Biology:Long non-coding RNA
Long non-coding RNAs (long ncRNAs, lncRNA) are a type of RNA, generally defined as transcripts more than 200 nucleotides that are not translated into protein.[2] This arbitrary limit distinguishes long ncRNAs from small non-coding RNAs, such as microRNAs (miRNAs), small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs), small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs), and other short RNAs.[3] Given that some lncRNAs have been reported to have the potential to encode small proteins or micro-peptides, the latest definition of lncRNA is a class of RNA molecules of over 200 nucleotides that have no or limited coding capacity.[4] Long intervening/intergenic noncoding RNAs (lincRNAs) are sequences of lncRNA which do not overlap protein-coding genes.[5]
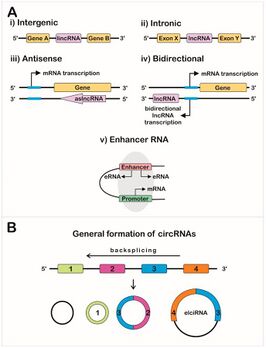
Long non-coding RNAs include intergenic lincRNAs, intronic ncRNAs, and sense and antisense lncRNAs, each type showing different genomic positions in relation to genes and exons.[1][3]
Abundance
Long non-coding transcripts are found in many species. Large-scale complementary DNA (cDNA) sequencing projects such as FANTOM reveal the complexity of these transcripts in humans.[6] The FANTOM3 project identified ~35,000 non-coding transcripts that bear many signatures of messenger RNAs, including 5' capping, splicing, and poly-adenylation, but have little or no open reading frame (ORF).[6] This number represents a conservative lower estimate, since it omitted many singleton transcripts and non-polyadenylated transcripts (tiling array data shows more than 40% of transcripts are non-polyadenylated).[7] Identifying ncRNAs within these cDNA libraries is challenging since it can be difficult to distinguish protein-coding transcripts from non-coding transcripts. It has been suggested through multiple studies that testis,[8] and neural tissues express the greatest amount of long non-coding RNAs of any tissue type.[9] Using FANTOM5, 27,919 long ncRNAs have been identified in various human sources.[10]
Quantitatively, lncRNAs demonstrate ~10-fold lower abundance than mRNAs,[11][12] which is explained by higher cell-to-cell variation of expression levels of lncRNA genes in the individual cells, when compared to protein-coding genes.[13] In general, the majority (~78%) of lncRNAs are characterized as tissue-specific, as opposed to only ~19% of mRNAs.[11] Only 3.6% of human lncRNA genes are expressed in various biological contexts and 34% of lncRNA genes are expressed at high level (top 25% of both lncRNAs and mRNAs) in at least one biological context.[14] In addition to higher tissue specificity, lncRNAs are characterized by higher developmental stage specificity,[15] and cell subtype specificity in tissues such as human neocortex[16] and other parts of the brain, regulating correct brain development and function.[17] In 2022, a comprehensive integration of lncRNAs from existing databases, revealed that there are 95,243 lncRNA genes and 323,950 transcripts in humans.[18]
In comparison to mammals relatively few studies have focused on the prevalence of lncRNAs in plants. However an extensive study considering 37 higher plant species and six algae identified ~200,000 non-coding transcripts using an in-silico approach,[19] which also established the associated Green Non-Coding Database (GreeNC), a repository of plant lncRNAs.
Genomic organization
In 2005 the landscape of the mammalian genome was described as numerous 'foci' of transcription that are separated by long stretches of intergenic space.[6] While some long ncRNAs are located within the intergenic stretches, the majority are overlapping sense and antisense transcripts that often include protein-coding genes,[20] giving rise to a complex hierarchy of overlapping isoforms.[21] Genomic sequences within these transcriptional foci are often shared within a number of coding and non-coding transcripts in the sense and antisense directions[22] For example, 3012 out of 8961 cDNAs previously annotated as truncated coding sequences within FANTOM2 were later designated as genuine ncRNA variants of protein-coding cDNAs.[6] While the abundance and conservation of these arrangements suggest they have biological relevance, the complexity of these foci frustrates easy evaluation.
The GENCODE consortium has collated and analysed a comprehensive set of human lncRNA annotations and their genomic organisation, modifications, cellular locations and tissue expression profiles.[9] Their analysis indicates human lncRNAs show a bias toward two-exon transcripts.[9]
Identification software
| Name | Taxonomic group | Web server | Repository | Input file | Main model / algorithm | Training set | Year published | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DeepPlnc | Plant | DeepPlnc Server | DeepPlnc | FASTA | Neural network | Yes | 2022 | [23] |
| RNAsamba | All | RNAsamba | RNAsamba | FASTA | Neural network | Yes | 2020 | [24] |
| LGC | Plant, animal | LGC | FASTA, BED, GTF | Relationship between ORF length and GC content | No | 2019 | [25] | |
| CPAT | Human, fly, mouse, zebrafish | CPAT | CPAT | FASTA/BED | Logistic regression | Yes | 2013 | [26] |
| COME | Plant, human, mouse, fly, worm | COME | COME | GTF | Random forest | Yes | 2017 | [27] |
| CNCI | Plant, animal | NA | FASTA, GTF | Support vector machine | No | 2013 | [28] | |
| PLEK | Vertebrate | NA | PLEK | FASTA | Support vector machine | No | 2014 | [28] |
| FEELnc | All | NA | FEELnc | FASTA, GTF | Random forest | Yes | 2017 | [29] |
| PhyloCSF | Vertebrate, fly, mosquito, yeast, worm | NA | FASTA | Phylogenetic codon model | Yes | 2011 | [30] | |
| slncky | All | NA | slncky | FASTA, BED | Evolutionary conservation | Yes | 2016 | [31] |
Translation
There has been considerable debate about whether lncRNAs have been misannotated and do in fact encode proteins. Several lncRNAs have been found to in fact encode for peptides with biologically significant function.[32][33][34] Ribosome profiling studies have suggested that anywhere from 40% to 90% of annotated lncRNAs are in fact translated,[35][36] although there is disagreement about the correct method for analyzing ribosome profiling data.[37] Additionally, it is thought that many of the peptides produced by lncRNAs may be highly unstable and without biological function.[36]
Conservation
Initial studies into lncRNA conservation noted that as a class, they were enriched for conserved sequence elements,[38] depleted in substitution and insertion/deletion rates[39] and depleted in rare frequency variants,[40] indicative of purifying selection maintaining lncRNA function. However, further investigations into vertebrate lncRNAs revealed that while lncRNAs are conserved in sequence, they are not conserved in transcription.[41][42][8] In other words, even when the sequence of a human lncRNA is conserved in another vertebrate species, there is often no transcription of a lncRNA in the orthologous genomic region. Some argue that these observations suggest non-functionality of the majority of lncRNAs,[43][44][45] while others argue that they may be indicative of rapid species-specific adaptive selection.[46]
While the turnover of lncRNA transcription is much higher than initially expected, it is important to note that still, hundreds of lncRNAs are conserved at the sequence level. There have been several attempts to delineate the different categories of selection signatures seen amongst lncRNAs including: lncRNAs with strong sequence conservation across the entire length of the gene, lncRNAs in which only a portion of the transcript (e.g. 5′ end, splice sites) is conserved, and lncRNAs that are transcribed from syntenic regions of the genome but have no recognizable sequence similarity.[47][48][49] Additionally, there have been attempts to identify conserved secondary structures in lncRNAs, though these studies have currently given way to conflicting results.[50][51]
Functions
Despite claims that the majority of long noncoding RNAs in mammals are likely to be functional,[52][53] it seems likely that most of them are transcriptional noise and only a relatively small proportion has been demonstrated to be biologically relevant.[45][54]
