PMID 16517606.
- ↑ Gorelik, Alexei; Illes, Katalin; Heinz, Leonhard X.; Superti-Furga, Giulio; Nagar, Bhushan (2016-07-20). "Crystal structure of mammalian acid sphingomyelinase" (in en). Nature Communications 7 (1): 12196. doi:10.1038/ncomms12196. ISSN 2041-1723. PMID 27435900.
Further reading
External links
- Sphingomyelin+Phosphodiesterase at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
 |