Biology:Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor
 Generic protein structure example |
The insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) receptor is a protein found on the surface of human cells. It is a transmembrane receptor that is activated by a hormone called insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) and by a related hormone called IGF-2. It belongs to the large class of tyrosine kinase receptors. This receptor mediates the effects of IGF-1, which is a polypeptide protein hormone similar in molecular structure to insulin. IGF-1 plays an important role in growth and continues to have anabolic effects in adults – meaning that it can induce hypertrophy of skeletal muscle and other target tissues. Mice lacking the IGF-1 receptor die late in development, and show a dramatic reduction in body mass. This testifies to the strong growth-promoting effect of this receptor.
Structure
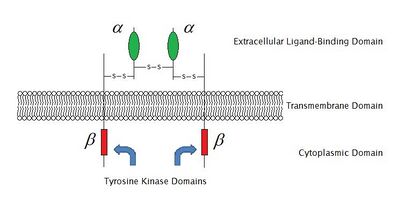
Two alpha subunits and two beta subunits make up the IGF-1 receptor. Both the α and β subunits are synthesized from a single mRNA precursor. The precursor is then glycosylated, proteolytically cleaved, and crosslinked by cysteine bonds to form a functional transmembrane αβ chain.[1] The α chains are located extracellularly, while the β subunit spans the membrane and is responsible for intracellular signal transduction upon ligand stimulation. The mature IGF-1R has a molecular weight of approximately 320 kDa.citation? The receptor is a member of a family which consists of the insulin receptor and the IGF-2R (and their respective ligands IGF-1 and IGF-2), along with several IGF-binding proteins.
IGF-1R and the insulin receptor both have a binding site for ATP, which is used to provide the phosphates for autophosphorylation. There is a 60% homology between IGF-1R and the insulin receptor. The structures of the autophosphorylation complexes of tyrosine residues 1165 and 1166 have been identified within crystals of the IGF1R kinase domain.[2]
In response to ligand binding, the α chains induce the tyrosine autophosphorylation of the β chains. This event triggers a cascade of intracellular signaling that, while cell type-specific, often promotes cell survival and cell proliferation.[3][4]
Family members
Tyrosine kinase receptors, including the IGF-1 receptor, mediate their activity by causing the addition of a phosphate groups to particular tyrosines on certain proteins within a cell. This addition of phosphate induces what are called "cell signaling" cascades - and the usual result of activation of the IGF-1 receptor is survival and proliferation in mitosis-competent cells, and growth (hypertrophy) in tissues such as skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle.
Function
Embryonic development
During embryonic development, the IGF-1R pathway is involved with the developing limb buds.
Lactation
The IGFR signalling pathway is of critical importance during normal development of mammary gland tissue during pregnancy and lactation. During pregnancy, there is intense proliferation of epithelial cells which form the duct and gland tissue. Following weaning, the cells undergo apoptosis and all the tissue is destroyed. Several growth factors and hormones are involved in this overall process, and IGF-1R is believed to have roles in the differentiation of the cells and a key role in inhibiting apoptosis until weaning is complete.
Insulin signaling
IGF-1 binds to at least two cell surface receptors: the IGF1 Receptor (IGFR), and the insulin receptor. The IGF-1 receptor seems to be the "physiologic" receptor—it binds IGF-1 at significantly higher affinity than it binds insulin.[5] Like the insulin receptor, the IGF-1 receptor is a receptor tyrosine kinase—meaning it signals by causing the addition of a phosphate molecule on particular tyrosines. IGF-1 activates the insulin receptor at approximately 10% the potency of insulin. Part of this signaling may be via IGF1R/insulin receptor heterodimers (the reason for the confusion is that binding studies show that IGF-1 binds the insulin receptor 100-fold less well than insulin, yet that does not correlate with the actual potency of IGF-1 in vivo at inducing phosphorylation of the insulin receptor, and hypoglycemia).
Aging
Studies in female mice have shown that both supraoptic nucleus (SON) and paraventricular nucleus (PVN) lose approximately one-third of IGF-1R immunoreactive cells with normal aging. Also, old calorically restricted (CR) mice lost higher numbers of IGF-1R non-immunoreactive cells while maintaining similar counts of IGF-1R immunoreactive cells in comparison to old-Al mice. Consequently, old-CR mice show a higher percentage of IGF-1R immunoreactive cells, reflecting increased hypothalamic sensitivity to IGF-1 in comparison to normally aging mice.[6][7]
Craniosynostosis
Mutations in IGF1R have been associated with craniosynostosis.[8]
Body size
IGF-1R has been shown to have a significant effect on body size in small dog breeds.[9] A "nonsynonymous SNP at chr3:44,706,389 that changes a highly conserved arginine at amino acid 204 to histidine" is associated with particularly tiny body size. "This mutation is predicted to prevent formation of several hydrogen bonds within the cysteine-rich domain of the receptor’s ligand-binding extracellular subunit. Nine of 13 tiny dog breeds carry the mutation and many dogs are homozygous for it." Smaller individuals within several small and medium-sized breeds were shown to carry this mutation as well.