Some lncRNAs have been functionally annotated in LncRNAdb (a database of literature described lncRNAs),[55][56] with the majority of these being described in humans. Over 2600 human lncRNAs with experimental evidences have been community-curated in LncRNAWiki (a wiki-based, publicly editable and open-content platform for community curation of human lncRNAs).[57] According to the curation of functional mechanisms of lncRNAs based on the literatures, lncRNAs are extensively reported to be involved in ceRNA regulation,transcriptional regulation, and epigenetic regulation.[57] A further large-scale sequencing study provides evidence that many transcripts thought to be lncRNAs may, in fact, be translated into proteins.[58]
In the regulation of gene transcription
In gene-specific transcription
In eukaryotes, RNA transcription is a tightly regulated process. Noncoding RNAs act upon different aspects of this process, targeting transcriptional modulators, RNA polymerase (RNAP) II and even the DNA duplex to regulate gene expression.[59]
NcRNAs modulate transcription by several mechanisms, including functioning themselves as co-regulators, modifying transcription factor activity, or regulating the association and activity of co-regulators. For example, the noncoding RNA Evf-2 functions as a co-activator for the homeobox transcription factor Dlx2, which plays important roles in forebrain development and neurogenesis.[60][61] Sonic hedgehog induces transcription of Evf-2 from an ultra-conserved element located between the Dlx5 and Dlx6 genes during forebrain development.[60] Evf-2 then recruits the Dlx2 transcription factor to the same ultra-conserved element whereby Dlx2 subsequently induces expression of Dlx5. The existence of other similar ultra- or highly conserved elements within the mammalian genome that are both transcribed and fulfill enhancer functions suggest Evf-2 may be illustrative of a generalised mechanism that regulates developmental genes with complex expression patterns during vertebrate growth.[62][63] Indeed, the transcription and expression of similar non-coding ultraconserved elements was shown to be abnormal in human leukaemia and to contribute to apoptosis in colon cancer cells, suggesting their involvement in tumorigenesis.[64][65]
Local ncRNAs can also recruit transcriptional programmes to regulate adjacent protein-coding gene expression. For example, divergent lncRNAs that are transcribed in the opposite direction to nearby protein-coding genes (~20% of total lncRNAs in mammalian genomes) possibly regulate the transcription of nearby adjacent essential developmental regulatory genes in pluripotent cells.[66][67]
The RNA binding protein TLS binds and inhibits the CREB binding protein and p300 histone acetyltransferase activities on a repressed gene target, cyclin D1. The recruitment of TLS to the promoter of cyclin D1 is directed by long ncRNAs expressed at low levels and tethered to 5' regulatory regions in response to DNA damage signals.[68] Moreover, these local ncRNAs act cooperatively as ligands to modulate the activities of TLS. In the broad sense, this mechanism allows the cell to harness RNA-binding proteins, which make up one of the largest classes within the mammalian proteome, and integrate their function in transcriptional programs. Nascent long ncRNAs have been shown to increase the activity of CREB binding protein, which in turn increases the transcription of that ncRNA.[69] A study found that a lncRNA in the antisense direction of the Apolipoprotein A1 (APOA1) regulates the transcription of APOA1 through epigenetic modifications.[70]
Recent evidence has raised the possibility that transcription of genes that escape from X-inactivation might be mediated by expression of long non-coding RNA within the escaping chromosomal domains.[71]
Regulating basal transcription machinery
NcRNAs also target general transcription factors required for the RNAP II transcription of all genes.[59] These general factors include components of the initiation complex that assemble on promoters or involved in transcription elongation. A ncRNA transcribed from an upstream minor promoter of the dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) gene forms a stable RNA-DNA triplex within the major promoter of DHFR to prevent the binding of the transcriptional co-factor TFIIB.[72] This novel mechanism of regulating gene expression may represent a widespread method of controlling promoter usage, as thousands of RNA-DNA triplexes exist in eukaryotic chromosome.[73] The U1 ncRNA can induce transcription by binding to and stimulating TFIIH to phosphorylate the C-terminal domain of RNAP II.[74] In contrast the ncRNA 7SK is able to repress transcription elongation by, in combination with HEXIM1/2, forming an inactive complex that prevents PTEFb from phosphorylating the C-terminal domain of RNAP II,[74][75][76] repressing global elongation under stressful conditions. These examples, which bypass specific modes of regulation at individual promoters provide a means of quickly affecting global changes in gene expression.
The ability to quickly mediate global changes is also apparent in the rapid expression of non-coding repetitive sequences. The short interspersed nuclear (SINE) Alu elements in humans and analogous B1 and B2 elements in mice have succeeded in becoming the most abundant mobile elements within the genomes, comprising ~10% of the human and ~6% of the mouse genome, respectively.[77][78] These elements are transcribed as ncRNAs by RNAP III in response to environmental stresses such as heat shock,[79] where they then bind to RNAP II with high affinity and prevent the formation of active pre-initiation complexes.[80][81][82][83] This allows for the broad and rapid repression of gene expression in response to stress.[80][83]
A dissection of the functional sequences within Alu RNA transcripts has drafted a modular structure analogous to the organization of domains in protein transcription factors.[84] The Alu RNA contains two 'arms', each of which may bind one RNAP II molecule, as well as two regulatory domains that are responsible for RNAP II transcriptional repression in vitro.[83] These two loosely structured domains may even be concatenated to other ncRNAs such as B1 elements to impart their repressive role.[83] The abundance and distribution of Alu elements and similar repetitive elements throughout the mammalian genome may be partly due to these functional domains being co-opted into other long ncRNAs during evolution, with the presence of functional repeat sequence domains being a common characteristic of several known long ncRNAs including Kcnq1ot1, Xlsirt and Xist.[85][86][87][88]
In addition to heat shock, the expression of SINE elements (including Alu, B1, and B2 RNAs) increases during cellular stress such as viral infection[89] in some cancer cells[90] where they may similarly regulate global changes to gene expression. The ability of Alu and B2 RNA to bind directly to RNAP II provides a broad mechanism to repress transcription.[81][83] Nevertheless, there are specific exceptions to this global response where Alu or B2 RNAs are not found at activated promoters of genes undergoing induction, such as the heat shock genes.[83] This additional hierarchy of regulation that exempts individual genes from the generalised repression also involves a long ncRNA, heat shock RNA-1 (HSR-1). It was argued that HSR-1 is present in mammalian cells in an inactive state, but upon stress is activated to induce the expression of heat shock genes.[91] This activation involves a conformational alteration of HSR-1 in response to rising temperatures, permitting its interaction with the transcriptional activator HSF-1, which trimerizes and induces the expression of heat shock genes.[91] In the broad sense, these examples illustrate a regulatory circuit nested within ncRNAs whereby Alu or B2 RNAs repress general gene expression, while other ncRNAs activate the expression of specific genes.
