Chemistry:Mipomersen
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Kynamro |
| Other names | ISIS 301012 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Multum Consumer Information |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Subcutaneous injection |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | ≥90% |
| Metabolism | Nucleases |
| Elimination half-life | 1–2 months |
| Excretion | <4% in urine in 24 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C230H305N67Na19O122P19S19 |
| Molar mass | 7594.76 g·mol−1 |
| |
| |
Mipomersen (INN; trade name Kynamro) is a drug used to treat homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia and is administered by subcutaneous injection. There is a serious risk of liver damage from this drug and it can only be prescribed in the context of a risk management plan.
Indications
Kynamro is used to treat homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia and is administered by injection.[1][2]
It cannot be freely prescribed; instead every person put on mipomersen is enrolled in a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies (REMS) program approved by the FDA.[1]
Pregnancy and lactation
Mipomersen is pregnancy category B; women who are pregnant or intending to become pregnant should only use this drug if needed. It is unknown if it is secreted in human breast milk, but it was found to be secreted in the breast milk of rats.[1]
Contraindications
The drug is contraindicated in people with moderate to severe liver impairment, active liver diseases, and unexplained high levels of transaminase liver enzymes.[1][3]
Adverse effects
The drug has a black box warning about the risk of liver damage; specifically it can cause elevations in the levels of transaminases and causes fatty liver disease.[1]
In clinical trials, 18% of subjects taking mipomersen stopped using the drug due to adverse effects; the most common adverse effects leading to discontinuation were injection site reactions, increases of transaminases, flu-like symptoms (fever, chills, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting), and abnormal liver tests.[1]
Other adverse effects include: heart problems including angina and palpitations, edema, pain in legs or arms, headache, insomnia, and hypertension.[1]
Interactions
Other drugs known for causing liver problems might add to mipomersen's risk of liver damage. No pharmacokinetic interactions have been described.[3]
Pharmacology
Mechanism of action
Mipomersen binds to the messenger RNA coding for apolipoprotein B-100 (ApoB-100), a protein that is the main component of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL). As a consequence, the RNA is degraded by the enzyme ribonuclease H, and ApoB-100 is not translated.[3]
Pharmacokinetics
After subcutaneous injection, mipomersen reaches highest blood levels after 3 to 4 hours. It accumulates in the liver,[citation needed] which is convenient since apolipoprotein B predominantly acts there. Protein binding is over 90%. The molecule is slowly broken up by endonucleases and subsequently by exonucleases. After 24 hours, less than 4% of the degradation products are found in the urine, and overall half-life is 1 to 2 months.[3]
Chemistry
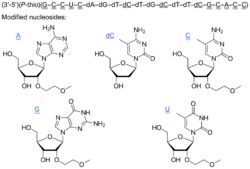
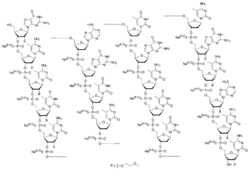
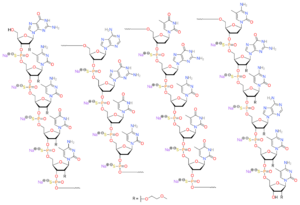
The compound is a 'second-generation' antisense oligonucleotide; the nucleotides are linked with phosphorothioate linkages rather than the phosphodiester linkages of RNA and DNA, and the sugar parts are deoxyribose in the middle part of the molecule and 2’-O-methoxyethyl-modified ribose at the two ends. These modifications make the drug resistant to degradation by nucleases, allowing it to be administered weekly.
The complete sequence is portrayed below:[5][1]: 10
5’—G*—mC*—mC*—mU*—mC*—dA—dG—dT—dmC—dT—dG—dmC—dT—dT—dmC—G*—mC*—A*—mC*—mC*—3’*= 2’-O-(2-methoxyethyl)m= 5-methyld= 2’-deoxy
History
The drug was discovered and developed to Phase 2 by Ionis Pharmaceuticals and subsequently licensed to Genzyme Corporation in 2008 by an auction bid. Ionis earned an upfront payment of $325 million, with payments of a further $825 million if milestones are met.[6]
Mipomersen was rejected by the European Medicines Agency in 2012[7] and again in 2013 due to concerns about the liver and cardiovascular adverse effects.[8]
In January 2013, The United States Food and Drug Administration approved mipomersen for the treatment of homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia.[9][10]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 "Kynamro (mipomersen sodium) Injection, Solution for Subcutaneous Injection. Full Prescribing Information". Kastle Therapeutics, Chicago, IL. http://www.kynamro.com/media/pdfs/Kynamro_Prescribing_information.pdf.
- ↑ "Cholesterol Lowering Drugs". Endotext [Internet]. South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc.. August 10, 2016. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK395573/.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Drugs.com: Mipomersen Professional Drug Facts.
- ↑ "International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN). Recommended International Nonproprietary Names: List 61". World Health Organization. 2009. https://www.who.int/medicines/publications/druginformation/innlists/RL61.pdf.
- ↑ "Clinical and preclinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of mipomersen (kynamro(®)): a second-generation antisense oligonucleotide inhibitor of apolipoprotein B". Clinical Pharmacokinetics 54 (2): 133–146. February 2015. doi:10.1007/s40262-014-0224-4. PMID 25559341.
- ↑ "Genzyme and Isis Complete Licensing of Mipomersen". FreshNews.com. 24 June 2008. http://www.freshnews.com/news/74972/genzyme-and-isis-complete-licensing-mipomersen.
- ↑ "EMA committee shoots down Sanofi's cholesterol drug mipomersen". FierceBiotech. December 14, 2012. http://www.fiercebiotech.com/regulatory/ema-committee-shoots-down-sanofi-s-cholesterol-drug-mipomersen.
- ↑ "Refusal of the marketing authorisation for Kynamro (mipomersen)". European Medicines Agency (EMA). March 21, 2013. http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Summary_of_opinion_-_Initial_authorisation/human/002429/WC500140678.pdf.
- ↑ "F.D.A. Approves Genetic Drug to Treat Rare Disease". The New York Times. 29 January 2013. https://www.nytimes.com/2013/01/30/business/fda-approves-genetic-drug-to-treat-rare-disease.html.
- ↑ "FDA approves new orphan drug Kynamro to treat inherited cholesterol disorder". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 29 January 2013. https://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm337195.htm.