Mice carrying only one functional copy of IGF-1R are normal, but exhibit a ~15% decrease in body mass. IGF-1R has also been shown to regulate body size in dogs. A mutated version of this gene is found in a number of small dog breeds.[9]
Gene inactivation/deletion
Deletion of the IGF-1 receptor gene in mice results in lethality during early embryonic development, and for this reason, IGF-1 insensitivity, unlike the case of growth hormone (GH) insensitivity (Laron syndrome), is not observed in the human population.[10]
Clinical significance
Cancer
The IGF-1R is implicated in several cancers,[11][12] including breast, prostate, and lung cancers. In some instances its anti-apoptotic properties allow cancerous cells to resist the cytotoxic properties of chemotherapeutic drugs or radiotherapy. In breast cancer, where EGFR inhibitors such as erlotinib are being used to inhibit the EGFR signaling pathway, IGF-1R confers resistance by forming one half of a heterodimer (see the description of EGFR signal transduction in the erlotinib page), allowing EGFR signaling to resume in the presence of a suitable inhibitor. This process is referred to as crosstalk between EGFR and IGF-1R. It is further implicated in breast cancer by increasing the metastatic potential of the original tumour by conferring the ability to promote vascularisation.
Increased levels of the IGF-IR are expressed in the majority of primary and metastatic prostate cancer patient tumors.[13] Evidence suggests that IGF-IR signaling is required for survival and growth when prostate cancer cells progress to androgen independence.[14] In addition, when immortalized prostate cancer cells mimicking advanced disease are treated with the IGF-1R ligand, IGF-1, the cells become more motile.[15] Members of the IGF receptor family and their ligands also seem to be involved in the carcinogenesis of mammary tumors of dogs.[16][17] IGF1R is amplified in several cancer types based on analysis of TCGA data, and gene amplification could be one mechanism for overexpression of IGF1R in cancer.[18]
Lung cancer cells stimulated using glucocorticoids were induced into a reversible dormancy state which was dependent on the IGF-1R and its accompanying survival signaling pathways.[19]
Inhibitors
Due to the similarity of the structures of IGF-1R and the insulin receptor (IR), especially in the regions of the ATP binding site and tyrosine kinase regions, synthesising selective inhibitors of IGF-1R is difficult. Prominent in current research are three main classes of inhibitor:
- Tyrphostins such as AG538[20] and AG1024. These are in early pre-clinical testing. They are not thought to be ATP-competitive, although they are when used in EGFR as described in QSAR studies. These show some selectivity towards IGF-1R over IR.
- Pyrrolo(2,3-d)-pyrimidine derivatives such as NVP-AEW541, invented by Novartis, which show far greater (100 fold) selectivity towards IGF-1R over IR.[21]
- Monoclonal antibodies are probably the most specific and promising therapeutic compounds. Teprotumumab is a novel therapy showing significant benefit for Thyroid Eye Disease.
Interactions
Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor has been shown to interact with:
- ARHGEF12,[22]
- C-src tyrosine kinase,[23]
- Cbl gene,[24]
- EHD1,[25]
- GRB10,[26][27][28][29]
- IRS1,[27][30][31]
- Mdm2,[24]
- NEDD4,[24][26]
- PIK3R3,[32]
- PTPN11,[30][33]
- RAS p21 protein activator 1,[33]
- SHC1[27][31][34]
- SOCS2,[35]
- SOCS3,[36] and
- YWHAE.[37]
Regulation
There is evidence to suggest that IGF1R is negatively regulated by the microRNA miR-7.[38]
See also
- Hypothalamic–pituitary–somatic axis
- Insulin receptor
- Linsitinib, an inhibitor of IGF-1R in clinical trials for cancer treatment
References
- ↑ "The IGF axis in the development and progression of prostate cancer". Recent Research Developments in Cancer: 437–462. 2001. ISBN 81-7895-002-2.
- ↑ "Identifying three-dimensional structures of autophosphorylation complexes in crystals of protein kinases". Science Signaling 8 (405): rs13. December 2015. doi:10.1126/scisignal.aaa6711. PMID 26628682.
- ↑ "Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins: biological actions". Endocrine Reviews 16 (1): 3–34. February 1995. doi:10.1210/edrv-16-1-3. PMID 7758431.
- ↑ "Molecular and cellular aspects of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor". Endocrine Reviews 16 (2): 143–63. April 1995. doi:10.1210/edrv-16-2-143. PMID 7540132.