Transcribed by RNA polymerase III
Many of the ncRNAs that interact with general transcription factors or RNAP II itself (including 7SK, Alu and B1 and B2 RNAs) are transcribed by RNAP III,[92] uncoupling their expression from RNAP II, which they regulate. RNAP III also transcribes other ncRNAs, such as BC2, BC200 and some microRNAs and snoRNAs, in addition to housekeeping ncRNA genes such as tRNAs, 5S rRNAs and snRNAs.[92] The existence of an RNAP III-dependent ncRNA transcriptome that regulates its RNAP II-dependent counterpart is supported by the finding of a set of ncRNAs transcribed by RNAP III with sequence homology to protein-coding genes. This prompted the authors to posit a 'cogene/gene' functional regulatory network,[93] showing that one of these ncRNAs, 21A, regulates the expression of its antisense partner gene, CENP-F in trans.
In post-transcriptional regulation
In addition to regulating transcription, ncRNAs also control various aspects of post-transcriptional mRNA processing. Similar to small regulatory RNAs such as microRNAs and snoRNAs, these functions often involve complementary base pairing with the target mRNA. The formation of RNA duplexes between complementary ncRNA and mRNA may mask key elements within the mRNA required to bind trans-acting factors, potentially affecting any step in post-transcriptional gene expression including pre-mRNA processing and splicing, transport, translation, and degradation.[94]
In splicing
The splicing of mRNA can induce its translation and functionally diversify the repertoire of proteins it encodes. The Zeb2 mRNA requires the retention of a 5'UTR intron that contains an internal ribosome entry site for efficient translation.[95] The retention of the intron depends on the expression of an antisense transcript that complements the intronic 5' splice site.[95] Therefore, the ectopic expression of the antisense transcript represses splicing and induces translation of the Zeb2 mRNA during mesenchymal development. Likewise, the expression of an overlapping antisense Rev-ErbAa2 transcript controls the alternative splicing of the thyroid hormone receptor ErbAa2 mRNA to form two antagonistic isoforms.[96]
In translation
NcRNA may also apply additional regulatory pressures during translation, a property particularly exploited in neurons where the dendritic or axonal translation of mRNA in response to synaptic activity contributes to changes in synaptic plasticity and the remodelling of neuronal networks. The RNAP III transcribed BC1 and BC200 ncRNAs, that previously derived from tRNAs, are expressed in the mouse and human central nervous system, respectively.[97][98] BC1 expression is induced in response to synaptic activity and synaptogenesis and is specifically targeted to dendrites in neurons.[99] Sequence complementarity between BC1 and regions of various neuron-specific mRNAs also suggest a role for BC1 in targeted translational repression.[100] Indeed, it was recently shown that BC1 is associated with translational repression in dendrites to control the efficiency of dopamine D2 receptor-mediated transmission in the striatum[101] and BC1 RNA-deleted mice exhibit behavioural changes with reduced exploration and increased anxiety.[102]
In siRNA-directed gene regulation
In addition to masking key elements within single-stranded RNA, the formation of double-stranded RNA duplexes can also provide a substrate for the generation of endogenous siRNAs (endo-siRNAs) in Drosophila and mouse oocytes.[103] The annealing of complementary sequences, such as antisense or repetitive regions between transcripts, forms an RNA duplex that may be processed by Dicer-2 into endo-siRNAs. Also, long ncRNAs that form extended intramolecular hairpins may be processed into siRNAs, compellingly illustrated by the esi-1 and esi-2 transcripts.[104] Endo-siRNAs generated from these transcripts seem particularly useful in suppressing the spread of mobile transposon elements within the genome in the germline. However, the generation of endo-siRNAs from antisense transcripts or pseudogenes may also silence the expression of their functional counterparts via RISC effector complexes, acting as an important node that integrates various modes of long and short RNA regulation, as exemplified by the Xist and Tsix (see above).[105]
In epigenetic regulation
Epigenetic modifications, including histone and DNA methylation, histone acetylation and sumoylation, affect many aspects of chromosomal biology, primarily including regulation of large numbers of genes by remodeling broad chromatin domains.[106][107] While it has been known for some time that RNA is an integral component of chromatin,[108][109] it is only recently that we are beginning to appreciate the means by which RNA is involved in pathways of chromatin modification.[110][111][112] For example, Oplr16 epigenetically induces the activation of stem cell core factors by coordinating intrachromosomal looping and recruitment of DNA demethylase TET2.[113]
In Drosophila, long ncRNAs induce the expression of the homeotic gene, Ubx, by recruiting and directing the chromatin modifying functions of the trithorax protein Ash1 to Hox regulatory elements.[112] Similar models have been proposed in mammals, where strong epigenetic mechanisms are thought to underlie the embryonic expression profiles of the Hox genes that persist throughout human development.[114][111] Indeed, the human Hox genes are associated with hundreds of ncRNAs that are sequentially expressed along both the spatial and temporal axes of human development and define chromatin domains of differential histone methylation and RNA polymerase accessibility.[111] One ncRNA, termed HOTAIR, that originates from the HOXC locus represses transcription across 40 kb of the HOXD locus by altering chromatin trimethylation state. HOTAIR is thought to achieve this by directing the action of Polycomb chromatin remodeling complexes in trans to govern the cells' epigenetic state and subsequent gene expression. Components of the Polycomb complex, including Suz12, EZH2 and EED, contain RNA binding domains that may potentially bind HOTAIR and probably other similar ncRNAs.[115][116][117] This example nicely illustrates a broader theme whereby ncRNAs recruit the function of a generic suite of chromatin modifying proteins to specific genomic loci, underscoring the complexity of recently published genomic maps.[107] Indeed, the prevalence of long ncRNAs associated with protein coding genes may contribute to localised patterns of chromatin modifications that regulate gene expression during development. For example, the majority of protein-coding genes have antisense partners, including many tumour suppressor genes that are frequently silenced by epigenetic mechanisms in cancer.[118] A recent study observed an inverse expression profile of the p15 gene and an antisense ncRNA in leukaemia.[118] A detailed analysis showed the p15 antisense ncRNA (CDKN2BAS) was able to induce changes to heterochromatin and DNA methylation status of p15 by an unknown mechanism, thereby regulating p15 expression.[118] Therefore, misexpression of the associated antisense ncRNAs may subsequently silence the tumour suppressor gene contributing towards cancer.
