Physics:Representation theory of the Lorentz group

The Lorentz group is a Lie group of symmetries of the spacetime of special relativity. This group can be realized as a collection of matrices, linear transformations, or unitary operators on some Hilbert space; it has a variety of representations.[nb 1] This group is significant because special relativity together with quantum mechanics are the two physical theories that are most thoroughly established,[nb 2] and the conjunction of these two theories is the study of the infinite-dimensional unitary representations of the Lorentz group. These have both historical importance in mainstream physics, as well as connections to more speculative present-day theories.
Development
The full theory of the finite-dimensional representations of the Lie algebra of the Lorentz group is deduced using the general framework of the representation theory of semisimple Lie algebras. The finite-dimensional representations of the connected component [math]\displaystyle{ \text{SO}(3; 1)^+ }[/math] of the full Lorentz group O(3; 1) are obtained by employing the Lie correspondence and the matrix exponential. The full finite-dimensional representation theory of the universal covering group (and also the spin group, a double cover) [math]\displaystyle{ \text{SL}(2,\Complex) }[/math] of [math]\displaystyle{ \text{SO}(3; 1)^+ }[/math] is obtained, and explicitly given in terms of action on a function space in representations of [math]\displaystyle{ \text{SL}(2,\Complex) }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{sl}(2,\Complex) }[/math]. The representatives of time reversal and space inversion are given in space inversion and time reversal, completing the finite-dimensional theory for the full Lorentz group. The general properties of the (m, n) representations are outlined. Action on function spaces is considered, with the action on spherical harmonics and the Riemann P-functions appearing as examples. The infinite-dimensional case of irreducible unitary representations are realized for the [math]\displaystyle{ \text{SL}(2,\Complex) }[/math] principal series and the complementary series. Finally, the Plancherel formula for [math]\displaystyle{ \text{SL}(2,\Complex) }[/math] is given, and representations of SO(3, 1) are classified and realized for Lie algebras.
The development of the representation theory has historically followed the development of the more general theory of representation theory of semisimple groups, largely due to Élie Cartan and Hermann Weyl, but the Lorentz group has also received special attention due to its importance in physics. Notable contributors are physicist E. P. Wigner and mathematician Valentine Bargmann with their Bargmann–Wigner program,[1] one conclusion of which is, roughly, a classification of all unitary representations of the inhomogeneous Lorentz group amounts to a classification of all possible relativistic wave equations.[2] The classification of the irreducible infinite-dimensional representations of the Lorentz group was established by Paul Dirac's doctoral student in theoretical physics, Harish-Chandra, later turned mathematician,[nb 3] in 1947. The corresponding classification for [math]\displaystyle{ \mathrm{SL}(2, \Complex) }[/math] was published independently by Bargmann and Israel Gelfand together with Mark Naimark in the same year.
Applications
Many of the representations, both finite-dimensional and infinite-dimensional, are important in theoretical physics. Representations appear in the description of fields in classical field theory, most importantly the electromagnetic field, and of particles in relativistic quantum mechanics, as well as of both particles and quantum fields in quantum field theory and of various objects in string theory and beyond. The representation theory also provides the theoretical ground for the concept of spin. The theory enters into general relativity in the sense that in small enough regions of spacetime, physics is that of special relativity.[3]
The finite-dimensional irreducible non-unitary representations together with the irreducible infinite-dimensional unitary representations of the inhomogeneous Lorentz group, the Poincare group, are the representations that have direct physical relevance.[4][5]
Infinite-dimensional unitary representations of the Lorentz group appear by restriction of the irreducible infinite-dimensional unitary representations of the Poincaré group acting on the Hilbert spaces of relativistic quantum mechanics and quantum field theory. But these are also of mathematical interest and of potential direct physical relevance in other roles than that of a mere restriction.[6] There were speculative theories,[7][8] (tensors and spinors have infinite counterparts in the expansors of Dirac and the expinors of Harish-Chandra) consistent with relativity and quantum mechanics, but they have found no proven physical application. Modern speculative theories potentially have similar ingredients per below.
Classical field theory
While the electromagnetic field together with the gravitational field are the only classical fields providing accurate descriptions of nature, other types of classical fields are important too. In the approach to quantum field theory (QFT) referred to as second quantization, the starting point is one or more classical fields, where e.g. the wave functions solving the Dirac equation are considered as classical fields prior to (second) quantization.[9] While second quantization and the Lagrangian formalism associated with it is not a fundamental aspect of QFT,[10] it is the case that so far all quantum field theories can be approached this way, including the standard model.[11] In these cases, there are classical versions of the field equations following from the Euler–Lagrange equations derived from the Lagrangian using the principle of least action. These field equations must be relativistically invariant, and their solutions (which will qualify as relativistic wave functions according to the definition below) must transform under some representation of the Lorentz group.
The action of the Lorentz group on the space of field configurations (a field configuration is the spacetime history of a particular solution, e.g. the electromagnetic field in all of space over all time is one field configuration) resembles the action on the Hilbert spaces of quantum mechanics, except that the commutator brackets are replaced by field theoretical Poisson brackets.[9]
Relativistic quantum mechanics
For the present purposes the following definition is made:[12] A relativistic wave function is a set of n functions ψα on spacetime which transforms under an arbitrary proper Lorentz transformation Λ as
[math]\displaystyle{ \psi'^\alpha(x) = D{[\Lambda]^\alpha}_\beta \psi^\beta \left(\Lambda^{-1} x\right), }[/math]
where D[Λ] is an n-dimensional matrix representative of Λ belonging to some direct sum of the (m, n) representations to be introduced below.
The most useful relativistic quantum mechanics one-particle theories (there are no fully consistent such theories) are the Klein–Gordon equation[13] and the Dirac equation[14] in their original setting. They are relativistically invariant and their solutions transform under the Lorentz group as Lorentz scalars ((m, n) = (0, 0)) and bispinors respectively ((0, 1/2) ⊕ (1/2, 0)). The electromagnetic field is a relativistic wave function according to this definition, transforming under (1, 0) ⊕ (0, 1).[15]
The infinite-dimensional representations may be used in the analysis of scattering.[16]
Quantum field theory
In quantum field theory, the demand for relativistic invariance enters, among other ways in that the S-matrix necessarily must be Poincaré invariant.[17] This has the implication that there is one or more infinite-dimensional representation of the Lorentz group acting on Fock space.[nb 4] One way to guarantee the existence of such representations is the existence of a Lagrangian description (with modest requirements imposed, see the reference) of the system using the canonical formalism, from which a realization of the generators of the Lorentz group may be deduced.[18]
The transformations of field operators illustrate the complementary role played by the finite-dimensional representations of the Lorentz group and the infinite-dimensional unitary representations of the Poincare group, witnessing the deep unity between mathematics and physics.[19] For illustration, consider the definition an n-component field operator:[20] A relativistic field operator is a set of n operator valued functions on spacetime which transforms under proper Poincaré transformations (Λ, a) according to[21][22]
[math]\displaystyle{ \Psi^\alpha(x) \to \Psi'^\alpha(x) = U[\Lambda, a]\Psi^\alpha(x) U^{-1} \left[\Lambda, a\right] = D{\left[\Lambda^{-1}\right]^\alpha}_\beta \Psi^\beta (\Lambda x + a) }[/math]
Here U[Λ, a] is the unitary operator representing (Λ, a) on the Hilbert space on which Ψ is defined and D is an n-dimensional representation of the Lorentz group. The transformation rule is the second Wightman axiom of quantum field theory.
By considerations of differential constraints that the field operator must be subjected to in order to describe a single particle with definite mass m and spin s (or helicity), it is deduced that[23][nb 5]
[math]\displaystyle{ \Psi^\alpha(x) = \sum_\sigma \int dp \left(a(\mathbf{p}, \sigma) u^\alpha(\mathbf{p}, \sigma) e^{ip \cdot x} + a^\dagger(\mathbf{p}, \sigma) v^\alpha(\mathbf{p}, \sigma) e^{-ip \cdot x} \right), }[/math] |
|
() |
where a†, a are interpreted as creation and annihilation operators respectively. The creation operator a† transforms according to[23][24]
[math]\displaystyle{ a^\dagger(\mathbf{p}, \sigma) \rightarrow a'^\dagger \left(\mathbf{p}, \sigma\right) = U[\Lambda]a^\dagger(\mathbf{p}, \sigma) U \left[\Lambda^{-1}\right] = a^\dagger(\Lambda \mathbf{p}, \rho) D^{(s)}{\left[R(\Lambda, \mathbf{p})^{-1}\right]^\rho}_\sigma, }[/math]
and similarly for the annihilation operator. The point to be made is that the field operator transforms according to a finite-dimensional non-unitary representation of the Lorentz group, while the creation operator transforms under the infinite-dimensional unitary representation of the Poincare group characterized by the mass and spin (m, s) of the particle. The connection between the two are the wave functions, also called coefficient functions
[math]\displaystyle{ u^\alpha(\mathbf{p}, \sigma) e^{ip \cdot x},\quad v^\alpha(\mathbf{p}, \sigma) e^{-ip \cdot x} }[/math]
that carry both the indices (x, α) operated on by Lorentz transformations and the indices (p, σ) operated on by Poincaré transformations. This may be called the Lorentz–Poincaré connection.[25] To exhibit the connection, subject both sides of equation (X1) to a Lorentz transformation resulting in for e.g. u,
[math]\displaystyle{ {D[\Lambda]^\alpha}_{\alpha'} u^{\alpha'}(\mathbf{p}, \lambda) = {D^{(s)}[R(\Lambda, \mathbf{p})]^{\lambda'}}_\lambda u^\alpha \left(\Lambda \mathbf{p}, \lambda'\right), }[/math]
where D is the non-unitary Lorentz group representative of Λ and D(s) is a unitary representative of the so-called Wigner rotation R associated to Λ and p that derives from the representation of the Poincaré group, and s is the spin of the particle.
All of the above formulas, including the definition of the field operator in terms of creation and annihilation operators, as well as the differential equations satisfied by the field operator for a particle with specified mass, spin and the (m, n) representation under which it is supposed to transform,[nb 6] and also that of the wave function, can be derived from group theoretical considerations alone once the frameworks of quantum mechanics and special relativity is given.[nb 7]
Speculative theories
In theories in which spacetime can have more than D = 4 dimensions, the generalized Lorentz groups O(D − 1; 1) of the appropriate dimension take the place of O(3; 1).[nb 8]
The requirement of Lorentz invariance takes on perhaps its most dramatic effect in string theory. Classical relativistic strings can be handled in the Lagrangian framework by using the Nambu–Goto action.[26] This results in a relativistically invariant theory in any spacetime dimension.[27] But as it turns out, the theory of open and closed bosonic strings (the simplest string theory) is impossible to quantize in such a way that the Lorentz group is represented on the space of states (a Hilbert space) unless the dimension of spacetime is 26.[28] The corresponding result for superstring theory is again deduced demanding Lorentz invariance, but now with supersymmetry. In these theories the Poincaré algebra is replaced by a supersymmetry algebra which is a Z2-graded Lie algebra extending the Poincaré algebra. The structure of such an algebra is to a large degree fixed by the demands of Lorentz invariance. In particular, the fermionic operators (grade 1) belong to a (0, 1/2) or (1/2, 0) representation space of the (ordinary) Lorentz Lie algebra.[29] The only possible dimension of spacetime in such theories is 10.[30]
Finite-dimensional representations
Representation theory of groups in general, and Lie groups in particular, is a very rich subject. The Lorentz group has some properties that makes it "agreeable" and others that make it "not very agreeable" within the context of representation theory; the group is simple and thus semisimple, but is not connected, and none of its components are simply connected. Furthermore, the Lorentz group is not compact.[31]
For finite-dimensional representations, the presence of semisimplicity means that the Lorentz group can be dealt with the same way as other semisimple groups using a well-developed theory. In addition, all representations are built from the irreducible ones, since the Lie algebra possesses the complete reducibility property.[nb 9][32] But, the non-compactness of the Lorentz group, in combination with lack of simple connectedness, cannot be dealt with in all the aspects as in the simple framework that applies to simply connected, compact groups. Non-compactness implies, for a connected simple Lie group, that no nontrivial finite-dimensional unitary representations exist.[33] Lack of simple connectedness gives rise to spin representations of the group.[34] The non-connectedness means that, for representations of the full Lorentz group, time reversal and reversal of spatial orientation have to be dealt with separately.[35][36]
History
The development of the finite-dimensional representation theory of the Lorentz group mostly follows that of representation theory in general. Lie theory originated with Sophus Lie in 1873.[37][38] By 1888 the classification of simple Lie algebras was essentially completed by Wilhelm Killing.[39][40] In 1913 the theorem of highest weight for representations of simple Lie algebras, the path that will be followed here, was completed by Élie Cartan.[41][42] Richard Brauer was during the period of 1935–38 largely responsible for the development of the Weyl-Brauer matrices describing how spin representations of the Lorentz Lie algebra can be embedded in Clifford algebras.[43][44] The Lorentz group has also historically received special attention in representation theory, see History of infinite-dimensional unitary representations below, due to its exceptional importance in physics. Mathematicians Hermann Weyl[41][45][37][46][47] and Harish-Chandra[48][49] and physicists Eugene Wigner[50][51] and Valentine Bargmann[52][53][54] made substantial contributions both to general representation theory and in particular to the Lorentz group.[55] Physicist Paul Dirac was perhaps the first to manifestly knit everything together in a practical application of major lasting importance with the Dirac equation in 1928.[56][57][nb 10]
The Lie algebra

This section addresses the irreducible complex linear representations of the complexification [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{so}(3; 1)_\Complex }[/math] of the Lie algebra [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{so}(3; 1) }[/math] of the Lorentz group. A convenient basis for [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{so}(3; 1) }[/math] is given by the three generators Ji of rotations and the three generators Ki of boosts. They are explicitly given in conventions and Lie algebra bases.
The Lie algebra is complexified, and the basis is changed to the components of its two ideals[58] [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{A} = \frac{\mathbf{J} + i \mathbf{K}}{2},\quad \mathbf{B} = \frac{\mathbf{J} - i \mathbf{K}}{2}. }[/math]
The components of A = (A1, A2, A3) and B = (B1, B2, B3) separately satisfy the commutation relations of the Lie algebra [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{su}(2) }[/math] and, moreover, they commute with each other,[59]
[math]\displaystyle{ \left[A_i, A_j\right] = i\varepsilon_{ijk} A_k,\quad \left[B_i, B_j\right] = i\varepsilon_{ijk} B_k,\quad \left[A_i, B_j\right] = 0, }[/math]
where i, j, k are indices which each take values 1, 2, 3, and εijk is the three-dimensional Levi-Civita symbol. Let [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{A}_\Complex }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{B}_\Complex }[/math] denote the complex linear span of A and B respectively.
