Chemistry:Lomitapide
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Juxtapid (US), Lojuxta (EU) |
| Other names | AEGR-773, BMS-201038 |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| Chemical and physical data | |
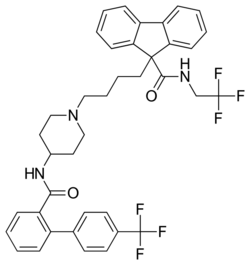
| Formula | C39H37F6N3O2 |
| Molar mass | 693.734 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Lomitapide , sold under the brand name Juxtapid in the US and Lojuxta in the EU, is a medication used as a lipid-lowering agent for the treatment of familial hypercholesterolemia, developed by Aegerion Pharmaceuticals.[3] It has been tested in clinical trials as single treatment and in combinations with atorvastatin, ezetimibe and fenofibrate.[4][5]
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved lomitapide in December 2012, as an orphan drug to reduce LDL cholesterol, total cholesterol, apolipoprotein B, and non-high-density lipoprotein (non-HDL) cholesterol in people with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH).[6]
In July 2013, the European Commission approved lomitapide as an adjunct to a low-fat diet and other lipid-lowering medicinal products with or without low density lipoprotein (LDL) apheresis in adults with HoFH.[2]
Mechanism of action
Lomitapide inhibits the microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTP or MTTP) which is necessary for very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) assembly and secretion in the liver.[3][7]
In December 2012, drug manufacturer Aegerion announced they had been approved by the FDA to as "an adjunct to a low-fat diet and other lipid-lowering treatments...in patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH)."[8][9]
Side effects
In a Phase III study, lomitapide led to elevated aminotransferase levels and fat accumulation in the liver.[7]
References
- ↑ "Juxtapid- lomitapide mesylate capsule". https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=e4c45bb5-15f4-437e-ab98-a649b3676d14.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Lojuxta EPAR". https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/lojuxta.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 H. Spreitzer (12 March 2007). "Neue Wirkstoffe – BMS-201038" (in German). Österreichische Apothekerzeitung (6/2007): 268.
- ↑ "Measures of obesity and outcomes after myocardial infarction". Circulation 118 (5): 469–71. July 2008. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.792689. PMID 18663098.
- ↑ "Aegerion Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Announces AEGR-733 Phase II Data Demonstrates Significant Lowering of LDL Cholesterol with Promising Hepatic Safety Profile". Business Wire. 9 November 2008. http://www.pr-inside.com/aegerion-pharmaceuticals-inc-announces-aegr-r904473.htm.
- ↑ "FDA approves new orphan drug for rare cholesterol disorder". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. https://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm333285.htm.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "Inhibition of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein in familial hypercholesterolemia". The New England Journal of Medicine 356 (2): 148–56. January 2007. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa061189. PMID 17215532.
- ↑ "FDA Approves Juxtapid for Homozygous Familial Hypercholesteolemia". 26 December 2012. http://www.dailyrx.com/juxtapid-reduces-cholesterol-patients-homozygous-familial-hypercholesterolemia.
- ↑ "FDA Approves Aegerion Pharmaceuticals' Juxtapid (lomitapide) Capsules for Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia (HoFH)" (Press release). Aegerion Pharmaceuticals. 24 December 2012. Archived from the original on 22 September 2016. Retrieved 1 January 2013.
External links
- "Lomitapide". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://druginfo.nlm.nih.gov/drugportal/name/lomitapide.
 |