- ↑ "Insulin-like growth factor - oestradiol crosstalk and mammary gland tumourigenesis". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Reviews on Cancer 1836 (2): 345–53. December 2013. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2013.10.005. PMID 24189571. http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/80781/1/Insulin%20like%20growth%20factor%20Oestradiol%20crosstalk%20and%20mammary%20gland%20tumourigenesis.pdf.
- ↑ "Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor immunoreactive cells are selectively maintained in the paraventricular hypothalamus of calorically restricted mice". International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience 25 (1): 23–8. February 2007. doi:10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2006.11.004. PMID 17194562.
- ↑ "Age-dependent loss of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor immunoreactive cells in the supraoptic hypothalamus is reduced in calorically restricted mice". International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience 24 (7): 431–6. November 2006. doi:10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2006.08.008. PMID 17034982.
- ↑ "IGF1R variants associated with isolated single suture craniosynostosis". American Journal of Medical Genetics. Part A 155A (1): 91–7. January 2011. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.33781. PMID 21204214.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 "The insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) contributes to reduced size in dogs". Mammalian Genome 23 (11–12): 780–90. December 2012. doi:10.1007/s00335-012-9417-z. PMID 22903739.
- ↑ Diseases of the Breast. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 28 March 2012. pp. 88–. ISBN 978-1-4511-4870-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=GLc8xYe239kC&pg=PT88.
- ↑ "The insulin-like growth factor-I receptor kinase inhibitor, NVP-ADW742, sensitizes small cell lung cancer cell lines to the effects of chemotherapy". Clinical Cancer Research 11 (4): 1563–71. February 2005. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-1544. PMID 15746061.
- ↑ "Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signalling and acquired resistance to gefitinib (ZD1839; Iressa) in human breast and prostate cancer cells". Endocrine-Related Cancer 11 (4): 793–814. December 2004. doi:10.1677/erc.1.00799. PMID 15613453.
- ↑ "Expression of the type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor is up-regulated in primary prostate cancer and commonly persists in metastatic disease". Cancer Research 62 (10): 2942–50. May 2002. PMID 12019176.
- ↑ "Increased insulin-like growth factor I receptor expression and signaling are components of androgen-independent progression in a lineage-derived prostate cancer progression model". Cancer Research 64 (23): 8620–9. December 2004. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-2446. PMID 15574769.
- ↑ "RhoC GTPase is required for PC-3 prostate cancer cell invasion but not motility". Oncogene 25 (16): 2285–96. April 2006. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209260. PMID 16314838.
- ↑ "Insulin receptor is expressed in normal canine mammary gland and benign adenomas but decreased in metastatic canine mammary carcinomas similar to human breast cancer". Veterinary and Comparative Oncology 8 (4): 293–301. December 2010. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5829.2009.00232.x. PMID 21062411.
- ↑ "Metastatic canine mammary carcinomas can be identified by a gene expression profile that partly overlaps with human breast cancer profiles". BMC Cancer 10: 618. November 2010. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-10-618. PMID 21062462.
- ↑ "Identification of druggable cancer driver genes amplified across TCGA datasets". PLOS ONE 9 (5): e98293. 2014. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0098293. PMID 24874471. Bibcode: 2014PLoSO...998293C.
- ↑ "Glucocorticoid receptor triggers a reversible drug-tolerant dormancy state with acquired therapeutic vulnerabilities in lung cancer". Nature Communications 12 (1): 4360. July 2021. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-24537-3. PMID 34272384. Bibcode: 2021NatCo..12.4360P.
- ↑ "Substrate competitive inhibitors of IGF-1 receptor kinase". Biochemistry 39 (51): 15705–12. December 2000. doi:10.1021/bi001516y. PMID 11123895.
- ↑ "Archived copy". http://www.targeting-the-kinome.org/images/Garcia-Echeverria3.pdf.
- ↑ "Direct interaction of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor with leukemia-associated RhoGEF". The Journal of Cell Biology 155 (5): 809–20. November 2001. doi:10.1083/jcb.200106139. PMID 11724822.
- ↑ "C-terminal Src kinase associates with ligand-stimulated insulin-like growth factor-I receptor". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 274 (9): 5422–8. February 1999. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.9.5422. PMID 10026153.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 24.2 "Identification of c-Cbl as a new ligase for insulin-like growth factor-I receptor with distinct roles from Mdm2 in receptor ubiquitination and endocytosis". Cancer Research 68 (14): 5669–77. July 2008. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6364. PMID 18632619.