One has the isomorphisms[60][nb 11]
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} \mathfrak{so}(3; 1) \hookrightarrow \mathfrak{so}(3; 1)_\Complex &\cong \mathbf{A}_\Complex \oplus \mathbf{B}_\Complex \cong \mathfrak{su}(2)_\Complex \oplus \mathfrak{su}(2)_\Complex \\[5pt] &\cong \mathfrak{sl}(2, \Complex) \oplus \mathfrak{sl}(2, \Complex) \\[5pt] &\cong \mathfrak{sl}(2, \Complex) \oplus i\mathfrak{sl}(2, \Complex) = \mathfrak{sl}(2, \Complex)_\Complex \hookleftarrow \mathfrak{sl}(2, \Complex), \end{align} }[/math] |
|
( ) |
where [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{sl}(2, \Complex) }[/math] is the complexification of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{su}(2) \cong \mathbf{A} \cong \mathbf{B}. }[/math]
The utility of these isomorphisms comes from the fact that all irreducible representations of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{su}(2) }[/math], and hence all irreducible complex linear representations of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{sl}(2, \Complex), }[/math] are known. The irreducible complex linear representation of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{sl}(2, \Complex) }[/math] is isomorphic to one of the highest weight representations. These are explicitly given in complex linear representations of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{sl}(2, \Complex). }[/math]
The unitarian trick

The Lie algebra [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{sl}(2, \Complex) \oplus \mathfrak{sl}(2, \Complex) }[/math] is the Lie algebra of [math]\displaystyle{ \text{SL}(2, \Complex) \times \text{SL}(2, \Complex). }[/math] It contains the compact subgroup SU(2) × SU(2) with Lie algebra [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{su}(2) \oplus \mathfrak{su}(2). }[/math] The latter is a compact real form of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{sl}(2, \Complex) \oplus \mathfrak{sl}(2, \Complex). }[/math] Thus from the first statement of the unitarian trick, representations of SU(2) × SU(2) are in one-to-one correspondence with holomorphic representations of [math]\displaystyle{ \text{SL}(2, \Complex) \times \text{SL}(2, \Complex). }[/math]
By compactness, the Peter–Weyl theorem applies to SU(2) × SU(2),[61] and hence orthonormality of irreducible characters may be appealed to. The irreducible unitary representations of SU(2) × SU(2) are precisely the tensor products of irreducible unitary representations of SU(2).[62]
By appeal to simple connectedness, the second statement of the unitarian trick is applied. The objects in the following list are in one-to-one correspondence:
- Holomorphic representations of [math]\displaystyle{ \text{SL}(2, \Complex) \times \text{SL}(2, \Complex) }[/math]
- Smooth representations of SU(2) × SU(2)
- Real linear representations of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{su}(2) \oplus \mathfrak{su}(2) }[/math]
- Complex linear representations of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{sl}(2, \Complex) \oplus \mathfrak{sl}(2, \Complex) }[/math]
Tensor products of representations appear at the Lie algebra level as either of[nb 12]
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} \pi_1\otimes\pi_2(X) &= \pi_1(X) \otimes \mathrm{Id}_V + \mathrm{Id}_U \otimes \pi_2(X) && X \in \mathfrak{g} \\ \pi_1\otimes\pi_2(X, Y) &= \pi_1(X) \otimes \mathrm{Id}_V + \mathrm{Id}_U \otimes \pi_2(Y) && (X, Y) \in \mathfrak{g} \oplus \mathfrak{g} \end{align} }[/math] |
|
( ) |
where Id is the identity operator. Here, the latter interpretation, which follows from (G6), is intended. The highest weight representations of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{sl}(2, \Complex) }[/math] are indexed by μ for μ = 0, 1/2, 1, .... (The highest weights are actually 2μ = 0, 1, 2, ..., but the notation here is adapted to that of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{so}(3; 1). }[/math]) The tensor products of two such complex linear factors then form the irreducible complex linear representations of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{sl}(2, \Complex) \oplus \mathfrak{sl}(2, \Complex). }[/math]
Finally, the [math]\displaystyle{ \R }[/math]-linear representations of the real forms of the far left, [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{so}(3; 1) }[/math], and the far right, [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{sl}(2, \Complex), }[/math][nb 13] in (A1) are obtained from the [math]\displaystyle{ \Complex }[/math]-linear representations of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{sl}(2, \Complex) \oplus \mathfrak{sl}(2, \Complex) }[/math] characterized in the previous paragraph.
The (μ, ν)-representations of sl(2, C)
The complex linear representations of the complexification of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{sl}(2, \Complex), \mathfrak{sl}(2, \Complex)_\Complex, }[/math] obtained via isomorphisms in (A1), stand in one-to-one correspondence with the real linear representations of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{sl}(2, \Complex). }[/math][63] The set of all real linear irreducible representations of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{sl}(2, \Complex) }[/math] are thus indexed by a pair (μ, ν). The complex linear ones, corresponding precisely to the complexification of the real linear [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{su}(2) }[/math] representations, are of the form (μ, 0), while the conjugate linear ones are the (0, ν).[63] All others are real linear only. The linearity properties follow from the canonical injection, the far right in (A1), of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{sl}(2, \Complex) }[/math] into its complexification. Representations on the form (ν, ν) or (μ, ν) ⊕ (ν, μ) are given by real matrices (the latter are not irreducible). Explicitly, the real linear (μ, ν)-representations of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{sl}(2, \Complex) }[/math] are [math]\displaystyle{ \varphi_{\mu, \nu}(X) = \left(\varphi_\mu \otimes \overline{\varphi_\nu}\right)(X) = \varphi_\mu(X) \otimes \operatorname{Id}_{\nu+1} + \operatorname{Id}_{\mu+1} \otimes \overline{\varphi_\nu(X)},\qquad X \in \mathfrak{sl}(2, \Complex) }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ \varphi_\mu, \mu = 0, \tfrac{1}{2}, 1, \tfrac{3}{2}, \ldots }[/math] are the complex linear irreducible representations of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{sl}(2, \Complex) }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \overline{\varphi_\nu}, \nu = 0, \tfrac{1}{2}, 1, \tfrac{3}{2}, \ldots }[/math] their complex conjugate representations. (The labeling is usually in the mathematics literature 0, 1, 2, ..., but half-integers are chosen here to conform with the labeling for the [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{so}(3, 1) }[/math] Lie algebra.) Here the tensor product is interpreted in the former sense of (A0). These representations are concretely realized below.
The (m, n)-representations of so(3; 1)
Via the displayed isomorphisms in (A1) and knowledge of the complex linear irreducible representations of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{sl}(2, \Complex) \oplus \mathfrak{sl}(2, \Complex) }[/math] upon solving for J and K, all irreducible representations of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{so}(3; 1)_\Complex, }[/math] and, by restriction, those of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{so}(3; 1) }[/math] are obtained. The representations of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{so}(3; 1) }[/math] obtained this way are real linear (and not complex or conjugate linear) because the algebra is not closed upon conjugation, but they are still irreducible.[60] Since [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{so}(3; 1) }[/math] is semisimple,[60] all its representations can be built up as direct sums of the irreducible ones.
Thus the finite dimensional irreducible representations of the Lorentz algebra are classified by an ordered pair of half-integers m = μ and n = ν, conventionally written as one of [math]\displaystyle{ (m, n) \equiv \pi_{(m,n)} : \mathfrak{so}(3;1) \to \mathfrak{gl}(V), }[/math] where V is a finite-dimensional vector space. These are, up to a similarity transformation, uniquely given by[nb 14]
[math]\displaystyle{ \pi_{(m,n)}(J_i) = J^{(m)}_i \otimes 1_{(2n+1)}+1_{(2m+1)} \otimes J^{(n)}_i }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ \pi_{(m,n)}(K_i) = -i \left(1_{(2m+1)} \otimes J^{(n)}_i - J^{(m)}_i \otimes 1_{(2n+1)}\right), }[/math] |
|
( ) |
where 1n is the n-dimensional unit matrix and [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{J}^{(n)} = \left(J^{(n)}_1, J^{(n)}_2, J^{(n)}_3\right) }[/math] are the (2n + 1)-dimensional irreducible representations of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{so}(3) \cong \mathfrak{su}(2) }[/math] also termed spin matrices or angular momentum matrices. These are explicitly given as[64] [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} \left(J_1^{(j)}\right)_{a'a} &= \frac{1}{2} \left(\sqrt{(j - a)(j + a + 1)}\delta_{a',a + 1} + \sqrt{(j + a)(j - a + 1)}\delta_{a',a - 1}\right) \\ \left(J_2^{(j)}\right)_{a'a} &= \frac{1}{2i}\left(\sqrt{(j - a)(j + a + 1)}\delta_{a',a + 1} - \sqrt{(j + a)(j - a + 1)}\delta_{a',a - 1}\right) \\ \left(J_3^{(j)}\right)_{a'a} &= a\delta_{a',a} \end{align} }[/math] where δ denotes the Kronecker delta. In components, with −m ≤ a, a′ ≤ m, −n ≤ b, b′ ≤ n, the representations are given by[65] [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} \left(\pi_{(m,n)}\left(J_i\right)\right)_{a'b', ab} &= \delta_{b'b} \left(J_i^{(m)}\right)_{a'a} + \delta_{a'a} \left(J_i^{(n)}\right)_{b'b}\\ \left(\pi_{(m,n)}\left(K_i\right)\right)_{a'b', ab} &= -i \left(\delta_{a'a} \left(J_i^{(n)}\right)_{b'b} - \delta_{b'b} \left(J_i^{(m)}\right)_{a'a}\right) \end{align} }[/math]
Common representations
| m = 0 | 1/2 | 1 | 3/2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 0 | Scalar (1) | Left-handed Weyl spinor (2) |
Self-dual 2-form (3) |
(4) |
| 1/2 | Right-handed Weyl spinor (2) |
4-vector (4) | (6) | (8) |
| 1 | Anti-self-dual 2-form (3) |
(6) | Traceless symmetric tensor (9) |
(12) |
| 3/2 | (4) | (8) | (12) | (16) |
- The (0, 0) representation is the one-dimensional trivial representation and is carried by relativistic scalar field theories.
- Fermionic supersymmetry generators transform under one of the (0, 1/2) or (1/2, 0) representations (Weyl spinors).[29]
- The four-momentum of a particle (either massless or massive) transforms under the (1/2, 1/2) representation, a four-vector.
- A physical example of a (1,1) traceless symmetric tensor field is the traceless[nb 15] part of the energy–momentum tensor Tμν.[66][nb 16]
Off-diagonal direct sums
Since for any irreducible representation for which m ≠ n it is essential to operate over the field of complex numbers, the direct sum of representations (m, n) and (n, m) have particular relevance to physics, since it permits to use linear operators over real numbers.
- (1/2, 0) ⊕ (0, 1/2) is the bispinor representation. See also Dirac spinor and Weyl spinors and bispinors below.
- (1, 1/2) ⊕ (1/2, 1) is the Rarita–Schwinger field representation.
- (3/2, 0) ⊕ (0, 3/2) would be the symmetry of the hypothesized gravitino.[nb 17] It can be obtained from the (1, 1/2) ⊕ (1/2, 1) representation.
- (1, 0) ⊕ (0, 1) is the representation of a parity-invariant 2-form field (a.k.a. curvature form). The electromagnetic field tensor transforms under this representation.
The group
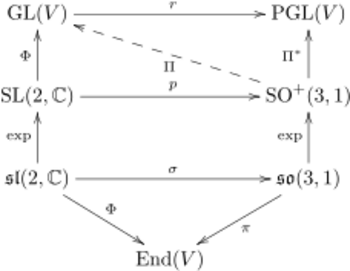
The approach in this section is based on theorems that, in turn, are based on the fundamental Lie correspondence.[67] The Lie correspondence is in essence a dictionary between connected Lie groups and Lie algebras.[68] The link between them is the exponential mapping from the Lie algebra to the Lie group, denoted [math]\displaystyle{ \exp : \mathfrak{g} \to G. }[/math]
If [math]\displaystyle{ \pi : \mathfrak{g} \to \mathfrak{gl}(V) }[/math] for some vector space V is a representation, a representation Π of the connected component of G is defined by
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} \Pi(g = e^{iX}) &\equiv e^{i\pi(X)}, && X \in \mathfrak g, \quad g = e^{iX} \in \mathrm{im}(\exp),\\ \Pi(g = g_1g_2\cdots g_n) &\equiv \Pi(g_1)\Pi(g_2)\cdots \Pi(g_n), && g \notin \mathrm{im}(\exp), \quad g_1 , g_2, \ldots, g_n \in \mathrm{im}(\exp). \end{align} }[/math] |
|
() |
This definition applies whether the resulting representation is projective or not.
Surjectiveness of exponential map for SO(3, 1)
From a practical point of view, it is important whether the first formula in (G2) can be used for all elements of the group. It holds for all [math]\displaystyle{ X \in \mathfrak{g} }[/math], however, in the general case, e.g. for [math]\displaystyle{ \text{SL}(2,\Complex) }[/math], not all g ∈ G are in the image of exp.
But [math]\displaystyle{ \exp : \mathfrak{so}(3;1) \to \text{SO}(3;1)^+ }[/math] is surjective. One way to show this is to make use of the isomorphism [math]\displaystyle{ \text{SO}(3; 1)^+ \cong \text{PGL}(2,\Complex), }[/math] the latter being the Möbius group. It is a quotient of [math]\displaystyle{ \text{GL}(n,\Complex) }[/math] (see the linked article). The quotient map is denoted with [math]\displaystyle{ p : \text{GL}(n,\Complex) \to \text{PGL}(2,\Complex). }[/math] The map [math]\displaystyle{ \exp : \mathfrak{gl}(n, \Complex) \to \text{GL}(n, \Complex) }[/math] is onto.[69] Apply (Lie) with π being the differential of p at the identity. Then
[math]\displaystyle{ \forall X \in \mathfrak{gl}(n, \Complex): \quad p ( \exp (iX)) =\exp ( i \pi (X)). }[/math]
Since the left hand side is surjective (both exp and p are), the right hand side is surjective and hence [math]\displaystyle{ \exp : \mathfrak{pgl}(2, \Complex) \to \text{PGL}(2, \Complex) }[/math] is surjective.[70] Finally, recycle the argument once more, but now with the known isomorphism between SO(3; 1)+ and [math]\displaystyle{ \text{PGL}(2, \Complex) }[/math] to find that exp is onto for the connected component of the Lorentz group.
Fundamental group
The Lorentz group is doubly connected, i. e. π1(SO(3; 1)) is a group with two equivalence classes of loops as its elements.
To exhibit the fundamental group of SO(3; 1)+, the topology of its covering group [math]\displaystyle{ \text{SL}(2,\Complex) }[/math] is considered. By the polar decomposition theorem, any matrix [math]\displaystyle{ \lambda \in \text{SL}(2,\Complex) }[/math] may be uniquely expressed as[71]
[math]\displaystyle{ \lambda = ue^h, }[/math]
where u is unitary with determinant one, hence in SU(2), and h is Hermitian with trace zero. The trace and determinant conditions imply:[72] [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} h &= \begin{pmatrix}c&a-ib\\a+ib&-c\end{pmatrix} && (a,b,c) \in \R^3 \\[4pt] u &= \begin{pmatrix}d+ie&f+ig\\-f+ig&d-ie\end{pmatrix} && (d,e,f,g) \in \R^4 \text{ subject to } d^2 + e^2 + f^2 + g^2 = 1. \end{align} }[/math]
The manifestly continuous one-to-one map is a homeomorphism with continuous inverse given by (the locus of u is identified with [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbb{S}^3 \subset \R^4 }[/math])
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{cases} \R^3 \times \mathbb{S}^3\to \text{SL}(2, \Complex) \\ (r,s) \mapsto u(s) e^{h(r)} \end{cases} }[/math]
explicitly exhibiting that [math]\displaystyle{ \text{SL}(2,\Complex) }[/math] is simply connected. But [math]\displaystyle{ \text{SO}(3; 1)\cong \text{SL}(2,\Complex)/\{\pm I\}, }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ \{\pm I\} }[/math] is the center of [math]\displaystyle{ \text{SL}(2,\Complex) }[/math]. Identifying λ and −λ amounts to identifying u with −u, which in turn amounts to identifying antipodal points on [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbb{S}^3. }[/math] Thus topologically,[72] [math]\displaystyle{ \text{SO}(3; 1) \cong \R^3 \times ( \mathbb{S}^3/\Z_2), }[/math]
where last factor is not simply connected: Geometrically, it is seen (for visualization purposes, [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbb{S}^3 }[/math] may be replaced by [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbb{S}^2 }[/math]) that a path from u to −u in [math]\displaystyle{ SU(2) \cong \mathbb{S}^3 }[/math] is a loop in [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbb{S}^3/\Z_2 }[/math] since u and −u are antipodal points, and that it is not contractible to a point. But a path from u to −u, thence to u again, a loop in [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbb{S}^3 }[/math] and a double loop (considering p(ueh) = p(−ueh), where [math]\displaystyle{ p : \text{SL}(2,\Complex)\to \text{SO}(3; 1) }[/math] is the covering map) in [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbb{S}^3/\Z_2 }[/math] that is contractible to a point (continuously move away from −u "upstairs" in [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbb{S}^3 }[/math] and shrink the path there to the point u).[72] Thus π1(SO(3; 1)) is a group with two equivalence classes of loops as its elements, or put more simply, SO(3; 1) is doubly connected.