Imprinting
Many emergent themes of ncRNA-directed chromatin modification were first apparent within the phenomenon of imprinting, whereby only one allele of a gene is expressed from either the maternal or the paternal chromosome. In general, imprinted genes are clustered together on chromosomes, suggesting the imprinting mechanism acts upon local chromosome domains rather than individual genes. These clusters are also often associated with long ncRNAs whose expression is correlated with the repression of the linked protein-coding gene on the same allele.[119] Indeed, detailed analysis has revealed a crucial role for the ncRNAs Kcnqot1 and Igf2r/Air in directing imprinting.[120]
Almost all the genes at the Kcnq1 loci are maternally inherited, except the paternally expressed antisense ncRNA Kcnqot1.[121] Transgenic mice with truncated Kcnq1ot fail to silence the adjacent genes, suggesting that Kcnqot1 is crucial to the imprinting of genes on the paternal chromosome.[122] It appears that Kcnqot1 is able to direct the trimethylation of lysine 9 (H3K9me3) and 27 of histone 3 (H3K27me3) to an imprinting centre that overlaps the Kcnqot1 promoter and actually resides within a Kcnq1 sense exon.[123] Similar to HOTAIR (see above), Eed-Ezh2 Polycomb complexes are recruited to the Kcnq1 loci paternal chromosome, possibly by Kcnqot1, where they may mediate gene silencing through repressive histone methylation.[123] A differentially methylated imprinting centre also overlaps the promoter of a long antisense ncRNA Air that is responsible for the silencing of neighbouring genes at the Igf2r locus on the paternal chromosome.[124][125] The presence of allele-specific histone methylation at the Igf2r locus suggests Air also mediates silencing via chromatin modification.[126]
Xist and X-chromosome inactivation
The inactivation of a X-chromosome in female placental mammals is directed by one of the earliest and best characterized long ncRNAs, Xist.[127] The expression of Xist from the future inactive X-chromosome, and its subsequent coating of the inactive X-chromosome, occurs during early embryonic stem cell differentiation. Xist expression is followed by irreversible layers of chromatin modifications that include the loss of the histone (H3K9) acetylation and H3K4 methylation that are associated with active chromatin, and the induction of repressive chromatin modifications including H4 hypoacetylation, H3K27 trimethylation,[127] H3K9 hypermethylation and H4K20 monomethylation as well as H2AK119 monoubiquitylation. These modifications coincide with the transcriptional silencing of the X-linked genes.[128] Xist RNA also localises the histone variant macroH2A to the inactive X–chromosome.[129] There are additional ncRNAs that are also present at the Xist loci, including an antisense transcript Tsix, which is expressed from the future active chromosome and able to repress Xist expression by the generation of endogenous siRNA.[105] Together these ncRNAs ensure that only one X-chromosome is active in female mammals.
Telomeric non-coding RNAs
Telomeres form the terminal region of mammalian chromosomes and are essential for stability and aging and play central roles in diseases such as cancer.[130] Telomeres have been long considered transcriptionally inert DNA-protein complexes until it was shown in the late 2000s that telomeric repeats may be transcribed as telomeric RNAs (TelRNAs)[131] or telomeric repeat-containing RNAs.[132] These ncRNAs are heterogeneous in length, transcribed from several sub-telomeric loci and physically localise to telomeres. Their association with chromatin, which suggests an involvement in regulating telomere specific heterochromatin modifications, is repressed by SMG proteins that protect chromosome ends from telomere loss.[132] In addition, TelRNAs block telomerase activity in vitro and may therefore regulate telomerase activity.[131] Although early, these studies suggest an involvement for telomeric ncRNAs in various aspects of telomere biology.
In regulation of DNA replication timing and chromosome stability
Asynchronously replicating autosomal RNAs (ASARs) are very long (~200kb) non-coding RNAs that are non-spliced, non-polyadenylated, and are required for normal DNA replication timing and chromosome stability.[133][134][135] Deletion of any one of the genetic loci containing ASAR6, ASAR15, or ASAR6-141 results in the same phenotype of delayed replication timing and delayed mitotic condensation (DRT/DMC) of the entire chromosome. DRT/DMC results in chromosomal segregation errors that lead to increased frequency of secondary rearrangements and an unstable chromosome. Similar to Xist, ASARs show random monoallelic expression and exist in asynchronous DNA replication domains. Although the mechanism of ASAR function is still under investigation, it is hypothesized that they work via similar mechanisms as the Xist lncRNA, but on smaller autosomal domains resulting in allele specific changes in gene expression.
Incorrect reparation of DNA double-strand breaks (DSB) leading to chromosomal rearrangements is one of the oncogenesis's primary causes. A number of lncRNAs are crucial at the different stages of the main pathways of DSB repair in eukaryotic cells: nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) and homology-directed repair (HDR). Gene mutations or variation in expression levels of such RNAs can lead to local DNA repair defects, increasing the chromosome aberration frequency. Moreover, it was demonstrated that some RNAs could stimulate long-range chromosomal rearrangements.[136]
In aging and disease
The discovery that long ncRNAs function in various aspects of cell biology has led to research on their role in disease. Tens of thousands of lncRNAs are potentially associated with diseases based on the multi-omics evidence.[137] A handful of studies have implicated long ncRNAs in a variety of disease states and support an involvement and co-operation in neurological disease and cancer.
The first published report of an alteration in lncRNA abundance in aging and human neurological disease was provided by Lukiw et al.[138] in a study using short post-mortem interval tissues from patients with Alzheimer's disease and non-Alzheimer's dementia (NAD) ; this early work was based on the prior identification of a primate brain-specific cytoplasmic transcript of the Alu repeat family by Watson and Sutcliffe in 1987 known as BC200 (brain, cytoplasmic, 200 nucleotide).[139]
While many association studies have identified unusual expression of long ncRNAs in disease states, there is little understanding of their role in causing disease. Expression analyses that compare tumor cells and normal cells have revealed changes in the expression of ncRNAs in several forms of cancer. For example, in prostate tumours, PCGEM1 (one of two overexpressed ncRNAs) is correlated with increased proliferation and colony formation suggesting an involvement in regulating cell growth.[140] PRNCR1 was found to promote tumor growth in several malignancies like prostate cancer, breast cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, oral squamous cell carcinoma and colorectal cancer.[141] MALAT1 (also known as NEAT2) was originally identified as an abundantly expressed ncRNA that is upregulated during metastasis of early-stage non-small cell lung cancer and its overexpression is an early prognostic marker for poor patient survival rates.[140] LncRNAs such as HEAT2 or KCNQ1OT1 have been shown to be regulated in the blood of patients with cardiovascular diseases such as heart failure or coronary artery disease and, moreover, to predict cardiovascular disease events.[142][143] More recently, the highly conserved mouse homologue of MALAT1 was found to be highly expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma.[144] Intronic antisense ncRNAs with expression correlated to the degree of tumor differentiation in prostate cancer samples have also been reported.[145] Despite a number of long ncRNAs having aberrant expression in cancer, their function and potential role in tumourigenesis is relatively unknown. For example, the ncRNAs HIS-1 and BIC have been implicated in cancer development and growth control, but their function in normal cells is unknown.[146][147] In addition to cancer, ncRNAs also exhibit aberrant expression in other disease states. Overexpression of PRINS is associated with psoriasis susceptibility, with PRINS expression being elevated in the uninvolved epidermis of psoriatic patients compared with both psoriatic lesions and healthy epidermis.[148]
Genome-wide profiling revealed that many transcribed non-coding ultraconserved regions exhibit distinct profiles in various human cancer states.[65] An analysis of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia, colorectal carcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma found that all three cancers exhibited aberrant expression profiles for ultraconserved ncRNAs relative to normal cells. Further analysis of one ultraconserved ncRNA suggested it behaved like an oncogene by mitigating apoptosis and subsequently expanding the number of malignant cells in colorectal cancers.[65] Many of these transcribed ultraconserved sites that exhibit distinct signatures in cancer are found at fragile sites and genomic regions associated with cancer. It seems likely that the aberrant expression of these ultraconserved ncRNAs within malignant processes results from important functions they fulfil in normal human development.
