Biology:VEGF receptor
| VEGF receptor | |
|---|---|
 fms-related tyrosine kinase 1 (vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor receptor) | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | VEGF |
| InterPro | IPR009135 |
| Membranome | 1335 |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| Symbol | FLT1 |
| Alt. symbols | FLT |
| NCBI gene | 2321 |
| HGNC | 3763 |
| OMIM | 165070 |
| RefSeq | NM_002019 |
| UniProt | P17948 |
| Other data | |
| EC number | 2.7.1.112 |
| Locus | Chr. 13 q12 |
| kinase insert domain receptor (a type III receptor tyrosine kinase) | |
|---|---|
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | KDR |
| Alt. symbols | FLK1, VEGFR, VEGFR2, CD309 |
| NCBI gene | 3791 |
| HGNC | 6307 |
| OMIM | 191306 |
| RefSeq | NM_002253 |
| UniProt | P35968 |
| Other data | |
| EC number | 2.7.1.112 |
| Locus | Chr. 4 q11-q12 |
| fms-related tyrosine kinase 4 | |
|---|---|
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | FLT4 |
| Alt. symbols | VEGFR3, PCL |
| NCBI gene | 2324 |
| HGNC | 3767 |
| OMIM | 136352 |
| RefSeq | NM_002020 |
| UniProt | P35916 |
| Other data | |
| EC number | 2.7.1.112 |
| Locus | Chr. 5 q34-q35 |
VEGF receptors (VEGFRs) are receptors for vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF).[1][2] There are three main subtypes of VEGFR, numbered 1, 2 and 3. Depending on alternative splicing, they may be membrane-bound (mbVEGFR) or soluble (sVEGFR).[3]
Inhibitors of VEGFR are used in the treatment of cancer.
VEGF
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is an important signaling protein involved in both vasculogenesis (the formation of the circulatory system) and angiogenesis (the growth of blood vessels from pre-existing vasculature). As its name implies, VEGF activity is restricted mainly to cells of the vascular endothelium, although it does have effects on a limited number of other cell types (e.g. stimulation monocyte/macrophage migration). In vitro, VEGF has been shown to stimulate endothelial cell mitogenesis and cell migration. VEGF also enhances microvascular permeability and is sometimes referred to as vascular permeability factor.
Receptor biology
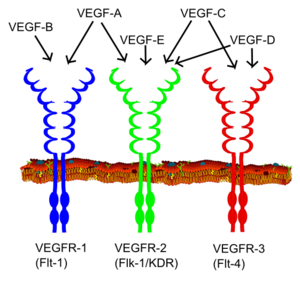
All members of the VEGF family stimulate cellular responses by binding to tyrosine kinase receptors (the VEGFRs) on the cell surface, causing them to dimerize and become activated through transphosphorylation. The VEGF receptors have an extracellular portion consisting of 7 immunoglobulin-like domains, a single transmembrane spanning region and an intracellular portion containing a split tyrosine-kinase domain.
VEGF-A binds to VEGFR-1 (Flt-1) and VEGFR-2 (KDR/Flk-1). VEGFR-2 appears to mediate almost all of the known cellular responses to VEGF.[1] The function of VEGFR-1 is less well defined, although it is thought to modulate VEGFR-2 signaling. Another function of VEGFR-1 is to act as a dummy/decoy receptor, sequestering VEGF from VEGFR-2 binding (this appears to be particularly important during vasculogenesis in the embryo). In fact, an alternatively spliced form of VEGFR-1 (sFlt1) is not a membrane bound protein but is secreted and functions primarily as a decoy.[6] A third receptor has been discovered (VEGFR-3), however, VEGF-A is not a ligand for this receptor. VEGFR-3 mediates lymphangiogenesis in response to VEGF-C and VEGF-D.
In addition to binding to VEGFRs, TACO VEGF binds to receptor complexes consisting of both neuropilins and VEGFRs. This receptor complex has increased VEGF signalling activity in endothelial cells (blood vessels).[7][8] Neuropilins (NRP) are pleiotropic receptors and therefore other molecules may interfere with the signalling of the NRP/VEGFR receptor complexes. For example, Class 3 semaphorins compete with VEGF165 for NRP binding and could therefore regulate VEGF-mediated angiogenesis.[9]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2: structure, function, intracellular signalling and therapeutic inhibition". Cellular Signalling 19 (10): 2003–12. October 2007. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2007.05.013. PMID 17658244.
- ↑ "Structure and function of VEGF receptors". IUBMB Life 61 (9): 915–22. September 2009. doi:10.1002/iub.234. PMID 19658168.
- ↑ "Vascular endothelial growth factor-A is a survival factor for nucleus pulposus cells in the intervertebral disc". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 372 (2): 367–72. July 2008. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.05.044. PMID 18492486.
- ↑ cancerpublications.com.
- ↑ Interactions of VEGF ligands and VEGF receptors ResearchVEGF.com, retrieved on November 13, 2009
- ↑ "Semaphorin-PlexinD1 signaling limits angiogenic potential via the VEGF decoy receptor sFlt1". Developmental Cell 21 (2): 301–14. August 2011. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2011.06.033. PMID 21802375.
- ↑ "Neuropilin-1 is expressed by endothelial and tumor cells as an isoform-specific receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor". Cell 92 (6): 735–45. March 1998. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81402-6. PMID 9529250.
- ↑ "VEGF binding to NRP1 is essential for VEGF stimulation of endothelial cell migration, complex formation between NRP1 and VEGFR2, and signaling via FAK Tyr407 phosphorylation". Molecular Biology of the Cell 22 (15): 2766–76. August 2011. doi:10.1091/mbc.E09-12-1061. PMID 21653826. PMC 3145551. http://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/1327618/1/Mol._Biol._Cell-2011-Herzog-2766-76.pdf.
- ↑ "A perspective on the role of class III semaphorin signaling in central nervous system trauma". Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience 8: 328. 2014. doi:10.3389/fncel.2014.00328. PMID 25386118.
External links
- VEGF+Receptors at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Proteopedia Vascular_Endothelial_Growth_Factor_Receptor - the Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor Structure in Interactive 3D
 |