Projective representations
Since π1(SO(3; 1)+) has two elements, some representations of the Lie algebra will yield projective representations.[73][nb 18] Once it is known whether a representation is projective, formula (G2) applies to all group elements and all representations, including the projective ones — with the understanding that the representative of a group element will depend on which element in the Lie algebra (the X in (G2)) is used to represent the group element in the standard representation.
For the Lorentz group, the (m, n)-representation is projective when m + n is a half-integer. See § Spinors.
For a projective representation Π of SO(3; 1)+, it holds that[72]
[math]\displaystyle{ \left[ \Pi(\Lambda_1)\Pi(\Lambda_2)\Pi^{-1}(\Lambda_1\Lambda_2) \right]^2 = 1 \Rightarrow \Pi(\Lambda_1\Lambda_2) = \pm\Pi(\Lambda_1)\Pi(\Lambda_2),\quad \Lambda_1, \Lambda_2 \in \mathrm{SO}(3; 1), }[/math] |
|
( ) |
since any loop in SO(3; 1)+ traversed twice, due to the double connectedness, is contractible to a point, so that its homotopy class is that of a constant map. It follows that Π is a double-valued function. It is not possible to consistently choose a sign to obtain a continuous representation of all of SO(3; 1)+, but this is possible locally around any point.[33]
The covering group SL(2, C)
Consider [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{sl}(2,\Complex) }[/math] as a real Lie algebra with basis
[math]\displaystyle{ \left(\frac{1}{2}\sigma_1, \frac{1}{2}\sigma_2, \frac{1}{2}\sigma_3, \frac{i}{2}\sigma_1, \frac{i}{2}\sigma_2, \frac{i}{2}\sigma_3\right)\equiv(j_1, j_2, j_3, k_1, k_2, k_3), }[/math]
where the sigmas are the Pauli matrices. From the relations
[math]\displaystyle{ [\sigma_i, \sigma_j] = 2i\epsilon_{ijk}\sigma_k }[/math] |
|
() |
is obtained
[math]\displaystyle{ [j_i, j_j] = i\epsilon_{ijk}j_k, \quad [j_i, k_j] = i\epsilon_{ijk}k_k, \quad [k_i, k_j] = -i\epsilon_{ijk}j_k, }[/math] |
|
() |
which are exactly on the form of the 3-dimensional version of the commutation relations for [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{so}(3; 1) }[/math] (see conventions and Lie algebra bases below). Thus, the map Ji ↔ ji, Ki ↔ ki, extended by linearity is an isomorphism. Since [math]\displaystyle{ \text{SL}(2,\Complex) }[/math] is simply connected, it is the universal covering group of SO(3; 1)+.
Non-surjectiveness of exponential mapping for SL(2, C)
The exponential mapping [math]\displaystyle{ \exp : \mathfrak{sl}(2,\Complex) \to \text{SL}(2,\Complex) }[/math] is not onto.[76] The matrix
[math]\displaystyle{ q = \begin{pmatrix} -1&1\\ 0&-1\\ \end{pmatrix} }[/math] |
|
() |
is in [math]\displaystyle{ \text{SL}(2,\Complex), }[/math] but there is no [math]\displaystyle{ Q\in \mathfrak{sl}(2,\Complex) }[/math] such that q = exp(Q).[nb 22]
In general, if g is an element of a connected Lie group G with Lie algebra [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{g}, }[/math] then, by (Lie),
[math]\displaystyle{ g = \exp(X_1) \cdots \exp(X_n), \qquad X_1, \ldots X_n \in \mathfrak{g}. }[/math] |
|
() |
The matrix q can be written
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} &\exp(-X)\exp(i\pi H) \\ {}={} &\exp \left(\begin{pmatrix} 0&-1\\ 0&0\\ \end{pmatrix}\right) \exp \left(i\pi \begin{pmatrix} 1&0\\ 0&-1\\ \end{pmatrix} \right) \\[6pt] {}={} &\begin{pmatrix} 1&-1\\ 0&1 \\ \end{pmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} -1&0\\ 0&-1\\ \end{pmatrix}\\[6pt] {}={} &\begin{pmatrix} -1&1\\ 0&-1\\ \end{pmatrix} \\ {}={} &q. \end{align} }[/math] |
|
( ) |
Realization of representations of SL(2, C) and sl(2, C) and their Lie algebras
The complex linear representations of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{sl}(2,\Complex) }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \text{SL}(2,\Complex) }[/math] are more straightforward to obtain than the [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{so}(3; 1)^+ }[/math] representations. They can be (and usually are) written down from scratch. The holomorphic group representations (meaning the corresponding Lie algebra representation is complex linear) are related to the complex linear Lie algebra representations by exponentiation. The real linear representations of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{sl}(2,\Complex) }[/math] are exactly the (μ, ν)-representations. They can be exponentiated too. The (μ, 0)-representations are complex linear and are (isomorphic to) the highest weight-representations. These are usually indexed with only one integer (but half-integers are used here).
The mathematics convention is used in this section for convenience. Lie algebra elements differ by a factor of i and there is no factor of i in the exponential mapping compared to the physics convention used elsewhere. Let the basis of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{sl}(2,\Complex) }[/math] be[77]
[math]\displaystyle{ H = \begin{pmatrix} 1&0\\ 0&-1\\ \end{pmatrix}, \quad X = \begin{pmatrix} 0&1\\ 0&0\\ \end{pmatrix}, \quad Y = \begin{pmatrix} 0&0\\ 1&0\\ \end{pmatrix}. }[/math] |
|
() |
This choice of basis, and the notation, is standard in the mathematical literature.
Complex linear representations
The irreducible holomorphic (n + 1)-dimensional representations [math]\displaystyle{ \text{SL}(2,\Complex), n \geqslant 2, }[/math] can be realized on the space of homogeneous polynomial of degree n in 2 variables [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{P}^2_n, }[/math][78][79] the elements of which are
[math]\displaystyle{ P\begin{pmatrix} z_1\\ z_2\\ \end{pmatrix} = c_n z_1^n + c_{n-1} z_1^{n-1}z_2 + \cdots + c_0 z_2^n, \quad c_0, c_1, \ldots, c_n \in \mathbb Z. }[/math]
The action of [math]\displaystyle{ \text{SL}(2,\Complex) }[/math] is given by[80][81]
[math]\displaystyle{ (\phi_n(g)P)\begin{pmatrix} z_1\\ z_2\\ \end{pmatrix} = \left [\phi_n \begin{pmatrix} a&b\\ c&d\\ \end{pmatrix} P\right ] \begin{pmatrix} z_1\\ z_2\\ \end{pmatrix} = P\left( \begin{pmatrix} a&b\\ c&d\\ \end{pmatrix}^{-1} \begin{pmatrix} z_1\\ z_2\\ \end{pmatrix} \right ), \qquad P \in \mathbf{P}^2_n. }[/math] |
|
() |
The associated [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{sl}(2,\Complex) }[/math]-action is, using (G6) and the definition above, for the basis elements of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{sl}(2,\Complex), }[/math][82]
[math]\displaystyle{ \phi_n(H) = -z_1\frac{\partial}{\partial z_1} + z_2\frac{\partial}{\partial z_2}, \quad \phi_n(X) = -z_2\frac{\partial}{\partial z_1}, \quad \phi_n(Y) = -z_1\frac{\partial}{\partial z_2}. }[/math] |
|
() |
With a choice of basis for [math]\displaystyle{ P \in \mathbf{P}^2_{n} }[/math], these representations become matrix Lie algebras.
Real linear representations
The (μ, ν)-representations are realized on a space of polynomials [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{P}^2_{\mu,\nu} }[/math] in [math]\displaystyle{ z_1, \overline{z_1}, z_2, \overline{z_2}, }[/math] homogeneous of degree μ in [math]\displaystyle{ z_1, z_2 }[/math] and homogeneous of degree ν in [math]\displaystyle{ \overline{z_1}, \overline{z_2}. }[/math][79] The representations are given by[83]
[math]\displaystyle{ (\phi_{\mu,\nu}(g)P)\begin{pmatrix} z_1\\ z_2\\ \end{pmatrix} =\left [\phi_{\mu,\nu} \begin{pmatrix} a&b\\ c&d\\ \end{pmatrix} P\right ] \begin{pmatrix} z_1\\ z_2\\ \end{pmatrix} = P \left( \begin{pmatrix} a&b\\ c&d\\ \end{pmatrix}^{-1} \begin{pmatrix} z_1\\ z_2\\ \end{pmatrix} \right ), \quad P \in \mathbf{P}^2_{\mu,\nu}. }[/math] |
|
() |
By employing (G6) again it is found that
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} \phi_{\mu,\nu}(E)P = &- \frac{\partial P}{\partial z_1} \left (E_{11}z_1 + E_{12}z_2 \right ) - \frac{\partial P}{\partial z_2} \left (E_{21}z_1 + E_{22}z_2 \right) \\ &- \frac{\partial P}{\partial \overline{z_1}}\left (\overline{E_{11}}\overline{z_1} + \overline{E_{12}}\overline{z_2} \right ) -\frac{\partial P}{\partial \overline{z_2}} \left (\overline{E_{21}}\overline{z_1} + \overline{E_{22}}\overline{z_2} \right ) \end{align}, \quad E \in \mathfrak{sl}(2, \mathbf{C}). }[/math] |
|
() |
In particular for the basis elements,
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} \phi_{\mu,\nu}(H) &= -z_1\frac{\partial}{\partial z_1} + z_2\frac{\partial}{\partial z_2}-\overline{z_1}\frac{\partial}{\partial \overline{z_1}} + \overline{z_2}\frac{\partial}{\partial \overline{z_2}} \\ \phi_{\mu,\nu}(X) &= -z_2\frac{\partial}{\partial z_1} - \overline{z_2}\frac{\partial}{\partial \overline{z_1}} \\ \phi_{\mu,\nu}(Y) &= -z_1\frac{\partial}{\partial z_2} - \overline{z_1}\frac{\partial}{\partial \overline{z_2}} \end{align} }[/math] |
|
() |
Properties of the (m, n) representations
The (m, n) representations, defined above via (A1) (as restrictions to the real form [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{sl}(3, 1) }[/math]) of tensor products of irreducible complex linear representations πm = μ and πn = ν of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{sl}(2,\Complex), }[/math] are irreducible, and they are the only irreducible representations.[61]
- Irreducibility follows from the unitarian trick[84] and that a representation Π of SU(2) × SU(2) is irreducible if and only if Π = Πμ ⊗ Πν,[nb 23] where Πμ, Πν are irreducible representations of SU(2).
- Uniqueness follows from that the Πm are the only irreducible representations of SU(2), which is one of the conclusions of the theorem of the highest weight.[85]
Dimension
The (m, n) representations are (2m + 1)(2n + 1)-dimensional.[86] This follows easiest from counting the dimensions in any concrete realization, such as the one given in representations of [math]\displaystyle{ \text{SL}(2,\Complex) }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{sl}(2, \Complex) }[/math]. For a Lie general algebra [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{g} }[/math] the Weyl dimension formula,[87] [math]\displaystyle{ \dim\pi_\rho = \frac{\Pi_{\alpha \in R^+} \langle\alpha, \rho + \delta \rangle}{\Pi_{\alpha \in R^+} \langle\alpha, \delta \rangle}, }[/math] applies, where R+ is the set of positive roots, ρ is the highest weight, and δ is half the sum of the positive roots. The inner product [math]\displaystyle{ \langle \cdot, \cdot \rangle }[/math] is that of the Lie algebra [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{g}, }[/math] invariant under the action of the Weyl group on [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{h} \subset \mathfrak{g}, }[/math] the Cartan subalgebra. The roots (really elements of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{h}^* }[/math] are via this inner product identified with elements of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{h}. }[/math] For [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{sl}(2,\Complex), }[/math] the formula reduces to dim πμ = 2μ + 1 = 2m + 1, where the present notation must be taken into account. The highest weight is 2μ.[88] By taking tensor products, the result follows.
Faithfulness
If a representation Π of a Lie group G is not faithful, then N = ker Π is a nontrivial normal subgroup.[89] There are three relevant cases.
- N is non-discrete and abelian.
- N is non-discrete and non-abelian.
- N is discrete. In this case N ⊂ Z, where Z is the center of G.[nb 24]
In the case of SO(3; 1)+, the first case is excluded since SO(3; 1)+ is semi-simple.[nb 25] The second case (and the first case) is excluded because SO(3; 1)+ is simple.[nb 26] For the third case, SO(3; 1)+ is isomorphic to the quotient [math]\displaystyle{ \text{SL}(2,\Complex)/\{\pm I\}. }[/math] But [math]\displaystyle{ \{\pm I\} }[/math] is the center of [math]\displaystyle{ \text{SL}(2,\Complex). }[/math] It follows that the center of SO(3; 1)+ is trivial, and this excludes the third case. The conclusion is that every representation Π : SO(3; 1)+ → GL(V) and every projective representation Π : SO(3; 1)+ → PGL(W) for V, W finite-dimensional vector spaces are faithful.
By using the fundamental Lie correspondence, the statements and the reasoning above translate directly to Lie algebras with (abelian) nontrivial non-discrete normal subgroups replaced by (one-dimensional) nontrivial ideals in the Lie algebra,[90] and the center of SO(3; 1)+ replaced by the center of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{sl}(3; 1)^+ }[/math]The center of any semisimple Lie algebra is trivial[91] and [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{so}(3; 1) }[/math] is semi-simple and simple, and hence has no non-trivial ideals.
A related fact is that if the corresponding representation of [math]\displaystyle{ \text{SL}(2,\Complex) }[/math] is faithful, then the representation is projective. Conversely, if the representation is non-projective, then the corresponding [math]\displaystyle{ \text{SL}(2,\Complex) }[/math] representation is not faithful, but is 2:1.
Non-unitarity
The (m, n) Lie algebra representation is not Hermitian. Accordingly, the corresponding (projective) representation of the group is never unitary.[nb 27] This is due to the non-compactness of the Lorentz group. In fact, a connected simple non-compact Lie group cannot have any nontrivial unitary finite-dimensional representations.[33] There is a topological proof of this.[92] Let u : G → GL(V), where V is finite-dimensional, be a continuous unitary representation of the non-compact connected simple Lie group G. Then u(G) ⊂ U(V) ⊂ GL(V) where U(V) is the compact subgroup of GL(V) consisting of unitary transformations of V. The kernel of u is a normal subgroup of G. Since G is simple, ker u is either all of G, in which case u is trivial, or ker u is trivial, in which case u is faithful. In the latter case u is a diffeomorphism onto its image,[93] u(G) ≅ G and u(G) is a Lie group. This would mean that u(G) is an embedded non-compact Lie subgroup of the compact group U(V). This is impossible with the subspace topology on u(G) ⊂ U(V) since all embedded Lie subgroups of a Lie group are closed[94] If u(G) were closed, it would be compact,[nb 28] and then G would be compact,[nb 29] contrary to assumption.[nb 30]
In the case of the Lorentz group, this can also be seen directly from the definitions. The representations of A and B used in the construction are Hermitian. This means that J is Hermitian, but K is anti-Hermitian.[95] The non-unitarity is not a problem in quantum field theory, since the objects of concern are not required to have a Lorentz-invariant positive definite norm.[96]
Restriction to SO(3)
The (m, n) representation is, however, unitary when restricted to the rotation subgroup SO(3), but these representations are not irreducible as representations of SO(3). A Clebsch–Gordan decomposition can be applied showing that an (m, n) representation have SO(3)-invariant subspaces of highest weight (spin) m + n, m + n − 1, ..., | m − n|,[97] where each possible highest weight (spin) occurs exactly once. A weight subspace of highest weight (spin) j is (2j + 1)-dimensional. So for example, the (1/2, 1/2) representation has spin 1 and spin 0 subspaces of dimension 3 and 1 respectively.