Recently, a number of association studies examining single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with disease states have been mapped to long ncRNAs. For example, SNPs that identified a susceptibility locus for myocardial infarction mapped to a long ncRNA, MIAT (myocardial infarction associated transcript).[149] Likewise, genome-wide association studies identified a region associated with coronary artery disease[150] that encompassed a long ncRNA, ANRIL.[151] ANRIL is expressed in tissues and cell types affected by atherosclerosis[152][153] and its altered expression is associated with a high-risk haplotype for coronary artery disease.[153][154]
The complexity of the transcriptome, and our evolving understanding of its structure may inform a reinterpretation of the functional basis for many natural polymorphisms associated with disease states. Many SNPs associated with certain disease conditions are found within non-coding regions and the complex networks of non-coding transcription within these regions make it particularly difficult to elucidate the functional effects of polymorphisms. For example, a SNP both within the truncated form of ZFAT and the promoter of an antisense transcript increases the expression of ZFAT not through increasing the mRNA stability, but rather by repressing the expression of the antisense transcript.[155]
The ability of long ncRNAs to regulate associated protein-coding genes may contribute to disease if misexpression of a long ncRNA deregulates a protein coding gene with clinical significance. In similar manner, an antisense long ncRNA that regulates the expression of the sense BACE1 gene, a crucial enzyme in Alzheimer's disease etiology, exhibits elevated expression in several regions of the brain in individuals with Alzheimer's disease[156] Alteration of the expression of ncRNAs may also mediate changes at an epigenetic level to affect gene expression and contribute to disease aetiology. For example, the induction of an antisense transcript by a genetic mutation led to DNA methylation and silencing of sense genes, causing β-thalassemia in a patient.[157]
Alongside their role in mediating pathological processes, long noncoding RNAs play a role in the immune response to vaccination, as identified for both the influenza vaccine and the yellow fever vaccine.[158]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Long Non-Coding RNAs in the Regulation of Gene Expression: Physiology and Disease". Non-Coding RNA 5 (1): 17. February 2019. doi:10.3390/ncrna5010017. PMID 30781588.
- ↑ "Visiting "noncodarnia"". BioTechniques 54 (6): 301, 303–4. June 2013. doi:10.2144/000114037. PMID 23750541. ""We're calling long noncoding RNAs a class, when actually the only definition is that they are longer than 200 bp," says Ana Marques, a Research Fellow at the University of Oxford who uses evolutionary approaches to understand lncRNA function.".
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "On the classification of long non-coding RNAs". RNA Biology 10 (6): 925–933. June 2013. doi:10.4161/rna.24604. PMID 23696037.
- ↑ Ma, Lina; Zhang, Zhang (September 2023). "The contribution of databases towards understanding the universe of long non-coding RNAs". Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology 24 (9): 601–602. doi:10.1038/s41580-023-00612-z. ISSN 1471-0080. PMID 37147495. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37147495.
- ↑ "The functions and unique features of long intergenic non-coding RNA". Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology 19 (3): 143–157. March 2018. doi:10.1038/nrm.2017.104. PMID 29138516.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 "The transcriptional landscape of the mammalian genome". Science 309 (5740): 1559–1563. September 2005. doi:10.1126/science.1112014. PMID 16141072. Bibcode: 2005Sci...309.1559F.
- ↑ "Transcriptional maps of 10 human chromosomes at 5-nucleotide resolution". Science 308 (5725): 1149–1154. May 2005. doi:10.1126/science.1108625. PMID 15790807. Bibcode: 2005Sci...308.1149C.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 "The evolution of lncRNA repertoires and expression patterns in tetrapods". Nature 505 (7485): 635–640. January 2014. doi:10.1038/nature12943. PMID 24463510. Bibcode: 2014Natur.505..635N.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 "The GENCODE v7 catalog of human long noncoding RNAs: analysis of their gene structure, evolution, and expression". Genome Research 22 (9): 1775–1789. September 2012. doi:10.1101/gr.132159.111. PMID 22955988.
- ↑ "An atlas of human long non-coding RNAs with accurate 5′ ends". Nature 543 (7644): 199–204. March 2017. doi:10.1038/nature21374. PMID 28241135. Bibcode: 2017Natur.543..199H.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 "Integrative annotation of human large intergenic noncoding RNAs reveals global properties and specific subclasses". Genes & Development 25 (18): 1915–1927. September 2011. doi:10.1101/gad.17446611. PMID 21890647.
- ↑ "Experimental validation of the regulated expression of large numbers of non-coding RNAs from the mouse genome". Genome Research 16 (1): 11–19. January 2006. doi:10.1101/gr.4200206. PMID 16344565.
- ↑ "HIPSTR and thousands of lncRNAs are heterogeneously expressed in human embryos, primordial germ cells and stable cell lines". Scientific Reports 6: 32753. September 2016. doi:10.1038/srep32753. PMID 27605307. Bibcode: 2016NatSR...632753Y.
- ↑ Li, Zhao; Liu, Lin; Jiang, Shuai; Li, Qianpeng; Feng, Changrui; Du, Qiang; Zou, Dong; Xiao, Jingfa et al. (2021-01-08). "LncExpDB: an expression database of human long non-coding RNAs". Nucleic Acids Research 49 (D1): D962–D968. doi:10.1093/nar/gkaa850. ISSN 1362-4962. PMID 33045751.
- ↑ "Single-cell RNA-Seq profiling of human preimplantation embryos and embryonic stem cells". Nature Structural & Molecular Biology 20 (9): 1131–1139. September 2013. doi:10.1038/nsmb.2660. PMID 23934149.
- ↑ "Single-cell analysis of long non-coding RNAs in the developing human neocortex". Genome Biology 17: 67. April 2016. doi:10.1186/s13059-016-0932-1. PMID 27081004.
- ↑ "Long Non-Coding RNA (lncRNA) Roles in Cell Biology, Neurodevelopment and Neurological Disorders". Non-Coding RNA 7 (2): 36. June 2021. doi:10.3390/ncrna7020036. PMID 34204536.
- ↑ Li, Zhao; Liu, Lin; Feng, Changrui; Qin, Yuxin; Xiao, Jingfa; Zhang, Zhang; Ma, Lina (2023-01-06). "LncBook 2.0: integrating human long non-coding RNAs with multi-omics annotations". Nucleic Acids Research 51 (D1): D186–D191. doi:10.1093/nar/gkac999. ISSN 1362-4962. PMID 36330950.
- ↑ "GREENC: a Wiki-based database of plant lncRNAs". Nucleic Acids Research 44 (D1): D1161–6. January 2016. doi:10.1093/nar/gkv1215. PMID 26578586.
- ↑ "RNA maps reveal new RNA classes and a possible function for pervasive transcription". Science 316 (5830): 1484–1488. June 2007. doi:10.1126/science.1138341. PMID 17510325. Bibcode: 2007Sci...316.1484K. http://lips.informatik.uni-leipzig.de/?q=node/1519.
- ↑ "Genome-wide transcription and the implications for genomic organization". Nature Reviews Genetics 8 (6): 413–423. June 2007. doi:10.1038/nrg2083. PMID 17486121.
- ↑ "Identification and analysis of functional elements in 1% of the human genome by the ENCODE pilot project". Nature 447 (7146): 799–816. June 2007. doi:10.1038/nature05874. PMID 17571346. Bibcode: 2007Natur.447..799B.
- ↑ "DeepPlnc: Bi-modal deep learning for highly accurate plant lncRNA discovery". Genomics 114 (5): 110443. September 2022. doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2022.110443. PMID 35931273.
