Chemistry:Sesamin
From HandWiki
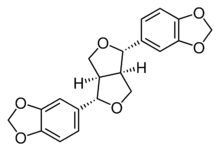
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(7α,7′α,8α,8′α)-3,4:3′,4′-Bis[methylenebis(oxy)]-7,9′:7′,9-diepoxylignane
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
5,5′-[(1S,3aR,4S,6aR)-Tetrahydro-1H,3H-furo[3,4-c]furan-1,4-diyl]bis(2H-1,3-benzodioxole) | |
| Other names
Fagarol
Sezamin Pseudocubebin Episesamin Asarinin Eleutheroside B4 D-(+)-Sesamin d-Sesamin (+)-Sesamin l-Sesamin | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H18O6 | |
| Molar mass | 354.35 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Sesamin is a lignan isolated from the bark of Fagara plants and from sesame oil. It has been used as a dietary fat-reduction supplement. Its major metabolite is enterolactone, which has an elimination half life of less than 6 hours.[1] Sesamin and sesamolin are minor components of sesame oil,[2] on average comprising only 0.14% of the oil by mass.[3]
See also
- Sesamol, another phenolic component of sesame oil
References
- ↑ Peñalvo JL; Heinonen SM; Aura AM; Adlercreutz H (May 2005). "Dietary sesamin is converted to enterolactone in humans". J. Nutr. 135 (5): 1056–1062. doi:10.1093/jn/135.5.1056. PMID 15867281.
- ↑ "Comparative analysis of sesame lignans (sesamin and sesamolin) in affecting hepatic fatty acid metabolism in rats.". Br J Nutr 97 (1): 85–95. Jan 2007. doi:10.1017/S0007114507252699. PMID 17217563.
- ↑ Ikan, Raphael (1991). Natural Products: A Laboratory Guide 2nd Ed.. San Diego: Academic Press, Inc.. p. 50. ISBN 978-0123705518. https://books.google.com/books?id=B7P8HQimBAIC&q=Natural+Products%3A+A+Laboratory+Guide+2nd+Ed..
 |