Since the angular momentum operator is given by J = A + B, the highest spin in quantum mechanics of the rotation sub-representation will be (m + n)ℏ and the "usual" rules of addition of angular momenta and the formalism of 3-j symbols, 6-j symbols, etc. applies.[98]
Spinors
It is the SO(3)-invariant subspaces of the irreducible representations that determine whether a representation has spin. From the above paragraph, it is seen that the (m, n) representation has spin if m + n is half-integer. The simplest are (1/2, 0) and (0, 1/2), the Weyl-spinors of dimension 2. Then, for example, (0, 3/2) and (1, 1/2) are a spin representations of dimensions 2⋅3/2 + 1 = 4 and (2 + 1)(2⋅1/2 + 1) = 6 respectively. According to the above paragraph, there are subspaces with spin both 3/2 and 1/2 in the last two cases, so these representations cannot likely represent a single physical particle which must be well-behaved under SO(3). It cannot be ruled out in general, however, that representations with multiple SO(3) subrepresentations with different spin can represent physical particles with well-defined spin. It may be that there is a suitable relativistic wave equation that projects out unphysical components, leaving only a single spin.[99]
Construction of pure spin n/2 representations for any n (under SO(3)) from the irreducible representations involves taking tensor products of the Dirac-representation with a non-spin representation, extraction of a suitable subspace, and finally imposing differential constraints.[100]
Dual representations
The following theorems are applied to examine whether the dual representation of an irreducible representation is isomorphic to the original representation:
- The set of weights of the dual representation of an irreducible representation of a semisimple Lie algebra is, including multiplicities, the negative of the set of weights for the original representation.[101]
- Two irreducible representations are isomorphic if and only if they have the same highest weight.[nb 31]
- For each semisimple Lie algebra there exists a unique element w0 of the Weyl group such that if μ is a dominant integral weight, then w0 ⋅ (−μ) is again a dominant integral weight.[102]
- If [math]\displaystyle{ \pi_{\mu_0} }[/math] is an irreducible representation with highest weight μ0, then [math]\displaystyle{ \pi^*_{\mu_0} }[/math] has highest weight w0 ⋅ (−μ).[102]
Here, the elements of the Weyl group are considered as orthogonal transformations, acting by matrix multiplication, on the real vector space of roots. If −I is an element of the Weyl group of a semisimple Lie algebra, then w0 = −I. In the case of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{sl}(2,\Complex), }[/math] the Weyl group is W = {I, −I}.[103] It follows that each πμ, μ = 0, 1, ... is isomorphic to its dual [math]\displaystyle{ \pi^*_{\mu}. }[/math] The root system of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{sl}(2,\Complex) \oplus \mathfrak{sl}(2,\Complex) }[/math] is shown in the figure to the right.[nb 32] The Weyl group is generated by [math]\displaystyle{ \{w_{\gamma}\} }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ w_\gamma }[/math] is reflection in the plane orthogonal to γ as γ ranges over all roots.[nb 33] Inspection shows that wα ⋅ wβ = −I so −I ∈ W. Using the fact that if π, σ are Lie algebra representations and π ≅ σ, then Π ≅ Σ,[104] the conclusion for SO(3; 1)+ is [math]\displaystyle{ \pi_{m, n}^{*} \cong \pi_{m, n}, \quad \Pi_{m, n}^{*} \cong \Pi_{m, n}, \quad 2m, 2n \in \mathbf{N}. }[/math]
Complex conjugate representations
If π is a representation of a Lie algebra, then [math]\displaystyle{ \overline{\pi} }[/math] is a representation, where the bar denotes entry-wise complex conjugation in the representative matrices. This follows from that complex conjugation commutes with addition and multiplication.[105] In general, every irreducible representation π of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{sl}(n,\Complex) }[/math] can be written uniquely as π = π+ + π−, where[106] [math]\displaystyle{ \pi^\pm(X) = \frac{1}{2}\left(\pi(X) \pm i\pi\left(i^{-1}X\right)\right), }[/math] with [math]\displaystyle{ \pi^+ }[/math] holomorphic (complex linear) and [math]\displaystyle{ \pi^- }[/math] anti-holomorphic (conjugate linear). For [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{sl}(2,\Complex), }[/math] since [math]\displaystyle{ \pi_\mu }[/math] is holomorphic, [math]\displaystyle{ \overline{\pi_\mu} }[/math] is anti-holomorphic. Direct examination of the explicit expressions for [math]\displaystyle{ \pi_{\mu, 0} }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \pi_{0, \nu} }[/math] in equation (S8) below shows that they are holomorphic and anti-holomorphic respectively. Closer examination of the expression (S8) also allows for identification of [math]\displaystyle{ \pi^+ }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \pi^- }[/math] for [math]\displaystyle{ \pi_{\mu, \nu} }[/math] as [math]\displaystyle{ \pi^+_{\mu, \nu} = \pi_\mu^{\oplus_{\nu+1}},\qquad \pi^-_{\mu, \nu} = \overline{\pi_\nu^{\oplus_{\mu+1}}}. }[/math]
Using the above identities (interpreted as pointwise addition of functions), for SO(3; 1)+ yields [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} \overline{\pi_{m, n}} &= \overline{\pi_{m, n}^+ + \pi_{m, n}^-}=\overline{\pi_m^{\oplus_{2n + 1}}} + \overline{\overline{\pi_n}^{\oplus_{2m + 1}}} \\ &=\pi_n^{\oplus_{2m + 1}} + \overline{\pi_m}^{\oplus_{2n + 1}} = \pi_{n, m}^+ + \pi_{n, m}^- = \pi_{n, m} \\ & &&2m, 2n \in \mathbb{N} \\ \overline{\Pi_{m, n}} &= \Pi_{n, m} \end{align} }[/math] where the statement for the group representations follow from exp(X) = exp(X). It follows that the irreducible representations (m, n) have real matrix representatives if and only if m = n. Reducible representations on the form (m, n) ⊕ (n, m) have real matrices too.
The adjoint representation, the Clifford algebra, and the Dirac spinor representation

In general representation theory, if (π, V) is a representation of a Lie algebra [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{g}, }[/math] then there is an associated representation of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{g}, }[/math] on End(V), also denoted π, given by
[math]\displaystyle{ \pi(X)(A) = [\pi(X), A],\qquad A \in \operatorname{End}(V),\ X \in \mathfrak{g}. }[/math] |
|
() |
Likewise, a representation (Π, V) of a group G yields a representation Π on End(V) of G, still denoted Π, given by[107]
[math]\displaystyle{ \Pi(g)(A) = \Pi(g)A\Pi(g)^{-1},\qquad A \in \operatorname{End}(V),\ g \in G. }[/math] |
|
() |
If π and Π are the standard representations on [math]\displaystyle{ \R^4 }[/math] and if the action is restricted to [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{so}(3, 1) \subset \text{End}(\R^4), }[/math] then the two above representations are the adjoint representation of the Lie algebra and the adjoint representation of the group respectively. The corresponding representations (some [math]\displaystyle{ \R^n }[/math] or [math]\displaystyle{ \Complex^n }[/math]) always exist for any matrix Lie group, and are paramount for investigation of the representation theory in general, and for any given Lie group in particular.
Applying this to the Lorentz group, if (Π, V) is a projective representation, then direct calculation using (G5) shows that the induced representation on End(V) is a proper representation, i.e. a representation without phase factors.
In quantum mechanics this means that if (π, H) or (Π, H) is a representation acting on some Hilbert space H, then the corresponding induced representation acts on the set of linear operators on H. As an example, the induced representation of the projective spin (1/2, 0) ⊕ (0, 1/2) representation on End(H) is the non-projective 4-vector (1/2, 1/2) representation.[108]
For simplicity, consider only the "discrete part" of End(H), that is, given a basis for H, the set of constant matrices of various dimension, including possibly infinite dimensions. The induced 4-vector representation of above on this simplified End(H) has an invariant 4-dimensional subspace that is spanned by the four gamma matrices.[109] (The metric convention is different in the linked article.) In a corresponding way, the complete Clifford algebra of spacetime, [math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal{Cl}_{3,1}(\R), }[/math] whose complexification is [math]\displaystyle{ \text{M}(4, \Complex), }[/math] generated by the gamma matrices decomposes as a direct sum of representation spaces of a scalar irreducible representation (irrep), the (0, 0), a pseudoscalar irrep, also the (0, 0), but with parity inversion eigenvalue −1, see the next section below, the already mentioned vector irrep, (1/2, 1/2), a pseudovector irrep, (1/2, 1/2) with parity inversion eigenvalue +1 (not −1), and a tensor irrep, (1, 0) ⊕ (0, 1).[110] The dimensions add up to 1 + 1 + 4 + 4 + 6 = 16. In other words,
[math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal{Cl}_{3,1}(\R) = (0,0) \oplus \left(\frac{1}{2}, \frac{1}{2}\right) \oplus [(1, 0) \oplus (0, 1)] \oplus \left(\frac{1}{2}, \frac{1}{2}\right)_p \oplus (0, 0)_p, }[/math] |
|
() |
where, as is customary, a representation is confused with its representation space.
The (1/2, 0) ⊕ (0, 1/2) spin representation
The six-dimensional representation space of the tensor (1, 0) ⊕ (0, 1)-representation inside [math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal{Cl}_{3,1}(\R) }[/math] has two roles. The[111]
[math]\displaystyle{ \sigma^{\mu\nu} = -\frac{i}{4} \left[\gamma^\mu, \gamma^\nu\right], }[/math] |
|
() |
where [math]\displaystyle{ \gamma^0, \ldots, \gamma^3 \in \mathcal{Cl}_{3,1}(\R) }[/math] are the gamma matrices, the sigmas, only 6 of which are non-zero due to antisymmetry of the bracket, span the tensor representation space. Moreover, they have the commutation relations of the Lorentz Lie algebra,[112]
[math]\displaystyle{ \left[\sigma^{\mu\nu}, \sigma^{\rho\tau}\right] = i \left(\eta^{\tau\mu}\sigma^{\rho\nu} + \eta^{\nu\tau}\sigma^{\mu\rho} - \eta^{\rho\mu}\sigma^{\tau\nu} - \eta^{\nu\rho}\sigma^{\mu\tau}\right), }[/math] |
|
() |
and hence constitute a representation (in addition to spanning a representation space) sitting inside [math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal{Cl}_{3,1}(\R), }[/math] the (1/2, 0) ⊕ (0, 1/2) spin representation. For details, see bispinor and Dirac algebra.
The conclusion is that every element of the complexified [math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal{Cl}_{3,1}(\R) }[/math] in End(H) (i.e. every complex 4×4 matrix) has well defined Lorentz transformation properties. In addition, it has a spin-representation of the Lorentz Lie algebra, which upon exponentiation becomes a spin representation of the group, acting on [math]\displaystyle{ \Complex^4, }[/math] making it a space of bispinors.
Reducible representations
There is a multitude of other representations that can be deduced from the irreducible ones, such as those obtained by taking direct sums, tensor products, and quotients of the irreducible representations. Other methods of obtaining representations include the restriction of a representation of a larger group containing the Lorentz group, e.g. [math]\displaystyle{ \text{GL}(n,\R) }[/math] and the Poincaré group. These representations are in general not irreducible.
The Lorentz group and its Lie algebra have the complete reducibility property. This means that every representation reduces to a direct sum of irreducible representations. The reducible representations will therefore not be discussed.
Space inversion and time reversal
The (possibly projective) (m, n) representation is irreducible as a representation SO(3; 1)+, the identity component of the Lorentz group, in physics terminology the proper orthochronous Lorentz group. If m = n it can be extended to a representation of all of O(3; 1), the full Lorentz group, including space parity inversion and time reversal. The representations (m, n) ⊕ (n, m) can be extended likewise.[113]
Space parity inversion
For space parity inversion, the adjoint action AdP of P ∈ SO(3; 1) on [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{so}(3; 1) }[/math] is considered, where P is the standard representative of space parity inversion, P = diag(1, −1, −1, −1), given by
[math]\displaystyle{ \mathrm{Ad}_P(J_i) = PJ_iP^{-1} = J_i, \qquad \mathrm{Ad}_P(K_i) = PK_iP^{-1} = -K_i. }[/math] |
|
() |
It is these properties of K and J under P that motivate the terms vector for K and pseudovector or axial vector for J. In a similar way, if π is any representation of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{so}(3; 1) }[/math] and Π is its associated group representation, then Π(SO(3; 1)+) acts on the representation of π by the adjoint action, π(X) ↦ Π(g) π(X) Π(g)−1 for [math]\displaystyle{ X \in \mathfrak{so}(3; 1), }[/math] g ∈ SO(3; 1)+. If P is to be included in Π, then consistency with (F1) requires that
[math]\displaystyle{ \Pi(P)\pi(B_i)\Pi(P)^{-1} = \pi(A_i) }[/math] |
|
() |
holds, where A and B are defined as in the first section. This can hold only if Ai and Bi have the same dimensions, i.e. only if m = n. When m ≠ n then (m, n) ⊕ (n, m) can be extended to an irreducible representation of SO(3; 1)+, the orthochronous Lorentz group. The parity reversal representative Π(P) does not come automatically with the general construction of the (m, n) representations. It must be specified separately. The matrix β = i γ0 (or a multiple of modulus −1 times it) may be used in the (1/2, 0) ⊕ (0, 1/2)[114] representation.
If parity is included with a minus sign (the 1×1 matrix [−1]) in the (0,0) representation, it is called a pseudoscalar representation.
Time reversal
Time reversal T = diag(−1, 1, 1, 1), acts similarly on [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{so}(3; 1) }[/math] by[115]
[math]\displaystyle{ \mathrm{Ad}_T(J_i) = TJ_iT^{-1} = -J_i, \qquad \mathrm{Ad}_T(K_i) = TK_iT^{-1} = K_i. }[/math] |
|
() |
By explicitly including a representative for T, as well as one for P, a representation of the full Lorentz group O(3; 1) is obtained. A subtle problem appears however in application to physics, in particular quantum mechanics. When considering the full Poincaré group, four more generators, the Pμ, in addition to the Ji and Ki generate the group. These are interpreted as generators of translations. The time-component P0 is the Hamiltonian H. The operator T satisfies the relation[116]
[math]\displaystyle{ \mathrm{Ad}_{T}(iH) = TiHT^{-1} = -iH }[/math] |
|
() |
in analogy to the relations above with [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{so}(3; 1) }[/math] replaced by the full Poincaré algebra. By just cancelling the i's, the result THT−1 = −H would imply that for every state Ψ with positive energy E in a Hilbert space of quantum states with time-reversal invariance, there would be a state Π(T−1)Ψ with negative energy −E. Such states do not exist. The operator Π(T) is therefore chosen antilinear and antiunitary, so that it anticommutes with i, resulting in THT−1 = H, and its action on Hilbert space likewise becomes antilinear and antiunitary.[117] It may be expressed as the composition of complex conjugation with multiplication by a unitary matrix.[118] This is mathematically sound, see Wigner's theorem, but with very strict requirements on terminology, Π is not a representation.
When constructing theories such as QED which is invariant under space parity and time reversal, Dirac spinors may be used, while theories that do not, such as the electroweak force, must be formulated in terms of Weyl spinors. The Dirac representation, (1/2, 0) ⊕ (0, 1/2), is usually taken to include both space parity and time inversions. Without space parity inversion, it is not an irreducible representation.