- ↑ "RNAsamba: neural network-based assessment of the protein-coding potential of RNA sequences". NAR Genomics and Bioinformatics 2 (1): lqz024. March 2020. doi:10.1093/nargab/lqz024. PMID 33575571.
- ↑ "Characterization and identification of long non-coding RNAs based on feature relationship". Bioinformatics 41 (Database issue): D246–D251. January 2019. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btz008. PMID 30649200.
- ↑ "CPAT: Coding-Potential Assessment Tool using an alignment-free logistic regression model". Nucleic Acids Research 41 (6): e74. April 2013. doi:10.1093/nar/gkt006. PMID 23335781.
- ↑ "COME: a robust coding potential calculation tool for lncRNA identification and characterization based on multiple features". Nucleic Acids Research 45 (1): e2. January 2017. doi:10.1093/nar/gkw798. PMID 27608726.
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 "Utilizing sequence intrinsic composition to classify protein-coding and long non-coding transcripts". Nucleic Acids Research 41 (17): e166. September 2013. doi:10.1093/nar/gkt646. PMID 23892401.
- ↑ "FEELnc: a tool for long non-coding RNA annotation and its application to the dog transcriptome". Nucleic Acids Research 45 (8): e57. May 2017. doi:10.1093/nar/gkw1306. PMID 28053114.
- ↑ "PhyloCSF: a comparative genomics method to distinguish protein coding and non-coding regions". Bioinformatics 27 (13): i275–i282. July 2011. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btr209. PMID 21685081.
- ↑ "Evolutionary analysis across mammals reveals distinct classes of long non-coding RNAs". Genome Biology 17 (19): 19. Feb 2016. doi:10.1186/s13059-016-0880-9. PMID 26838501.
- ↑ "A micropeptide encoded by a putative long noncoding RNA regulates muscle performance". Cell 160 (4): 595–606. February 2015. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2015.01.009. PMID 25640239.
- ↑ "mTORC1 and muscle regeneration are regulated by the LINC00961-encoded SPAR polypeptide". Nature 541 (7636): 228–232. January 2017. doi:10.1038/nature21034. PMID 28024296. Bibcode: 2017Natur.541..228M.
- ↑ "Toddler: an embryonic signal that promotes cell movement via Apelin receptors". Science 343 (6172): 1248636. February 2014. doi:10.1126/science.1248636. PMID 24407481.
- ↑ "Ribosome profiling of mouse embryonic stem cells reveals the complexity and dynamics of mammalian proteomes". Cell 147 (4): 789–802. November 2011. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.10.002. PMID 22056041.
- ↑ 36.0 36.1 "Many lncRNAs, 5'UTRs, and pseudogenes are translated and some are likely to express functional proteins". eLife 4: e08890. December 2015. doi:10.7554/eLife.08890. PMID 26687005.
- ↑ "Ribosome profiling provides evidence that large noncoding RNAs do not encode proteins". Cell 154 (1): 240–251. July 2013. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.06.009. PMID 23810193.
- ↑ "Chromatin signature reveals over a thousand highly conserved large non-coding RNAs in mammals". Nature 458 (7235): 223–227. March 2009. doi:10.1038/nature07672. PMID 19182780. Bibcode: 2009Natur.458..223G.
- ↑ "Functionality or transcriptional noise? Evidence for selection within long noncoding RNAs". Genome Research 17 (5): 556–565. May 2007. doi:10.1101/gr.6036807. PMID 17387145.
- ↑ "Mutations within lncRNAs are effectively selected against in fruitfly but not in human". Genome Biology 14 (5): R49. May 2013. doi:10.1186/gb-2013-14-5-r49. PMID 23710818.
- ↑ "Evolutionary dynamics and tissue specificity of human long noncoding RNAs in six mammals". Genome Research 24 (4): 616–628. April 2014. doi:10.1101/gr.165035.113. PMID 24429298.
- ↑ "Rapid turnover of long noncoding RNAs and the evolution of gene expression". PLOS Genetics 8 (7): e1002841. 2012. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1002841. PMID 22844254.
- ↑ "Waste not, want not—transcript excess in multicellular eukaryotes". Trends in Genetics 21 (5): 287–288. May 2005. doi:10.1016/j.tig.2005.02.014. PMID 15851065.
- ↑ "Transcriptional noise and the fidelity of initiation by RNA polymerase II". Nature Structural & Molecular Biology 14 (2): 103–105. February 2007. doi:10.1038/nsmb0207-103. PMID 17277804.
- ↑ 45.0 45.1 "Non-coding RNA: what is functional and what is junk?". Frontiers in Genetics 6: 2. 2015-01-26. doi:10.3389/fgene.2015.00002. PMID 25674102.
- ↑ "Volatile evolution of long noncoding RNA repertoires: mechanisms and biological implications". Trends in Genetics 30 (10): 439–452. October 2014. doi:10.1016/j.tig.2014.08.004. PMID 25218058.
- ↑ "Evolutionary analysis across mammals reveals distinct classes of long non-coding RNAs". Genome Biology 17: 19. February 2016. doi:10.1186/s13059-016-0880-9. PMID 26838501.
- ↑ "Evolution to the rescue: using comparative genomics to understand long non-coding RNAs". Nature Reviews Genetics 17 (10): 601–614. October 2016. doi:10.1038/nrg.2016.85. PMID 27573374.
- ↑ "Principles of long noncoding RNA evolution derived from direct comparison of transcriptomes in 17 species". Cell Reports 11 (7): 1110–1122. May 2015. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2015.04.023. PMID 25959816.
- ↑ "Evolutionary conservation of long non-coding RNAs; sequence, structure, function". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - General Subjects 1840 (3): 1063–1071. March 2014. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.10.035. PMID 24184936.
- ↑ "A statistical test for conserved RNA structure shows lack of evidence for structure in lncRNAs". Nature Methods 14 (1): 45–48. January 2017. doi:10.1038/nmeth.4066. PMID 27819659.
- ↑ "Long non-coding RNAs: insights into functions". Nature Reviews Genetics 10 (3): 155–159. March 2009. doi:10.1038/nrg2521. PMID 19188922.
- ↑ "Pervasive transcription of the eukaryotic genome: functional indices and conceptual implications". Briefings in Functional Genomics & Proteomics 8 (6): 407–423. November 2009. doi:10.1093/bfgp/elp038. PMID 19770204.
- ↑ "Genome-Wide Analysis of Human Long Noncoding RNAs: A Provocative Review". Annual Review of Genomics and Human Genetics 23: 153-172. 2022. doi:10.1146/annurev-genom-112921-123710.
- ↑ "lncRNAdb: a reference database for long noncoding RNAs". Nucleic Acids Research 39 (Database issue): D146–51. January 2011. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq1138. PMID 21112873.
- ↑ "lncRNAdb v2.0: expanding the reference database for functional long noncoding RNAs". Nucleic Acids Research 43 (Database issue): D168–73. January 2015. doi:10.1093/nar/gku988. PMID 25332394.
- ↑ 57.0 57.1 Liu, Lin; Li, Zhao; Liu, Chang; Zou, Dong; Li, Qianpeng; Feng, Changrui; Jing, Wei; Luo, Sicheng et al. (2022-01-07). "LncRNAWiki 2.0: a knowledgebase of human long non-coding RNAs with enhanced curation model and database system". Nucleic Acids Research 50 (D1): D190–D195. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab998. ISSN 1362-4962. PMID 34751395.
