Chemistry:Magnolol
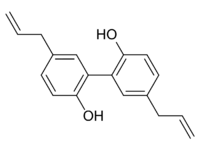
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3,3′-Neoligna-8,8′-diene-4,4′-diol
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
5,5′-Di(prop-2-en-1-yl)[1,1′-biphenyl]-2,2′-diol | |
| Other names
Dehydrodichavicol
5,5'-Diallyl-2,2'-dihydroxybiphenyl 5,5'-Diallyl-2,2'-biphenyldiol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H18O2 | |
| Molar mass | 266.340 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Magnolol is an organic compound that is classified as lignan. It is a bioactive compound found in the bark of the Houpu magnolia (Magnolia officinalis) and in M. grandiflora.[2] The compound exists at the level of a few percent in the bark of species of magnolia, the extracts of which have been used in traditional Chinese and Japanese medicine. In addition to magnolol, related lignans occur in the extracts including honokiol, which is an isomer of magnolol.
Bioactivity
It is known to act on the GABAA receptors in rat cells in vitro[3] as well as having antifungal properties.[4] Magnolol has a number of osteoblast-stimulating and osteoclast-inhibiting activities in cell culture and has been suggested as a candidate for screening for anti-osteoporosis activity.[5] It has anti-periodontal disease activity in a rat model.[6] Structural analogues have been studied and found to be strong allosteric modulators of GABAA.[7]
Magnolol is also binding in dimeric mode to PPARγ, acting as an agonist of this nuclear receptor.[8]
Magnolol may interact with cannabinoid receptors, acting as a partial agonist of CB2 receptors, with lower affinity for the CB1 receptor.[9]
References
- ↑ Magnolol at Sigma-Aldrich
- ↑ Lee, Young-Jung; Lee, Yoot Mo; Lee, Chong-Kil; Jung, Jae Kyung; Han, Sang Bae; Hong, Jin Tae (2011). "Therapeutic applications of compounds in the Magnolia family". Pharmacology & Therapeutics 130 (2): 157–76. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2011.01.010. PMID 21277893.
- ↑ Ai, Jinglu; Wang, Xiaomei; Nielsen, Mogens (2001). "Honokiol and Magnolol Selectively Interact with GABAA Receptor Subtypes in vitro". Pharmacology 63 (1): 34–41. doi:10.1159/000056110. PMID 11408830.
- ↑ Bang, Kyu Ho; Kim, Yoon Kwan; Min, Byung Sun; Na, Min Kyun; Rhee, Young Ha; Lee, Jong Pill; Bae, Ki Hwan (2000). "Antifungal activity of magnolol and honokiol". Archives of Pharmacal Research 23 (1): 46–9. doi:10.1007/BF02976465. PMID 10728656.
- ↑ Kwak, Eun Jung; Lee, Young Soon; Choi, Eun Mi (2012). "Effect of Magnolol on the Function of Osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 Cells". Mediators of Inflammation 2012: 1–7. doi:10.1155/2012/829650. PMID 22474400.
- ↑ Lu, Sheng-Hua; Huang, Ren-Yeong; Chou, Tz-Chong (2013). "Magnolol Ameliorates Ligature-Induced Periodontitis in Rats and Osteoclastogenesis: In Vivo and in Vitro Study". Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2013: 1–12. doi:10.1155/2013/634095. PMID 23573141.
- ↑ Fuchs, Alexander; Baur, Roland; Schoeder, Clara; Sigel, Erwin; Müller, Christa E. (December 2014). "Structural analogues of the natural products magnolol and honokiol as potent allosteric potentiators of GABAA receptors". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 22 (24): 6908–6917. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2014.10.027. PMID 25456080.
- ↑ Dreier, Dominik; Latkolik, Simone; Rycek, Lukas; Schnürch, Michael; Dymáková, Andrea; Atanasov, Atanas G.; Ladurner, Angela; Heiss, Elke H. et al. (20 October 2017). "Linked magnolol dimer as a selective PPARγ agonist – Structure-based rational design, synthesis, and bioactivity evaluation". Scientific Reports 7 (1): 13002. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-12628-5. PMID 29057944.
- ↑ Rempel, Viktor; Fuchs, Alexander; Hinz, Sonja; Karcz, Tadeusz; Lehr, Matthias; Koetter, Uwe; Müller, Christa E. (10 January 2013). "Magnolia Extract, Magnolol, and Metabolites: Activation of Cannabinoid CB 2 Receptors and Blockade of the Related GPR55". ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters 4 (1): 41–45. doi:10.1021/ml300235q. PMID 24900561.
Further reading
- Squires, Richard F.; Ai, Jinglu; Witt, Michael-Robin; Kahnberg, Pia; Saederup, Else; Sterner, Olov; Nielsen, Mogens (1999). "Honokiol and magnolol increase the number of 3H muscimol binding sites three-fold in rat forebrain membranes in vitro using a filtration assay, by allosterically increasing the affinities of low-affinity sites". Neurochemical Research 24 (12): 1593–602. doi:10.1023/A:1021116502548. PMID 10591411.
- "Metal-assisted synthesis of unsymmetrical magnolol and honokiol analogs and their biological assessment as GABAA receptor ligands". Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 25 (2): 400–3. 2015. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2014.10.091. PMID 25510374.
 |