The third discrete symmetry entering in the CPT theorem along with P and T, charge conjugation symmetry C, has nothing directly to do with Lorentz invariance.[119]
Action on function spaces
If V is a vector space of functions of a finite number of variables n, then the action on a scalar function [math]\displaystyle{ f \in V }[/math] given by
[math]\displaystyle{ (\Pi(g)f)(x) = f\left(\Pi_x(g)^{-1} x\right),\qquad x \in \R^n, f \in V }[/math] |
|
() |
produces another function Πf ∈ V. Here Πx is an n-dimensional representation, and Π is a possibly infinite-dimensional representation. A special case of this construction is when V is a space of functions defined on the a linear group G itself, viewed as a n-dimensional manifold embedded in [math]\displaystyle{ \R^{m^2} }[/math] (with m the dimension of the matrices).[120] This is the setting in which the Peter–Weyl theorem and the Borel–Weil theorem are formulated. The former demonstrates the existence of a Fourier decomposition of functions on a compact group into characters of finite-dimensional representations.[61] The latter theorem, providing more explicit representations, makes use of the unitarian trick to yield representations of complex non-compact groups, e.g. [math]\displaystyle{ \text{SL}(2,\Complex). }[/math]
The following exemplifies action of the Lorentz group and the rotation subgroup on some function spaces.
Euclidean rotations
The subgroup SO(3) of three-dimensional Euclidean rotations has an infinite-dimensional representation on the Hilbert space [math]\displaystyle{ L^2 \left(\mathbb{S}^2\right) = \operatorname{span} \left\{ Y^l_m, l \in \mathbb{N}^+, -l \leqslant m \leqslant l \right\}, }[/math]
where [math]\displaystyle{ Y^l_m }[/math] are the spherical harmonics. An arbitrary square integrable function f on the unit sphere can be expressed as[121]
[math]\displaystyle{ f(\theta, \varphi) = \sum_{l = 1}^\infty\sum_{m = -l}^l f_{lm} Y^l_m(\theta, \varphi), }[/math] |
|
() |
where the flm are generalized Fourier coefficients.
The Lorentz group action restricts to that of SO(3) and is expressed as
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} (\Pi(R)f)(\theta(x), \varphi(x)) &= \sum_{l = 1}^\infty\sum_{m, = -l}^l\sum_{m' = -l}^lD^{(l)}_{mm'}(R) f_{lm'} Y^l_m \left(\theta\left(R^{-1} x\right), \varphi\left(R^{-1}x\right) \right), \\[5pt] & R \in \mathrm{SO}(3), x \in \mathbb{S}^2, \end{align} }[/math] |
|
() |
where the Dl are obtained from the representatives of odd dimension of the generators of rotation.
The Möbius group
The identity component of the Lorentz group is isomorphic to the Möbius group M. This group can be thought of as conformal mappings of either the complex plane or, via stereographic projection, the Riemann sphere. In this way, the Lorentz group itself can be thought of as acting conformally on the complex plane or on the Riemann sphere.
In the plane, a Möbius transformation characterized by the complex numbers a, b, c, d acts on the plane according to[122]
[math]\displaystyle{ f(z) = \frac{a z + b}{c z + d}, \qquad ad - bc \neq 0 }[/math]. |
|
() |
and can be represented by complex matrices
[math]\displaystyle{ \Pi_f = \begin{pmatrix} A & B \\ C & D \end{pmatrix} = \lambda \begin{pmatrix} a & b \\ c & d \end{pmatrix}, \qquad \lambda \in \Complex - \{0\}, \operatorname{det} \Pi_f = 1, }[/math] |
|
() |
since multiplication by a nonzero complex scalar does not change f. These are elements of [math]\displaystyle{ \text{SL}(2,\Complex) }[/math] and are unique up to a sign (since ±Πf give the same f), hence [math]\displaystyle{ \text{SL}(2, \Complex) / \{\pm I\} \cong \text{SO}(3; 1)^+. }[/math]
The Riemann P-functions
The Riemann P-functions, solutions of Riemann's differential equation, are an example of a set of functions that transform among themselves under the action of the Lorentz group. The Riemann P-functions are expressed as[123]
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} w(z) &= P \left\{ \begin{matrix} a & b & c & \\ \alpha & \beta & \gamma & \; z \\ \alpha' & \beta' & \gamma' & \end{matrix} \right\} \\ &= \left(\frac{z - a}{z - b}\right)^\alpha \left(\frac{z - c}{z - b}\right)^\gamma P \left\{ \begin{matrix} 0 & \infty & 1 & \\ 0 & \alpha + \beta + \gamma & 0 & \;\frac{(z - a)(c - b)}{(z - b)(c - a)} \\ \alpha' - \alpha & \alpha + \beta' + \gamma & \gamma' - \gamma & \end{matrix} \right\}\end{align}, }[/math] |
|
() |
where the a, b, c, α, β, γ, α′, β′, γ′ are complex constants. The P-function on the right hand side can be expressed using standard hypergeometric functions. The connection is[124]
[math]\displaystyle{ P \left\{ \begin{matrix} 0 & \infty & 1 & \\ 0 & a & 0 & \;z \\ 1 - c & b & c - a - b & \end{matrix} \right\} = {}_2 F_1(a,\, b;\, c;\, z). }[/math] |
|
() |
The set of constants 0, ∞, 1 in the upper row on the left hand side are the regular singular points of the Gauss' hypergeometric equation.[125] Its exponents, i. e. solutions of the indicial equation, for expansion around the singular point 0 are 0 and 1 − c ,corresponding to the two linearly independent solutions,[nb 34] and for expansion around the singular point 1 they are 0 and c − a − b.[126] Similarly, the exponents for ∞ are a and b for the two solutions.[127]
One has thus
[math]\displaystyle{ w(z) = \left(\frac{z - a}{z - b}\right)^\alpha \left(\frac{z - c}{z - b}\right)^\gamma {}_2F_1 \left(\alpha + \beta + \gamma,\, \alpha + \beta' + \gamma;\, 1 + \alpha - \alpha';\, \frac{(z - a)(c - b)}{(z - b)(c - a)}\right), }[/math] |
|
() |
where the condition (sometimes called Riemann's identity)[128] [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha + \alpha' + \beta + \beta' + \gamma + \gamma' = 1 }[/math] on the exponents of the solutions of Riemann's differential equation has been used to define γ′.
The first set of constants on the left hand side in (T1), a, b, c denotes the regular singular points of Riemann's differential equation. The second set, α, β, γ, are the corresponding exponents at a, b, c for one of the two linearly independent solutions, and, accordingly, α′, β′, γ′ are exponents at a, b, c for the second solution.
Define an action of the Lorentz group on the set of all Riemann P-functions by first setting
[math]\displaystyle{ u(\Lambda)(z) = \frac{Az + B}{Cz + D}, }[/math] |
|
() |
where A, B, C, D are the entries in
[math]\displaystyle{ \lambda = \begin{pmatrix} A & B \\ C & D \end{pmatrix} \in \text{SL}(2, \Complex), }[/math] |
|
() |
for Λ = p(λ) ∈ SO(3; 1)+ a Lorentz transformation.
Define
[math]\displaystyle{ [\Pi(\Lambda) P](z) = P[u(\Lambda)(z)], }[/math] |
|
() |
where P is a Riemann P-function. The resulting function is again a Riemann P-function. The effect of the Möbius transformation of the argument is that of shifting the poles to new locations, hence changing the critical points, but there is no change in the exponents of the differential equation the new function satisfies. The new function is expressed as
[math]\displaystyle{ [\Pi(\Lambda) P](u) = P \left\{ \begin{matrix} \eta & \zeta & \theta & \\ \alpha & \beta & \gamma & \;u \\ \alpha' & \beta' & \gamma' & \end{matrix} \right\}, }[/math] |
|
() |
where
[math]\displaystyle{ \eta = \frac{Aa + B}{Ca + D} \quad \text{ and } \quad \zeta = \frac{Ab + B}{Cb + D} \quad \text{ and } \quad \theta = \frac{Ac + B}{Cc + D}. }[/math] |
|
() |
Infinite-dimensional unitary representations
History
The Lorentz group SO(3; 1)+ and its double cover [math]\displaystyle{ \text{SL}(2,\Complex) }[/math] also have infinite dimensional unitary representations, studied independently by (Bargmann 1947), (Gelfand Naimark) and (Harish-Chandra 1947) at the instigation of Paul Dirac.[129][130] This trail of development begun with (Dirac 1936) where he devised matrices U and B necessary for description of higher spin (compare Dirac matrices), elaborated upon by (Fierz 1939), see also (Fierz Pauli), and proposed precursors of the Bargmann-Wigner equations.[131] In (Dirac 1945) he proposed a concrete infinite-dimensional representation space whose elements were called expansors as a generalization of tensors.[nb 35] These ideas were incorporated by Harish–Chandra and expanded with expinors as an infinite-dimensional generalization of spinors in his 1947 paper.
The Plancherel formula for these groups was first obtained by Gelfand and Naimark through involved calculations. The treatment was subsequently considerably simplified by (Harish-Chandra 1951) and (Gelfand Graev), based on an analogue for [math]\displaystyle{ \text{SL}(2,\Complex) }[/math] of the integration formula of Hermann Weyl for compact Lie groups.[132] Elementary accounts of this approach can be found in (Rühl 1970) and (Knapp 2001).
The theory of spherical functions for the Lorentz group, required for harmonic analysis on the hyperboloid model of 3-dimensional hyperbolic space sitting in Minkowski space is considerably easier than the general theory. It only involves representations from the spherical principal series and can be treated directly, because in radial coordinates the Laplacian on the hyperboloid is equivalent to the Laplacian on [math]\displaystyle{ \R. }[/math] This theory is discussed in (Takahashi 1963), (Helgason 1968), (Helgason 2000) and the posthumous text of (Jorgenson Lang).
Principal series for SL(2, C)
The principal series, or unitary principal series, are the unitary representations induced from the one-dimensional representations of the lower triangular subgroup B of [math]\displaystyle{ G = \text{SL}(2,\Complex). }[/math] Since the one-dimensional representations of B correspond to the representations of the diagonal matrices, with non-zero complex entries z and z−1, they thus have the form [math]\displaystyle{ \chi_{\nu,k}\begin{pmatrix}z& 0\\ c& z^{-1}\end{pmatrix}=r^{i\nu} e^{ik\theta}, }[/math] for k an integer, ν real and with z = reiθ. The representations are irreducible; the only repetitions, i.e. isomorphisms of representations, occur when k is replaced by −k. By definition the representations are realized on L2 sections of line bundles on [math]\displaystyle{ G/B = \mathbb{S}^2, }[/math] which is isomorphic to the Riemann sphere. When k = 0, these representations constitute the so-called spherical principal series.
The restriction of a principal series to the maximal compact subgroup K = SU(2) of G can also be realized as an induced representation of K using the identification G/B = K/T, where T = B ∩ K is the maximal torus in K consisting of diagonal matrices with | z | = 1. It is the representation induced from the 1-dimensional representation zkT, and is independent of ν. By Frobenius reciprocity, on K they decompose as a direct sum of the irreducible representations of K with dimensions |k| + 2m + 1 with m a non-negative integer.
Using the identification between the Riemann sphere minus a point and [math]\displaystyle{ \Complex, }[/math] the principal series can be defined directly on [math]\displaystyle{ L^2(\Complex) }[/math] by the formula[133] [math]\displaystyle{ \pi_{\nu,k}\begin{pmatrix}a& b\\ c& d\end{pmatrix}^{-1}f(z)=|cz+d|^{-2-i\nu} \left({cz+d\over |cz+d|}\right)^{-k}f\left({az+b\over cz+d}\right). }[/math]
Irreducibility can be checked in a variety of ways:
- The representation is already irreducible on B. This can be seen directly, but is also a special case of general results on irreducibility of induced representations due to François Bruhat and George Mackey, relying on the Bruhat decomposition G = B ∪ BsB where s is the Weyl group element[134] [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{pmatrix}0& -1\\ 1& 0\end{pmatrix} }[/math].
- The action of the Lie algebra [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{g} }[/math] of G can be computed on the algebraic direct sum of the irreducible subspaces of K can be computed explicitly and the it can be verified directly that the lowest-dimensional subspace generates this direct sum as a [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{g} }[/math]-module.[8][135]
Complementary series for SL(2, C)
The for 0 < t < 2, the complementary series is defined on [math]\displaystyle{ L^2(\Complex) }[/math] for the inner product[136] [math]\displaystyle{ (f,g)_t =\iint \frac{f(z) \overline{g(w)}}{|z-w|^{2-t}} \, dz\, dw, }[/math] with the action given by[137][138] [math]\displaystyle{ \pi_{t}\begin{pmatrix}a& b\\ c& d\end{pmatrix}^{-1}f(z)=|cz+d|^{-2-t} f\left({az+b\over cz+d}\right). }[/math]
The representations in the complementary series are irreducible and pairwise non-isomorphic. As a representation of K, each is isomorphic to the Hilbert space direct sum of all the odd dimensional irreducible representations of K = SU(2). Irreducibility can be proved by analyzing the action of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{g} }[/math] on the algebraic sum of these subspaces[8][135] or directly without using the Lie algebra.[139][140]
Plancherel theorem for SL(2, C)
The only irreducible unitary representations of [math]\displaystyle{ \text{SL}(2,\Complex) }[/math] are the principal series, the complementary series and the trivial representation. Since −I acts as (−1)k on the principal series and trivially on the remainder, these will give all the irreducible unitary representations of the Lorentz group, provided k is taken to be even.
To decompose the left regular representation of G on [math]\displaystyle{ L^2(G) }[/math] only the principal series are required. This immediately yields the decomposition on the subrepresentations [math]\displaystyle{ L^2(G/\{\pm I\}), }[/math] the left regular representation of the Lorentz group, and [math]\displaystyle{ L^2(G/K), }[/math] the regular representation on 3-dimensional hyperbolic space. (The former only involves principal series representations with k even and the latter only those with k = 0.)
The left and right regular representation λ and ρ are defined on [math]\displaystyle{ L^2(G) }[/math] by [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} (\lambda(g)f)(x) &= f\left(g^{-1}x\right) \\ (\rho(g)f) (x) &= f(xg) \end{align} }[/math]
Now if f is an element of Cc(G), the operator [math]\displaystyle{ \pi_{\nu, k}(f) }[/math] defined by [math]\displaystyle{ \pi_{\nu, k}(f) = \int_G f(g)\pi(g)\, dg }[/math] is Hilbert–Schmidt. Define a Hilbert space H by [math]\displaystyle{ H = \bigoplus_{k\geqslant 0} \text{HS} \left(L^2(\Complex)\right) \otimes L^2 \left(\R, c_k\sqrt{\nu^2 + k^2} d\nu \right), }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ c_k = \begin{cases} \frac{1}{4\pi^{3/2}} & k = 0 \\ \frac{1}{(2\pi)^{3/2}} & k \neq 0 \end{cases} }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \text{HS}\left(L^2(\Complex)\right) }[/math] denotes the Hilbert space of Hilbert–Schmidt operators on [math]\displaystyle{ L^2(\Complex). }[/math][nb 36] Then the map U defined on Cc(G) by [math]\displaystyle{ U(f)(\nu, k) = \pi_{\nu,k}(f) }[/math] extends to a unitary of [math]\displaystyle{ L^2(G) }[/math] onto H.