- ↑ "Translation of small open reading frames within unannotated RNA transcripts in Saccharomyces cerevisiae". Cell Reports 7 (6): 1858–1866. June 2014. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2014.05.023. PMID 24931603.
- ↑ 59.0 59.1 "Non-coding-RNA regulators of RNA polymerase II transcription". Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 7 (8): 612–616. August 2006. doi:10.1038/nrm1946. PMID 16723972.
- ↑ 60.0 60.1 "The Evf-2 noncoding RNA is transcribed from the Dlx-5/6 ultraconserved region and functions as a Dlx-2 transcriptional coactivator". Genes & Development 20 (11): 1470–1484. June 2006. doi:10.1101/gad.1416106. PMID 16705037.
- ↑ "Developmental functions of the Distal-less/Dlx homeobox genes". Development 129 (19): 4371–4386. October 2002. doi:10.1242/dev.129.19.4371. PMID 12223397. http://dev.biologists.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=12223397.
- ↑ "In vivo enhancer analysis of human conserved non-coding sequences". Nature 444 (7118): 499–502. November 2006. doi:10.1038/nature05295. PMID 17086198. Bibcode: 2006Natur.444..499P. https://digital.library.unt.edu/ark:/67531/metadc895300/.
- ↑ "Ultraconservation identifies a small subset of extremely constrained developmental enhancers". Nature Genetics 40 (2): 158–160. February 2008. doi:10.1038/ng.2007.55. PMID 18176564.
- ↑ "Cloning of the mRNA of overexpression in colon carcinoma-1: a sequence overexpressed in a subset of colon carcinomas". Cancer Genetics and Cytogenetics 133 (1): 55–60. February 2002. doi:10.1016/S0165-4608(01)00634-3. PMID 11890990.
- ↑ 65.0 65.1 65.2 "Ultraconserved regions encoding ncRNAs are altered in human leukemias and carcinomas". Cancer Cell 12 (3): 215–229. September 2007. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2007.07.027. PMID 17785203.
- ↑ "Divergent lncRNAs Regulate Gene Expression and Lineage Differentiation in Pluripotent Cells". Cell Stem Cell 18 (5): 637–652. May 2016. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2016.01.024. PMID 26996597.
- ↑ Laure D Bernard, Agnès Dubois, Victor Heurtier, Véronique Fischer, Inma Gonzalez, Almira Chervova, Alexandra Tachtsidi, Noa Gil, Nick Owens, Lawrence E Bates, Sandrine Vandormael-Pournin, José C R Silva, Igor Ulitsky, Michel Cohen-Tannoudji, Pablo Navarro, OCT4 activates a Suv39h1-repressive antisense lncRNA to couple histone H3 Lysine 9 methylation to pluripotency, Nucleic Acids Research, Volume 50, Issue 13, 22 July 2022, Pages 7367–7379, https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac550
- ↑ "Induced ncRNAs allosterically modify RNA-binding proteins in cis to inhibit transcription". Nature 454 (7200): 126–130. July 2008. doi:10.1038/nature06992. PMID 18509338. Bibcode: 2008Natur.454..126W.
- ↑ "Non-coding RNA: More uses for genomic junk". Nature 543 (7644): 183–185. March 2017. doi:10.1038/543183a. PMID 28277509. Bibcode: 2017Natur.543..183A.
- ↑ "Regulation of the apolipoprotein gene cluster by a long noncoding RNA". Cell Reports 6 (1): 222–230. January 2014. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2013.12.015. PMID 24388749.
- ↑ "Female-biased expression of long non-coding RNAs in domains that escape X-inactivation in mouse". BMC Genomics 11: 614. November 2010. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-11-614. PMID 21047393.
- ↑ "Repression of the human dihydrofolate reductase gene by a non-coding interfering transcript". Nature 445 (7128): 666–670. February 2007. doi:10.1038/nature05519. PMID 17237763.
- ↑ "A monoclonal antibody to triplex DNA binds to eucaryotic chromosomes". Nucleic Acids Research 15 (3): 1047–1061. February 1987. doi:10.1093/nar/15.3.1047. PMID 2434928.
- ↑ 74.0 74.1 "U1 snRNA associates with TFIIH and regulates transcriptional initiation". Nature Structural Biology 9 (11): 800–805. November 2002. doi:10.1038/nsb862. PMID 12389039.
- ↑ "Specific double-stranded RNA interference in undifferentiated mouse embryonic stem cells". Molecular and Cellular Biology 21 (22): 7807–7816. November 2001. doi:10.1128/MCB.21.22.7807-7816.2001. PMID 11604515.
- ↑ "Inhibition of P-TEFb (CDK9/Cyclin T) kinase and RNA polymerase II transcription by the coordinated actions of HEXIM1 and 7SK snRNA". Molecular Cell 12 (4): 971–982. October 2003. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(03)00388-5. PMID 14580347.
- ↑ "Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome". Nature 409 (6822): 860–921. February 2001. doi:10.1038/35057062. PMID 11237011. Bibcode: 2001Natur.409..860L.
- ↑ "Initial sequencing and comparative analysis of the mouse genome". Nature 420 (6915): 520–562. December 2002. doi:10.1038/nature01262. PMID 12466850. Bibcode: 2002Natur.420..520W.
- ↑ "Cell stress and translational inhibitors transiently increase the abundance of mammalian SINE transcripts". Nucleic Acids Research 23 (10): 1758–1765. May 1995. doi:10.1093/nar/23.10.1758. PMID 7784180.
- ↑ 80.0 80.1 "Evolution of microRNA genes by inverted duplication of target gene sequences in Arabidopsis thaliana". Nature Genetics 36 (12): 1282–1290. December 2004. doi:10.1038/ng1478. PMID 15565108.
- ↑ 81.0 81.1 "B2 RNA binds directly to RNA polymerase II to repress transcript synthesis". Nature Structural & Molecular Biology 11 (9): 822–829. September 2004. doi:10.1038/nsmb812. PMID 15300239.
- ↑ "Characterization of the structure, function, and mechanism of B2 RNA, an ncRNA repressor of RNA polymerase II transcription". RNA 13 (4): 583–596. April 2007. doi:10.1261/rna.310307. PMID 17307818.
- ↑ 83.0 83.1 83.2 83.3 83.4 83.5 "Human Alu RNA is a modular transacting repressor of mRNA transcription during heat shock". Molecular Cell 29 (4): 499–509. February 2008. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2007.12.013. PMID 18313387.
- ↑ "Modular RNA heats up". Molecular Cell 29 (4): 415–417. February 2008. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2008.02.001. PMID 18313380.
- ↑ "Challenging the dogma: the hidden layer of non-protein-coding RNAs in complex organisms". BioEssays 25 (10): 930–939. October 2003. doi:10.1002/bies.10332. PMID 14505360.
- ↑ "Kcnq1ot1/Lit1 noncoding RNA mediates transcriptional silencing by targeting to the perinucleolar region". Molecular and Cellular Biology 28 (11): 3713–3728. June 2008. doi:10.1128/MCB.02263-07. PMID 18299392.
- ↑ "Chromosomal silencing and localization are mediated by different domains of Xist RNA". Nature Genetics 30 (2): 167–174. February 2002. doi:10.1038/ng820. PMID 11780141.