- ↑ "Association of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor with EHD1 and SNAP29". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 276 (35): 33054–60. August 2001. doi:10.1074/jbc.M009913200. PMID 11423532.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 "The Grb10/Nedd4 complex regulates ligand-induced ubiquitination and stability of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor". Molecular and Cellular Biology 23 (9): 3363–72. May 2003. doi:10.1128/mcb.23.9.3363-3372.2003. PMID 12697834.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 27.2 "Evidence for the direct interaction of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor with IRS-1, Shc, and Grb10". Molecular Endocrinology 10 (6): 631–41. June 1996. doi:10.1210/mend.10.6.8776723. PMID 8776723.
- ↑ "Grb10 interacts differentially with the insulin receptor, insulin-like growth factor I receptor, and epidermal growth factor receptor via the Grb10 Src homology 2 (SH2) domain and a second novel domain located between the pleckstrin homology and SH2 domains". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 273 (12): 6860–7. March 1998. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.12.6860. PMID 9506989.
- ↑ "Grb10: A new substrate of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor". Cancer Research 56 (14): 3165–7. July 1996. PMID 8764099.
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 "Concerted activity of tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 and focal adhesion kinase in regulation of cell motility". Molecular and Cellular Biology 19 (4): 3125–35. April 1999. doi:10.1128/mcb.19.4.3125. PMID 10082579.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 "Evidence for a differential interaction of SHC and the insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) with the insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) receptor in the yeast two-hybrid system". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 270 (40): 23456–60. October 1995. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.40.23456. PMID 7559507.
- ↑ "Interaction of wild type and dominant-negative p55PIK regulatory subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase with insulin-like growth factor-1 signaling proteins". Molecular Endocrinology 11 (13): 1911–23. December 1997. doi:10.1210/mend.11.13.0029. PMID 9415396. http://www.whitelabs.org/publications/pdf/1997/MFW_NOT%20IN%20CV.pdf.
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 "Localization of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor binding sites for the SH2 domain proteins p85, Syp, and GTPase activating protein". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 270 (32): 19151–7. August 1995. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.32.19151. PMID 7642582.
- ↑ "Long-term estradiol deprivation in breast cancer cells up-regulates growth factor signaling and enhances estrogen sensitivity". Endocrine-Related Cancer. 12 12 (Suppl 1): S61-73. July 2005. doi:10.1677/erc.1.01018. PMID 16113100.
- ↑ "Interaction of human suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS)-2 with the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 273 (37): 24095–101. September 1998. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.37.24095. PMID 9727029.
- ↑ "Suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS)-3 protein interacts with the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 278 (1): 38–43. November 2000. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2000.3762. PMID 11071852. https://zenodo.org/record/1229526.
- ↑ "14-3-3 (epsilon) interacts with the insulin-like growth factor I receptor and insulin receptor substrate I in a phosphoserine-dependent manner". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 272 (17): 11663–9. April 1997. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.17.11663. PMID 9111084.
- ↑ "MicroRNA-7 targets IGF1R (insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor) in tongue squamous cell carcinoma cells". The Biochemical Journal 432 (1): 199–205. November 2010. doi:10.1042/BJ20100859. PMID 20819078.
Further reading
- "IGF-I: a mitogen also involved in differentiation processes in mammalian cells". The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology 28 (5): 499–510. May 1996. doi:10.1016/1357-2725(95)00168-9. PMID 8697095.
- "Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signal transduction: at the interface between physiology and cell biology". Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. Part B, Biochemistry & Molecular Biology 121 (1): 19–26. September 1998. doi:10.1016/S0305-0491(98)10106-2. PMID 9972281. https://zenodo.org/record/1260019.
- "Tyrosine kinase signalling in breast cancer: insulin-like growth factors and their receptors in breast cancer". Breast Cancer Research 2 (3): 170–5. 2001. doi:10.1186/bcr50. PMID 11250706.
- "The type-1 insulin-like growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase and breast cancer: biology and therapeutic relevance". Cancer and Metastasis Reviews 22 (4): 327–36. December 2003. doi:10.1023/A:1023720928680. PMID 12884909.
- "Signalling by the type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor: interplay with the epidermal growth factor receptor". Growth Factors 22 (2): 89–95. June 2004. doi:10.1080/08977190410001700998. PMID 15253384.
- "Role of estrogen receptor alpha in modulating IGF-I receptor signaling and function in breast cancer". Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research 23 (3): 385–94. September 2004. PMID 15595626.
- Insulin-like growth factor signaling in fish. International Review of Cytology. 243. 2005. pp. 215–85. doi:10.1016/S0074-7696(05)43004-1. ISBN 9780123646477.
- "Transcriptional regulation of the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor gene in breast cancer". Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology 252 (1–2): 241–6. June 2006. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2006.03.018. PMID 16647191.
External links
- IGF-1+Receptor at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Overview of all the structural information available in the PDB for UniProt: P08069 (Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor) at the PDBe-KB.
 |