The map U satisfies the intertwining property [math]\displaystyle{ U(\lambda(x)\rho(y)f)(\nu,k) = \pi_{\nu,k}(x)^{-1} \pi_{\nu,k}(f)\pi_{\nu,k}(y). }[/math]
If f1, f2 are in Cc(G) then by unitarity [math]\displaystyle{ (f_1, f_2) = \sum_{k\geqslant 0} c_k^2 \int_{-\infty}^\infty \operatorname{Tr} \left(\pi_{\nu,k}(f_1)\pi_{\nu,k}(f_2)^*\right) \left(\nu^2 + k^2\right) \, d\nu. }[/math]
Thus if [math]\displaystyle{ f = f_1 * f_2^* }[/math] denotes the convolution of [math]\displaystyle{ f_1 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ f_2^*, }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ f_2^*(g)=\overline{f_2(g^{-1})}, }[/math] then[141] [math]\displaystyle{ f(1) = \sum_{k\geqslant 0} c_k^2 \int_{-\infty}^\infty \operatorname{Tr} \left(\pi_{\nu,k}(f) \right) \left(\nu^2 + k^2\right)\, d\nu. }[/math]
The last two displayed formulas are usually referred to as the Plancherel formula and the Fourier inversion formula respectively.
The Plancherel formula extends to all [math]\displaystyle{ f_i \in L^2(G). }[/math] By a theorem of Jacques Dixmier and Paul Malliavin, every smooth compactly supported function on [math]\displaystyle{ G }[/math] is a finite sum of convolutions of similar functions, the inversion formula holds for such f. It can be extended to much wider classes of functions satisfying mild differentiability conditions.[61]
Classification of representations of SO(3, 1)
The strategy followed in the classification of the irreducible infinite-dimensional representations is, in analogy to the finite-dimensional case, to assume they exist, and to investigate their properties. Thus first assume that an irreducible strongly continuous infinite-dimensional representation ΠH on a Hilbert space H of SO(3; 1)+ is at hand.[142] Since SO(3) is a subgroup, ΠH is a representation of it as well. Each irreducible subrepresentation of SO(3) is finite-dimensional, and the SO(3) representation is reducible into a direct sum of irreducible finite-dimensional unitary representations of SO(3) if ΠH is unitary.[143]
The steps are the following:[144]
- Choose a suitable basis of common eigenvectors of J2 and J3.
- Compute matrix elements of J1, J2, J3 and K1, K2, K3.
- Enforce Lie algebra commutation relations.
- Require unitarity together with orthonormality of the basis.[nb 37]
Step 1
One suitable choice of basis and labeling is given by [math]\displaystyle{ \left |j_0\, j_1;j\, m\right\rangle. }[/math]
If this were a finite-dimensional representation, then j0 would correspond the lowest occurring eigenvalue j(j + 1) of J2 in the representation, equal to |m − n|, and j1 would correspond to the highest occurring eigenvalue, equal to m + n. In the infinite-dimensional case, j0 ≥ 0 retains this meaning, but j1 does not.[66] For simplicity, it is assumed that a given j occurs at most once in a given representation (this is the case for finite-dimensional representations), and it can be shown[145] that the assumption is possible to avoid (with a slightly more complicated calculation) with the same results.
Step 2
The next step is to compute the matrix elements of the operators J1, J2, J3 and K1, K2, K3 forming the basis of the Lie algebra of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{so}(3; 1). }[/math] The matrix elements of [math]\displaystyle{ J_\pm = J_1 \pm iJ_2 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ J_3 }[/math] (the complexified Lie algebra is understood) are known from the representation theory of the rotation group, and are given by[146][147] [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} \left\langle j\, m \right|J_+ \left| j\, m - 1 \right\rangle = \left\langle j\, m - 1 \right|J_- \left| j\, m \right\rangle &= \sqrt{(j + m)(j - m + 1)}, \\ \left\langle j\, m \right|J_3 \left| j\, m \right\rangle &= m, \end{align} }[/math] where the labels j0 and j1 have been dropped since they are the same for all basis vectors in the representation.
Due to the commutation relations [math]\displaystyle{ [J_i,K_j] = i \epsilon_{ijk} K_k, }[/math] the triple (K1, K2, K3) ≡ K is a vector operator[148] and the Wigner–Eckart theorem[149] applies for computation of matrix elements between the states represented by the chosen basis.[150] The matrix elements of [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} K^{(1)}_0 &= K_3,\\ K^{(1)}_{\pm 1} &= \mp\frac{1}{\sqrt 2}(K_1 \pm iK_2), \end{align} }[/math]
where the superscript (1) signifies that the defined quantities are the components of a spherical tensor operator of rank k = 1 (which explains the factor √2 as well) and the subscripts 0, ±1 are referred to as q in formulas below, are given by[151] [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} \left\langle j' m'\left|K^{(1)}_0 \right|j\,m\right\rangle &= \left \langle j' \, m' \,k = 1 \,q = 0 | j \, m \right \rangle \left \langle j \left \| K^{(1)} \right \| j' \right \rangle,\\ \left\langle j' m'\left|K^{(1)}_{\pm 1}\right |j\,m\right\rangle &= \left \langle j' \, m' \, k= 1 \,q = \pm 1 | j \, m \right \rangle \left \langle j \left \| K^{(1)} \right \| j' \right \rangle. \end{align} }[/math]
Here the first factors on the right hand sides are Clebsch–Gordan coefficients for coupling j′ with k to get j. The second factors are the reduced matrix elements. They do not depend on m, m′ or q, but depend on j, j′ and, of course, K. For a complete list of non-vanishing equations, see (Harish-Chandra 1947).
Step 3
The next step is to demand that the Lie algebra relations hold, i.e. that [math]\displaystyle{ [K_\pm, K_3] = \pm J_\pm, \quad [K_+, K_-] = -2J_3. }[/math]
This results in a set of equations[152] for which the solutions are[153] [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} \left \langle j \left \| K^{(1)} \right \| j \right \rangle &= i\frac{j_1j_0}{\sqrt{j(j+1)}},\\ \left \langle j \left \| K^{(1)} \right \| j-1 \right \rangle &= -B_j\xi_j\sqrt{j(2j-1)},\\ \left \langle j-1 \left \| K^{(1)} \right \| j \right \rangle &= B_j\xi_j^{-1}\sqrt{j(2j+1)}, \end{align} }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ B_j = \sqrt{\frac{(j^2 - j_0^2)(j^2 - j_1^2)}{j^2(4j^2 - 1)}}, \quad j_0=0, \tfrac{1}{2}, 1, \ldots \quad \text{and} \quad j_1, \xi_j \in \Complex. }[/math]
Step 4
The imposition of the requirement of unitarity of the corresponding representation of the group restricts the possible values for the arbitrary complex numbers j0 and ξj. Unitarity of the group representation translates to the requirement of the Lie algebra representatives being Hermitian, meaning [math]\displaystyle{ K_\pm^\dagger = K_\mp,\quad K_3^\dagger = K_3. }[/math]
This translates to[154] [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} \left \langle j \left \| K^{(1)} \right \| j \right \rangle &= \overline{\left \langle j \left \| K^{(1)} \right \| j \right \rangle},\\ \left \langle j \left \| K^{(1)} \right \| j - 1 \right \rangle &= -\overline{\left \langle j - 1 \left \| K^{(1)} \right \| j \right \rangle}, \end{align} }[/math] leading to[155] [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} j_0 \left(j_1 + \overline{j_1}\right) &= 0, \\ \left|B_j\right| \left(\left|\xi_j\right|^2 - e^{-2i\beta_j}\right) &= 0, \end{align} }[/math] where βj is the angle of Bj on polar form. For |Bj| ≠ 0 follows [math]\displaystyle{ \left|\xi_j\right|^2 = 1 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \xi_j = 1 }[/math] is chosen by convention. There are two possible cases:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \underline{j_1 + \overline{j_1} = 0.} }[/math] In this case j1 = − iν, ν real,[156] [math]\displaystyle{ \left \langle j \left \| K^{(1)} \right \| j \right \rangle = \frac{\nu j_0}{j(j + 1)} \quad \text{and} \quad B_j = \sqrt{\frac{(j^2 - j_0^2)(j^2 + \nu^2)}{4j^2 - 1}} }[/math] This is the principal series. Its elements are denoted [math]\displaystyle{ (j_0, \nu), 2j_0 \in \N, \nu \in \R. }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \underline{j_0=0.} }[/math] It follows:[157] [math]\displaystyle{ \left \langle j \left \| K^{(1)} \right \| j \right \rangle = 0 \quad \text{and} \quad B_j = \sqrt{\frac{j^2 - \nu^2}{4j^2 - 1}} }[/math] Since B0 = Bj0, B2j is real and positive for j = 1, 2, ..., leading to −1 ≤ ν ≤ 1. This is complementary series. Its elements are denoted (0, ν), −1 ≤ ν ≤ 1
This shows that the representations of above are all infinite-dimensional irreducible unitary representations.
Explicit formulas
Conventions and Lie algebra bases
The metric of choice is given by η = diag(−1, 1, 1, 1), and the physics convention for Lie algebras and the exponential mapping is used. These choices are arbitrary, but once they are made, fixed. One possible choice of basis for the Lie algebra is, in the 4-vector representation, given by: [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} J_1 = J^{23} = -J^{32} &= i\begin{pmatrix} 0&0&0&0\\ 0&0&0&0\\ 0&0&0&-1\\ 0&0&1&0 \end{pmatrix},& K_1 = J^{01} = -J^{10} &= i\begin{pmatrix} 0&1&0&0\\ 1&0&0&0\\ 0&0&0&0\\ 0&0&0&0 \end{pmatrix},\\[8pt] J_2 = J^{31} = -J^{13} &= i\begin{pmatrix} 0&0&0&0\\ 0&0&0&1\\ 0&0&0&0\\ 0&-1&0&0 \end{pmatrix},& K_2 = J^{02} = -J^{20} &= i\begin{pmatrix} 0&0&1&0\\ 0&0&0&0\\ 1&0&0&0\\ 0&0&0&0 \end{pmatrix},\\[8pt] J_3 = J^{12} = -J^{21} &= i\begin{pmatrix} 0&0&0&0\\ 0&0&-1&0\\ 0&1&0&0\\ 0&0&0&0 \end{pmatrix},& K_3 = J^{03} = -J^{30} &= i\begin{pmatrix} 0&0&0&1\\ 0&0&0&0\\ 0&0&0&0\\ 1&0&0&0 \end{pmatrix}.\\[8pt] \end{align} }[/math]
The commutation relations of the Lie algebra [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{so}(3; 1) }[/math] are:[158] [math]\displaystyle{ \left[J^{\mu\nu}, J^{\rho\sigma}\right] = i\left( \eta^{\sigma\mu}J^{\rho\nu} + \eta^{\nu\sigma}J^{\mu\rho} - \eta^{\rho\mu}J^{\sigma\nu} - \eta^{\nu\rho} J^{\mu\sigma} \right). }[/math]
In three-dimensional notation, these are[159] [math]\displaystyle{ \left[J_i, J_j\right] = i\epsilon_{ijk}J_k,\quad \left[J_i, K_j\right] = i\epsilon_{ijk}K_k,\quad \left[K_i, K_j\right] = -i\epsilon_{ijk}J_k. }[/math]
The choice of basis above satisfies the relations, but other choices are possible. The multiple use of the symbol J above and in the sequel should be observed.
For example, a typical boost and a typical rotation exponentiate as, [math]\displaystyle{ \exp (-i\xi K_1)=\begin{pmatrix} \cosh \xi &\sinh \xi &0&0\\ \sinh \xi &\cosh \xi &0&0\\ 0&0&1&0\\ 0&0&0&1 \end{pmatrix}, \qquad \exp (-i\theta J_1)=\begin{pmatrix} 1&0&0&0\\ 0&1&0&0\\ 0&0&\cos \theta &-\sin\theta\\ 0&0&\sin\theta&\cos\theta \end{pmatrix}, }[/math] symmetric and orthogonal, respectively.
Weyl spinors and bispinors

By taking, in turn, m = 1/2, n = 0 and m = 0, n = 1/2 and by setting [math]\displaystyle{ J_i^{\left( \frac{1}{2} \right)} = \frac{1}{2}\sigma_i }[/math] in the general expression (G1), and by using the trivial relations 11 = 1 and J(0) = 0, it follows
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} \pi_{\left( \frac{1}{2}, 0 \right)}(J_i) &= \frac{1}{2} \left( \sigma_i \otimes 1_{(1)} + 1_{(2)} \otimes J^{(0)}_i \right) = \frac{1}{2}\sigma_i \\ \pi_{\left( \frac{1}{2}, 0 \right)}(K_i) &= \frac{-i}{2} \left( 1_{(2)} \otimes J^{(0)}_i - \sigma_i \otimes 1_{(1)} \right) = \frac{i}{2}\sigma_i \\[6pt] \pi_{\left (0, \frac{1}{2} \right)}(J_i) &= \frac{1}{2} \left( J^{(0)}_i \otimes 1_{(2)} + 1_{(1)} \otimes \sigma_i \right) = \frac{1}{2}\sigma_i \\ \pi_{\left( 0, \frac{1}{2} \right)}(K_i) &= \frac{-i}{2} \left( 1_{(1)} \otimes \sigma_i - J^{(0)}_i \otimes 1_{(2)} \right) = \frac{-i}{2}\sigma_i \end{align} }[/math] |
|
( ) |
These are the left-handed and right-handed Weyl spinor representations. They act by matrix multiplication on 2-dimensional complex vector spaces (with a choice of basis) VL and VR, whose elements ΨL and ΨR are called left- and right-handed Weyl spinors respectively. Given [math]\displaystyle{ \left( \pi_{\left(\frac{1}{2}, 0 \right)}, V_\text{L} \right) \quad \text{and} \quad \left( \pi_{\left( 0, \frac{1}{2} \right)}, V_\text{R} \right) }[/math] their direct sum as representations is formed,[160]
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} \pi_{\left( \frac{1}{2}, 0 \right) \oplus \left( 0, \frac{1}{2} \right)}\left(J_i\right) &= \frac{1}{2} \begin{pmatrix} \sigma_i&0\\ 0&\sigma_i \end{pmatrix} \\[8pt] \pi_{\left( \frac{1}{2}, 0 \right) \oplus \left( 0, \frac{1}{2} \right)}\left(K_i\right) &= \frac{i}{2} \begin{pmatrix} \sigma_i&0\\ 0&-\sigma_i \end{pmatrix} \end{align} }[/math] |
|
( ) |
This is, up to a similarity transformation, the (1/2,0) ⊕ (0,1/2) Dirac spinor representation of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{so}(3; 1). }[/math] It acts on the 4-component elements (ΨL, ΨR) of (VL ⊕ VR), called bispinors, by matrix multiplication. The representation may be obtained in a more general and basis independent way using Clifford algebras. These expressions for bispinors and Weyl spinors all extend by linearity of Lie algebras and representations to all of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{so}(3; 1). }[/math] Expressions for the group representations are obtained by exponentiation.
Open problems
The classification and characterization of the representation theory of the Lorentz group was completed in 1947. But in association with the Bargmann–Wigner programme, there are yet unresolved purely mathematical problems, linked to the infinite-dimensional unitary representations.
The irreducible infinite-dimensional unitary representations may have indirect relevance to physical reality in speculative modern theories since the (generalized) Lorentz group appears as the little group of the Poincaré group of spacelike vectors in higher spacetime dimension. The corresponding infinite-dimensional unitary representations of the (generalized) Poincaré group are the so-called tachyonic representations. Tachyons appear in the spectrum of bosonic strings and are associated with instability of the vacuum.[161][162] Even though tachyons may not be realized in nature, these representations must be mathematically understood in order to understand string theory. This is so since tachyon states turn out to appear in superstring theories too in attempts to create realistic models.[163]
One open problem is the completion of the Bargmann–Wigner programme for the isometry group SO(D − 2, 1) of the de Sitter spacetime dSD−2. Ideally, the physical components of wave functions would be realized on the hyperboloid dSD−2 of radius μ > 0 embedded in [math]\displaystyle{ \R^{D-2, 1} }[/math] and the corresponding O(D−2, 1) covariant wave equations of the infinite-dimensional unitary representation to be known.[162]
See also
- Bargmann–Wigner equations
- Dirac algebra
- Gamma matrices
- Lorentz group
- Möbius transformation
- Poincaré group
- Representation theory of the Poincaré group
- Symmetry in quantum mechanics
- Wigner's classification
Remarks
- ↑ The way in which one represents the spacetime symmetries may take many shapes depending on the theory at hand. While not being the present topic, some details will be provided in footnotes labeled "nb", and in the section applications.
- ↑ Weinberg 2002, p. 1 "If it turned out that a system could not be described by a quantum field theory, it would be a sensation; if it turned out it did not obey the rules of quantum mechanics and relativity, it would be a cataclysm."
- ↑ In 1945 Harish-Chandra came to see Dirac in Cambridge. Harish-Chandra became convinced that theoretical physics was not the field he should be in. He had found an error in a proof by Dirac in his work on the Lorentz group. Dirac said "I am not interested in proofs but only interested in what nature does." Harish-Chandra later wrote "This remark confirmed my growing conviction that I did not have the mysterious sixth sense which one needs in order to succeed in physics and I soon decided to move over to mathematics." Dirac did however suggest the topic of Harish-Chandra's thesis, the classification of the irreducible infinite-dimensional representations of the Lorentz group. See Dalitz & Peierls 1986
- ↑ See formula (1) in S-matrix for how free multi-particle states transform.
- ↑ Weinberg 2002, Equations 5.1.4–5. Weinberg deduces the necessity of creation and annihilation operators from another consideration, the cluster decomposition principle, (Weinberg 2002)
- ↑ A prescription for how the particle should behave under CPT symmetry may be required as well.
- ↑ For instance, there are versions (free field equations, i.e. without interaction terms) of the Klein–Gordon equation, the Dirac equation, the Maxwell equations, the Proca equation, the Rarita–Schwinger equation, and the Einstein field equations that can systematically be deduced by starting from a given representation of the Lorentz group. In general, these are collectively the quantum field theory versions of the Bargmann–Wigner equations.
See (Weinberg 2002), (Tung 1985) and references given in these works.
It should be remarked that high spin theories (s > 1) encounter difficulties. See (Weinberg 2002), on general (m, n) fields, where this is discussed in some depth, and references therein. High spin particles do without a doubt exist, e.g. nuclei, the known ones are just not elementary.
- ↑ For part of their representation theory, see (Bekaert Boulanger), which is dedicated to representation theory of the Poincare group. These representations are obtained by the method of induced representations or, in physics parlance, the method of the little group, pioneered by Wigner in 1939 for this type of group and put on firm mathematical footing by George Mackey in the fifties.
- ↑ (Hall 2015)
One says that a group has the complete reducibility property if every representation decomposes as a direct sum of irreducible representations.
- ↑ Dirac suggested the topic of (Wigner 1939) as early as 1928 (as acknowledged in Wigner's paper). He also published one of the first papers on explicit infinite-dimensional unitary representations in (Dirac 1945) (Langlands 1985), and suggested the topic for Harish-Chandra's thesis classifying irreducible infinite-dimensional representations (Dalitz & Peierls 1986).
- ↑ Knapp 2001 The rather mysterious looking third isomorphism is proved in chapter 2, paragraph 4.
- ↑ Tensor products of representations, πg ⊗ πh of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{g} \oplus \mathfrak{h} }[/math] can, when both factors come from the same Lie algebra [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{h} = \mathfrak{g}, }[/math] either be thought of as a representation of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{g} }[/math] or [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{g} \oplus \mathfrak{g} }[/math].
- ↑ When complexifying a complex Lie algebra, it should be thought of as a real Lie algebra of real dimension twice its complex dimension. Likewise, a real form may actually also be complex as is the case here.
- ↑ Combine (Weinberg 2002) with (Hall 2015) about Lie algebra representations of group tensor product representations.
- ↑ The "traceless" property can be expressed as Sαβgαβ = 0, or Sαα = 0, or Sαβgαβ = 0 depending on the presentation of the field: covariant, mixed, and contravariant respectively.
- ↑ This doesn't necessarily come symmetric directly from the Lagrangian by using Noether's theorem, but it can be symmetrized as the Belinfante–Rosenfeld stress–energy tensor.
- ↑ This is provided parity is a symmetry. Else there would be two flavors, (3/2, 0) and (0, 3/2) in analogy with neutrinos.
- ↑ The terminology differs between mathematics and physics. In the linked article term projective representation has a slightly different meaning than in physics, where a projective representation is thought of as a local section (a local inverse) of the covering map from the covering group onto the group being covered, composed with a proper representation of the covering group. Since this can be done (locally) continuously in two ways in the case at hand as explained below, the terminology of a double-valued or two-valued representation is natural.
- ↑ In particular, A commutes with the Pauli matrices, hence with all of SU(2) making Schur's lemma applicable.
- ↑ Meaning the kernel is trivial, to see this recall that the kernel of a Lie algebra homomorphism is an ideal and hence a subspace. Since p is 2:1 and both [math]\displaystyle{ \text{SL}(2,\Complex) }[/math] and SO(3; 1)+ are 6-dimensional, the kernel must be 0-dimensional, hence {0}.
- ↑ The exponential map is one-to-one in a neighborhood of the identity in [math]\displaystyle{ \text{SL}(2,\Complex), }[/math] hence the composition [math]\displaystyle{ \exp \circ \sigma \circ \log : \text{SL}(2,\Complex) \to \text{SO}(3; 1)^+, }[/math] where σ is the Lie algebra isomorphism, is onto an open neighborhood U ⊂ SO(3; 1)+ containing the identity. Such a neighborhood generates the connected component.
- ↑ Rossmann 2002 From Example 4 in section 2.1 : This can be seen as follows. The matrix q has eigenvalues {−1, −1}, but it is not diagonalizable. If q = exp(Q), then Q has eigenvalues λ, −λ with λ = iπ + 2πik for some k because elements of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathfrak{sl}(2,\Complex) }[/math] are traceless. But then Q is diagonalizable, hence q is diagonalizable, which is a contradiction.
- ↑ Rossmann 2002, Proposition 10, paragraph 6.3. This is easiest proved using character theory.
- ↑ Any discrete normal subgroup of a path connected group G is contained in the center Z of G.
Hall 2015, Exercise 11, chapter 1.
- ↑ A semisimple Lie group does not have any non-discrete normal abelian subgroups. This can be taken as the definition of semisimplicity.
- ↑ A simple group does not have any non-discrete normal subgroups.
- ↑ By contrast, there is a trick, also called Weyl's unitarian trick, but unrelated to the unitarian trick of above showing that all finite-dimensional representations are, or can be made, unitary. If (Π, V) is a finite-dimensional representation of a compact Lie group G and if (·, ·) is any inner product on V, define a new inner product (·, ·)Π by (x, y)Π = ∫G(Π(g)x, Π(g)y dμ(g), where μ is Haar measure on G. Then Π is unitary with respect to (·, ·)Π. See (Hall 2015)
Another consequence is that every compact Lie group has the complete reducibility property, meaning that all its finite-dimensional representations decompose as a direct sum of irreducible representations. (Hall 2015)
It is also true that there are no infinite-dimensional irreducible unitary representations of compact Lie groups, stated, but not proved in (Greiner Müller).
- ↑ Lee 2003 Lemma A.17 (c). Closed subsets of compact sets are compact.
- ↑ Lee 2003 Lemma A.17 (a). If f : X → Y is continuous, X is compact, then f(X) is compact.
- ↑ The non-unitarity is a vital ingredient in the proof of the Coleman–Mandula theorem, which has the implication that, contrary to in non-relativistic theories, there can exist no ordinary symmetry relating particles of different spin. See (Weinberg 2000)
- ↑ This is one of the conclusions of Cartan's theorem, the theorem of the highest weight.(Hall 2015)
- ↑ Hall 2015, Section 8.2 The root system is the union of two copies of A1, where each copy resides in its own dimensions in the embedding vector space.
- ↑ Rossmann 2002 This definition is equivalent to the definition in terms of the connected Lie group whose Lie algebra is the Lie algebra of the root system under consideration.
- ↑ See (Simmons 1972) for precise conditions under which two Frobenius method yields two linearly independent solutions. If the exponents do not differ by an integer, this is always the case.
- ↑ "This is as close as one comes to the source of the theory of infinite-dimensional representations of semisimple and reductive groups...", (Langlands 1985), referring to an introductory passage in Dirac's 1945 paper.
- ↑ Note that for a Hilbert space H, HS(H) may be identified canonically with the Hilbert space tensor product of H and its conjugate space.
- ↑ If finite-dimensionality is demanded, the results is the (m, n) representations, see (Tung 1985) If neither is demanded, then a broader classification of all irreducible representations is obtained, including the finite-dimensional and the unitary ones. This approach is taken in (Harish-Chandra 1947).
Notes
- ↑ Bargmann & Wigner 1948
- ↑ Bekaert & Boulanger 2006
- ↑ Misner, Thorne & Wheeler 1973
- ↑ Weinberg 2002, Section 2.5, Chapter 5.
- ↑ Tung 1985, Sections 10.3, 10.5.
- ↑ Tung 1985, Section 10.4.
- ↑ Dirac 1945
- ↑ Jump up to: 8.0 8.1 8.2 Harish-Chandra 1947
- ↑ Jump up to: 9.0 9.1 Greiner & Reinhardt 1996, Chapter 2.
- ↑ Weinberg 2002, Foreword and introduction to chapter 7.
- ↑ Weinberg 2002, Introduction to chapter 7.
- ↑ Tung 1985, Definition 10.11.
- ↑ (Greiner Müller)
- ↑ (Greiner Müller)
- ↑ Tung 1985, p. 203.
- ↑ Delbourgo, Salam & Strathdee 1967
- ↑ (Weinberg 2002)
- ↑ (Weinberg 2002)
- ↑ Tung 1985, Introduction to chapter 10.
- ↑ Tung 1985, Definition 10.12.
- ↑ Tung 1985, Equation 10.5-2.
- ↑ Weinberg 2002, Equations 5.1.6–7.
- ↑ Jump up to: 23.0 23.1 Tung 1985, Equation 10.5–18.
- ↑ Weinberg 2002, Equations 5.1.11–12.
- ↑ Tung 1985, Section 10.5.3.
- ↑ Zwiebach 2004, Section 6.4.
- ↑ Zwiebach 2004, Chapter 7.
- ↑ Zwiebach 2004, Section 12.5.
- ↑ Jump up to: 29.0 29.1 Weinberg 2000, Section 25.2.
- ↑ Zwiebach 2004, Last paragraph, section 12.6.
- ↑ These facts can be found in most introductory mathematics and physics texts. See e.g. (Rossmann 2002), (Hall 2015) and (Tung 1985).
- ↑ (Hall 2015)
- ↑ Jump up to: 33.0 33.1 33.2 Wigner 1939
- ↑ Hall 2015, Appendix D2.
- ↑ Greiner & Reinhardt 1996
- ↑ Weinberg 2002, Section 2.6 and Chapter 5.
- ↑ Jump up to: 37.0 37.1 Coleman 1989, p. 30.
- ↑ Lie 1888, 1890, 1893. Primary source.
- ↑ Coleman 1989, p. 34.
- ↑ Killing 1888 Primary source.
- ↑ Jump up to: 41.0 41.1 Rossmann 2002, Historical tidbits scattered across the text.
- ↑ Cartan 1913 Primary source.
- ↑ Green 1998, p=76.
- ↑ Brauer & Weyl 1935 Primary source.
- ↑ Tung 1985, Introduction.
- ↑ Weyl 1931 Primary source.
- ↑ Weyl 1939 Primary source.
- ↑ Langlands 1985, pp. 203–205
- ↑ Harish-Chandra 1947 Primary source.
- ↑ Tung 1985, Introduction
- ↑ Wigner 1939 Primary source.
- ↑ Klauder 1999
- ↑ Bargmann 1947 Primary source.
- ↑ Bargmann was also a mathematician. He worked as Albert Einsteins assistant at the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton ((Klauder 1999)).
- ↑ Bargmann & Wigner 1948 Primary source.
- ↑ Dalitz & Peierls 1986
- ↑ Dirac 1928 Primary source.
- ↑ Weinberg 2002, Equations 5.6.7–8.
- ↑ Weinberg 2002, Equations 5.6.9–11.
- ↑ Jump up to: 60.0 60.1 60.2 Hall 2003, Chapter 6.
- ↑ Jump up to: 61.0 61.1 61.2 61.3 Knapp 2001
- ↑ This is an application of Rossmann 2002, Section 6.3, Proposition 10.
- ↑ Jump up to: 63.0 63.1 Knapp 2001, p. 32.
- ↑ Weinberg 2002, Equations 5.6.16–17.
- ↑ Weinberg 2002, Section 5.6. The equations follow from equations 5.6.7–8 and 5.6.14–15.
- ↑ Jump up to: 66.0 66.1 Tung 1985
- ↑ Lie 1888
- ↑ Rossmann 2002, Section 2.5.
- ↑ Hall 2015, Theorem 2.10.
- ↑ Bourbaki 1998, p. 424.
- ↑ Weinberg 2002, Section 2.7 p.88.
- ↑ Jump up to: 72.0 72.1 72.2 72.3 72.4 Weinberg 2002, Section 2.7.
- ↑ Hall 2015, Appendix C.3.
- ↑ Wigner 1939, p. 27.
- ↑ Gelfand, Minlos & Shapiro 1963 This construction of the covering group is treated in paragraph 4, section 1, chapter 1 in Part II.
- ↑ Rossmann 2002, Section 2.1.
- ↑ Hall 2015, First displayed equations in section 4.6.
- ↑ Hall 2015, Example 4.10.
- ↑ Jump up to: 79.0 79.1 Knapp 2001, Chapter 2.
- ↑ Knapp 2001 Equation 2.1.
- ↑ Hall 2015, Equation 4.2.
- ↑ Hall 2015, Equation before 4.5.
- ↑ Knapp 2001 Equation 2.4.
- ↑ Knapp 2001, Section 2.3.
- ↑ Hall 2015, Theorems 9.4–5.
- ↑ Weinberg 2002, Chapter 5.
- ↑ Hall 2015, Theorem 10.18.
- ↑ Hall 2003, p. 235.
- ↑ See any text on basic group theory.
- ↑ Rossmann 2002 Propositions 3 and 6 paragraph 2.5.
- ↑ Hall 2003 See exercise 1, Chapter 6.
- ↑ Bekaert & Boulanger 2006 p.4.
- ↑ Hall 2003 Proposition 1.20.
- ↑ Lee 2003, Theorem 8.30.
- ↑ Weinberg 2002, Section 5.6, p. 231.
- ↑ Weinberg 2002, Section 5.6.
- ↑ Weinberg 2002, p. 231.
- ↑ Weinberg 2002, Sections 2.5, 5.7.
- ↑ Tung 1985, Section 10.5.
- ↑ Weinberg 2002 This is outlined (very briefly) on page 232, hardly more than a footnote.
- ↑ Hall 2003, Proposition 7.39.
- ↑ Jump up to: 102.0 102.1 Hall 2003, Theorem 7.40.
- ↑ Hall 2003, Section 6.6.
- ↑ Hall 2003, Second item in proposition 4.5.
- ↑ Hall 2003, p. 219.
- ↑ Rossmann 2002, Exercise 3 in paragraph 6.5.
- ↑ Hall 2003 See appendix D.3
- ↑ Weinberg 2002, Equation 5.4.8.
- ↑ Jump up to: 109.0 109.1 Weinberg 2002, Section 5.4.
- ↑ Weinberg 2002, pp. 215–216.
- ↑ Weinberg 2002, Equation 5.4.6.
- ↑ Weinberg 2002 Section 5.4.
- ↑ Weinberg 2002, Section 5.7, pp. 232–233.
- ↑ Weinberg 2002, Section 5.7, p. 233.
- ↑ Weinberg 2002 Equation 2.6.5.
- ↑ Weinberg 2002 Equation following 2.6.6.
- ↑ Weinberg 2002, Section 2.6.
- ↑ For a detailed discussion of the spin 0, 1/2 and 1 cases, see Greiner & Reinhardt 1996.
- ↑ Weinberg 2002, Chapter 3.
- ↑ Rossmann 2002 See section 6.1 for more examples, both finite-dimensional and infinite-dimensional.
- ↑ Gelfand, Minlos & Shapiro 1963
- ↑ Churchill & Brown 2014, Chapter 8 pp. 307–310.
- ↑ Gonzalez, P. A.; Vasquez, Y. (2014). "Dirac Quasinormal Modes of New Type Black Holes in New Massive Gravity". Eur. Phys. J. C 74:2969 (7): 3. doi:10.1140/epjc/s10052-014-2969-1. ISSN 1434-6044. Bibcode: 2014EPJC...74.2969G.
- ↑ Abramowitz & Stegun 1965, Equation 15.6.5.
- ↑ Simmons 1972, Sections 30, 31.
- ↑ Simmons 1972, Sections 30.
- ↑ Simmons 1972, Section 31.
- ↑ Simmons 1972, Equation 11 in appendix E, chapter 5.
- ↑ Langlands 1985, p. 205.
- ↑ Varadarajan 1989, Sections 3.1. 4.1.
- ↑ Langlands 1985, p. 203.
- ↑ Varadarajan 1989, Section 4.1.
- ↑ Gelfand, Graev & Pyatetskii-Shapiro 1969
- ↑ Knapp 2001, Chapter II.
- ↑ Jump up to: 135.0 135.1 Taylor 1986
- ↑ Knapp 2001 Chapter 2. Equation 2.12.
- ↑ Bargmann 1947
- ↑ Gelfand & Graev 1953
- ↑ Gelfand & Naimark 1947
- ↑ Takahashi 1963, p. 343.
- ↑ Knapp 2001, Equation 2.24.
- ↑ Folland 2015, Section 3.1.
- ↑ Folland 2015, Theorem 5.2.
- ↑ Tung 1985, Section 10.3.3.
- ↑ Harish-Chandra 1947, Footnote p. 374.
- ↑ Tung 1985, Equations 7.3–13, 7.3–14.
- ↑ Harish-Chandra 1947, Equation 8.
- ↑ Hall 2015, Proposition C.7.
- ↑ Hall 2015, Appendix C.2.
- ↑ Tung 1985, Step II section 10.2.
- ↑ Tung 1985, Equations 10.3–5. Tung's notation for Clebsch–Gordan coefficients differ from the one used here.
- ↑ Tung 1985, Equation VII-3.
- ↑ Tung 1985, Equations 10.3–5, 7, 8.
- ↑ Tung 1985, Equation VII-9.
- ↑ Tung 1985, Equations VII-10, 11.
- ↑ Tung 1985, Equations VII-12.
- ↑ Tung 1985, Equations VII-13.
- ↑ Weinberg 2002, Equation 2.4.12.
- ↑ Weinberg 2002, Equations 2.4.18–2.4.20.
- ↑ Weinberg 2002, Equations 5.4.19, 5.4.20.
- ↑ Zwiebach 2004, Section 12.8.
- ↑ Jump up to: 162.0 162.1 Bekaert & Boulanger 2006, p. 48.
- ↑ Zwiebach 2004, Section 18.8.
Freely available online references
- Bekaert, X.; Boulanger, N. (2006). "The unitary representations of the Poincare group in any spacetime dimension". arXiv:hep-th/0611263. Expanded version of the lectures presented at the second Modave summer school in mathematical physics (Belgium, August 2006).
- Curtright, T L; Fairlie, D B; Zachos, C K (2014), "A compact formula for rotations as spin matrix polynomials", SIGMA 10: 084, doi:10.3842/SIGMA.2014.084, Bibcode: 2014SIGMA..10..084C Group elements of SU(2) are expressed in closed form as finite polynomials of the Lie algebra generators, for all definite spin representations of the rotation group.
References
- Abramowitz, M.; Stegun, I. A. (1965). Handbook of Mathematical Functions: with Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables. Dover Books on Mathematics. New York: Dover Publications. ISBN 978-0486612720. https://books.google.com/books?id=MtU8uP7XMvoC&pg=PR9.
- Bargmann, V. (1947), "Irreducible unitary representations of the Lorenz group", Ann. of Math. 48 (3): 568–640, doi:10.2307/1969129 (the representation theory of SO(2,1) and SL(2, R); the second part on SO(3; 1) and SL(2, C), described in the introduction, was never published).
- Bargmann, V.; Wigner, E. P. (1948), "Group theoretical discussion of relativistic wave equations", Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 34 (5): 211–23, doi:10.1073/pnas.34.5.211, PMID 16578292, Bibcode: 1948PNAS...34..211B
- Bourbaki, N. (1998). Lie Groups and Lie Algebras: Chapters 1-3. Springer. ISBN 978-3-540-64242-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=brSYF_rB2ZcC.
- Brauer, R.; Weyl, H. (1935), "Spinors in n dimensions", Amer. J. Math. 57 (2): 425–449, doi:10.2307/2371218
- Bäuerle, G.G.A; de Kerf, E.A. (1990). Finite and infinite dimensional Lie algebras and their application in physics. Studies in mathematical physics. 1. North-Holland. ISBN 978-0-444-88776-4.
- Bäuerle, G.G.A; de Kerf, E.A.; ten Kroode, A.P.E. (1997). Finite and infinite dimensional Lie algebras and their application in physics. Studies in mathematical physics. 7. North-Holland. ISBN 978-0-444-82836-1. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/bookseries/09258582.
- Cartan, Élie (1913), "Les groupes projectifs qui ne laissant invariante aucun multiplicité plane" (in fr), Bull. Soc. Math. Fr. 41: 53–96, doi:10.24033/bsmf.916
- Churchill, R. V.; Brown, J. W. (2014). Complex Variables and Applications (9th ed.). New York: McGraw–Hill. ISBN 978-0073-383-170.
- Coleman, A. J. (1989). "The Greatest Mathematical Paper of All Time". The Mathematical Intelligencer 11 (3): 29–38. doi:10.1007/BF03025189. ISSN 0343-6993.
- Dalitz, R. H.; Peierls, Rudolf (1986). "Paul Adrien Maurice Dirac. 8 August 1902–20 October 1984". Biogr. Mem. Fellows R. Soc. 32: 138–185. doi:10.1098/rsbm.1986.0006.
- Delbourgo, R.; Salam, A.; Strathdee, J. (1967). "Harmonic analysis in terms of the homogeneous Lorentz group". Physics Letters B 25 (3): 230–32. doi:10.1016/0370-2693(67)90050-0. Bibcode: 1967PhLB...25..230D.
- Dirac, P. A. M. (1928), "The Quantum Theory of the Electron", Proc. R. Soc. A 117 (778): 610–624, doi:10.1098/rspa.1928.0023, Bibcode: 1928RSPSA.117..610D (free access)
- Dirac, P. A. M. (1936), "Relativistic wave equations", Proc. R. Soc. A 155 (886): 447–459, doi:10.1098/rspa.1936.0111, Bibcode: 1936RSPSA.155..447D
- Dirac, P. A. M. (1945), "Unitary representations of the Lorentz group", Proc. R. Soc. A 183 (994): 284–295, doi:10.1098/rspa.1945.0003, Bibcode: 1945RSPSA.183..284D
- Dixmier, J.; Malliavin, P. (1978), "Factorisations de fonctions et de vecteurs indéfiniment différentiables" (in fr), Bull. Sci. Math. 102: 305–330
- Fierz, M. (1939), "Über die relativistische theorie Kräftefreier teilchen mit beliebigem spin" (in de), Helv. Phys. Acta 12 (1): 3–37, doi:10.5169/seals-110930, Bibcode: 1939AcHPh..12....3F(pdf download available)
- Fierz, M.; Pauli, W. (1939), "On relativistic wave equations for particles of arbitrary spin in an electromagnetic field", Proc. R. Soc. A 173 (953): 211–232, doi:10.1098/rspa.1939.0140, Bibcode: 1939RSPSA.173..211F
- Folland, G. (2015). A Course in Abstract Harmonic Analysis (2nd ed.). CRC Press. ISBN 978-1498727136.
- Fulton, W.; Harris, J. (1991). Representation theory. A first course. Graduate Texts in Mathematics. 129. New York: Springer-Verlag. ISBN 978-0-387-97495-8.
- Gelfand, I. M.; Graev, M. I. (1953), "On a general method of decomposition of the regular representation of a Lie group into irreducible representations", Doklady Akademii Nauk SSSR 92: 221–224
- Gelfand, I. M.; Graev, M. I.; Vilenkin, N. Ya. (1966), "Harmonic analysis on the group of complex unimodular matrices in two dimensions", Generalized functions. Vol. 5: Integral geometry and representation theory, Academic Press, pp. 202–267, ISBN 978-1-4832-2975-1
- Gelfand, I. M.; Graev, M. I.; Pyatetskii-Shapiro, I. I. (1969), Representation theory and automorphic functions, Academic Press, ISBN 978-0-12-279506-0
- Gelfand, I.M.; Minlos, R.A.; Shapiro, Z. Ya. (1963), Representations of the Rotation and Lorentz Groups and their Applications, New York: Pergamon Press
- Gelfand, I. M.; Naimark, M. A. (1947), "Unitary representations of the Lorentz group" (in ru), Izvestiya Akad. Nauk SSSR. Ser. Mat. 11 (5): 411–504, http://www.mathnet.ru/links/716f895de8c01ce39ce0a83666f73303/im3007.pdf, retrieved 2014-12-15(Pdf from Math.net.ru)
- Green, J. A. (1998). "Richard Dagobert Brauer". Biographical Memoirs. 75. National Academy Press. pp. 70–95. ISBN 978-0309062954. http://www.nasonline.org/publications/biographical-memoirs/memoir-pdfs/brauer-richard-d.pdf.
- Greiner, W.; Müller, B. (1994). Quantum Mechanics: Symmetries (2nd ed.). Springer. ISBN 978-3540580805. https://archive.org/details/quantummechanics0001grei.
- Greiner, W.; Reinhardt, J. (1996), Field Quantization, Springer, ISBN 978-3-540-59179-5, https://archive.org/details/fieldquantizatio0000grei
- Harish-Chandra (1947), "Infinite irreducible representations of the Lorentz group", Proc. R. Soc. A 189 (1018): 372–401, doi:10.1098/rspa.1947.0047, Bibcode: 1947RSPSA.189..372H
- Harish-Chandra (1951), "Plancherel formula for complex semi-simple Lie groups", Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 37 (12): 813–818, doi:10.1073/pnas.37.12.813, PMID 16589034, Bibcode: 1951PNAS...37..813H
- Hall, Brian C. (2003), Lie Groups, Lie Algebras, and Representations: An Elementary Introduction, Graduate Texts in Mathematics, 222 (1st ed.), Springer, ISBN 978-0-387-40122-5
- Hall, Brian C. (2015), Lie groups, Lie algebras, and Representations: An Elementary Introduction, Graduate Texts in Mathematics, 222 (2nd ed.), Springer, doi:10.1007/978-3-319-13467-3, ISBN 978-3319134666, ISSN 0072-5285
- Helgason, S. (1968), Lie groups and symmetric spaces, Battelle Rencontres, Benjamin, pp. 1–71 (a general introduction for physicists)
- Helgason, S. (2000), Groups and geometric analysis. Integral geometry, invariant differential operators, and spherical functions (corrected reprint of the 1984 original), Mathematical Surveys and Monographs, 83, American Mathematical Society, ISBN 978-0-8218-2673-7
- Jorgenson, J.; Lang, S. (2008), The heat kernel and theta inversion on SL(2,C), Springer Monographs in Mathematics, Springer, ISBN 978-0-387-38031-5
- Killing, Wilhelm (1888), "Die Zusammensetzung der stetigen/endlichen Transformationsgruppen" (in de), Mathematische Annalen 31 (2 (June)): 252–290, doi:10.1007/bf01211904, https://zenodo.org/record/1428182
- Kirillov, A. (2008). An Introduction to Lie Groups and Lie Algebras. Cambridge Studies in Advanced Mathematics. 113. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0521889698. https://books.google.com/books?id=-Z3cDQAAQBAJ&q=Introduction+to+Lie+groups+and+Lie+algebras.
- Klauder, J. R. (1999). "Valentine Bargmann". Biographical Memoirs. 76. National Academy Press. pp. 37–50. ISBN 978-0-309-06434-7. http://www.nasonline.org/publications/biographical-memoirs/memoir-pdfs/bargmann-valentine.pdf.
- Knapp, Anthony W. (2001), Representation theory of semisimple groups. An overview based on examples., Princeton Landmarks in Mathematics, Princeton University Press, ISBN 978-0-691-09089-4 (elementary treatment for SL(2,C))
- Langlands, R. P. (1985). "Harish-Chandra". Biogr. Mem. Fellows R. Soc. 31: 198–225. doi:10.1098/rsbm.1985.0008.
- Lee, J. M. (2003), Introduction to Smooth manifolds, Springer Graduate Texts in Mathematics, 218, ISBN 978-0-387-95448-6
- Lie, Sophus (1888) (in de), Theorie der Transformationsgruppen I(1888), II(1890), III(1893)
- Misner, Charles W.; Thorne, Kip. S.; Wheeler, John A. (1973), Gravitation, W. H. Freeman, ISBN 978-0-7167-0344-0
- Naimark, M.A. (1964), Linear representations of the Lorentz group (translated from the Russian original by Ann Swinfen and O. J. Marstrand), Macmillan
- Rossmann, Wulf (2002), Lie Groups – An Introduction Through Linear Groups, Oxford Graduate Texts in Mathematics, Oxford Science Publications, ISBN 0-19-859683-9
- Rühl, W. (1970), The Lorentz group and harmonic analysis, Benjamin (a detailed account for physicists)
- Simmons, G. F. (1972). Differential Equations with Applications and historical Notes (T M H ed.). New Dheli: Tata McGra–Hill Publishing Company Ltd. ISBN 978-0-07-099572-7. https://archive.org/details/differentialequa00simm.
- Stein, Elias M. (1970), "Analytic continuation of group representations", Advances in Mathematics 4 (2): 172–207, doi:10.1016/0001-8708(70)90022-8 (James K. Whittemore Lectures in Mathematics given at Yale University, 1967)
- Takahashi, R. (1963), "Sur les représentations unitaires des groupes de Lorentz généralisés" (in fr), Bull. Soc. Math. France 91: 289–433, doi:10.24033/bsmf.1598
- Taylor, M. E. (1986), Noncommutative harmonic analysis, Mathematical Surveys and Monographs, 22, American Mathematical Society, ISBN 978-0-8218-1523-6, Chapter 9, SL(2, C) and more general Lorentz groups
- Tung, Wu-Ki (1985). Group Theory in Physics (1st ed.). New Jersey·London·Singapore·Hong Kong: World Scientific. ISBN 978-9971966577.
- Varadarajan, V. S. (1989). An Introduction to Harmonic Analysis on Semisimple Lie Groups. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0521663625.
- Weinberg, S. (2002), Foundations, The Quantum Theory of Fields, 1, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-55001-7, https://archive.org/details/quantumtheoryoff00stev
- Weinberg, S. (2000). Supersymmetry. The Quantum Theory of Fields. 3 (1st ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0521670555.
- Weyl, H. (1939), The Classical Groups. Their Invariants and Representations, Princeton University Press, ISBN 978-0-691-05756-9, https://books.google.com/books?isbn=0691057567
- Weyl, H. (1931), The Theory of Groups and Quantum Mechanics, Dover, ISBN 978-0-486-60269-1
- Wigner, E. P. (1939), "On unitary representations of the inhomogeneous Lorentz group", Annals of Mathematics 40 (1): 149–204, doi:10.2307/1968551, Bibcode: 1939AnMat..40..149W.
- Zwiebach, B. (2004). A First Course in String Theory. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-83143-1.
 |