- ↑ "Identification of new Xlsirt family members in the Xenopus laevis oocyte". Mechanisms of Development 120 (4): 503–509. April 2003. doi:10.1016/S0925-4773(02)00459-8. PMID 12676327.
- ↑ "Expression of enhanced levels of small RNA polymerase III transcripts encoded by the B2 repeats in simian virus 40-transformed mouse cells". Nature 314 (6011): 553–556. 1985. doi:10.1038/314553a0. PMID 2581137. Bibcode: 1985Natur.314..553S.
- ↑ "Increased level of polymerase III transcribed Alu RNA in hepatocellular carcinoma tissue". Molecular Carcinogenesis 42 (2): 93–96. February 2005. doi:10.1002/mc.20057. PMID 15593371.
- ↑ 91.0 91.1 "Gene control by large noncoding RNAs". Science's STKE 2006 (355): pe40. October 2006. doi:10.1126/stke.3552006pe40. PMID 17018852.
- ↑ 92.0 92.1 "The expanding RNA polymerase III transcriptome". Trends in Genetics 23 (12): 614–622. December 2007. doi:10.1016/j.tig.2007.09.001. PMID 17977614.
- ↑ "Molecular basis of RNA recognition by the embryonic polarity determinant MEX-5". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 282 (12): 8883–8894. March 2007. doi:10.1074/jbc.M700079200. PMID 17264081.
- ↑ "Posttranscriptional gene regulation by long noncoding RNA". The Journal of Molecular Biology 425 (19): 3723–3730. October 2013. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2012.11.024. PMID 23178169.
- ↑ 95.0 95.1 "A natural antisense transcript regulates Zeb2/Sip1 gene expression during Snail1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition". Genes & Development 22 (6): 756–769. March 2008. doi:10.1101/gad.455708. PMID 18347095.
- ↑ "Inhibition of c-erbA mRNA splicing by a naturally occurring antisense RNA". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 266 (33): 22083–22086. November 1991. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)54535-X. PMID 1657988. http://www.jbc.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=1657988.
- ↑ "Primary structure, neural-specific expression, and dendritic location of human BC200 RNA". The Journal of Neuroscience 13 (6): 2382–2390. June 1993. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-06-02382.1993. PMID 7684772.
- ↑ "Dendritic location of neural BC1 RNA". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 88 (6): 2093–2097. March 1991. doi:10.1073/pnas.88.6.2093. PMID 1706516. Bibcode: 1991PNAS...88.2093T.
- ↑ "Activity-dependent regulation of dendritic BC1 RNA in hippocampal neurons in culture". The Journal of Cell Biology 141 (7): 1601–1611. June 1998. doi:10.1083/jcb.141.7.1601. PMID 9647652.
- ↑ "Dendritic BC1 RNA in translational control mechanisms". The Journal of Cell Biology 171 (5): 811–821. December 2005. doi:10.1083/jcb.200506006. PMID 16330711.
- ↑ "The brain cytoplasmic RNA BC1 regulates dopamine D2 receptor-mediated transmission in the striatum". The Journal of Neuroscience 27 (33): 8885–8892. August 2007. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0548-07.2007. PMID 17699670.
- ↑ "Role of a neuronal small non-messenger RNA: behavioural alterations in BC1 RNA-deleted mice". Behavioural Brain Research 154 (1): 273–289. September 2004. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2004.02.015. PMID 15302134.
- ↑ "An inside job for siRNAs". Molecular Cell 31 (3): 309–312. August 2008. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2008.07.008. PMID 18691963.
- ↑ "An endogenous small interfering RNA pathway in Drosophila". Nature 453 (7196): 798–802. June 2008. doi:10.1038/nature07007. PMID 18463631. Bibcode: 2008Natur.453..798C.
- ↑ 105.0 105.1 "Intersection of the RNA interference and X-inactivation pathways". Science 320 (5881): 1336–1341. June 2008. doi:10.1126/science.1157676. PMID 18535243. Bibcode: 2008Sci...320.1336O.
- ↑ "Epigenetics in development". Developmental Dynamics 236 (4): 1144–1156. April 2007. doi:10.1002/dvdy.21094. PMID 17304537.
- ↑ 107.0 107.1 "Genome-wide maps of chromatin state in pluripotent and lineage-committed cells". Nature 448 (7153): 553–560. August 2007. doi:10.1038/nature06008. PMID 17603471. Bibcode: 2007Natur.448..553M.
- ↑ "Chromatin architecture and nuclear RNA". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 86 (1): 177–181. January 1989. doi:10.1073/pnas.86.1.177. PMID 2911567. Bibcode: 1989PNAS...86..177N.
- ↑ "RNA is an integral component of chromatin that contributes to its structural organization". PLOS ONE 2 (11): e1182. November 2007. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0001182. PMID 18000552. Bibcode: 2007PLoSO...2.1182R.
- ↑ "Integration of external signaling pathways with the core transcriptional network in embryonic stem cells". Cell 133 (6): 1106–1117. June 2008. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.04.043. PMID 18555785.
- ↑ 111.0 111.1 111.2 "Functional demarcation of active and silent chromatin domains in human HOX loci by noncoding RNAs". Cell 129 (7): 1311–1323. June 2007. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.05.022. PMID 17604720.
- ↑ 112.0 112.1 "Noncoding RNAs of trithorax response elements recruit Drosophila Ash1 to Ultrabithorax". Science 311 (5764): 1118–1123. February 2006. doi:10.1126/science.1117705. PMID 16497925. Bibcode: 2006Sci...311.1118S.
- ↑ "Oplr16 serves as a novel chromatin factor to control stem cell fate by modulating pluripotency-specific chromosomal looping and TET2-mediated DNA demethylation". Nucleic Acids Research 48 (7): 3935–3948. 2020. doi:10.1093/nar/gkaa097. PMID 32055844.
- ↑ "Transcriptional interference: an unexpected layer of complexity in gene regulation". Journal of Cell Science 120 (Pt 16): 2755–2761. August 2007. doi:10.1242/jcs.007633. PMID 17690303.
- ↑ "Long non-coding RNA-polycomb intimate rendezvous". Open Biology 10 (9): 200126. September 2020. doi:10.1098/rsob.200126. PMID 32898472.
- ↑ "Point mutations in the WD40 domain of Eed block its interaction with Ezh2". Molecular and Cellular Biology 18 (10): 5634–5642. October 1998. doi:10.1128/MCB.18.10.5634. PMID 9742080.
- ↑ "Antisense transcription in the mammalian transcriptome". Science 309 (5740): 1564–1566. September 2005. doi:10.1126/science.1112009. PMID 16141073. Bibcode: 2005Sci...309.1564R.
- ↑ 118.0 118.1 118.2 "Epigenetic silencing of tumour suppressor gene p15 by its antisense RNA". Nature 451 (7175): 202–206. January 2008. doi:10.1038/nature06468. PMID 18185590. Bibcode: 2008Natur.451..202Y.
- ↑ "Silencing by imprinted noncoding RNAs: is transcription the answer?". Trends in Genetics 23 (6): 284–292. June 2007. doi:10.1016/j.tig.2007.03.018. PMID 17445943.
- ↑ "The Air noncoding RNA: an imprinted cis-silencing transcript". Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology 69: 55–66. 2004. doi:10.1101/sqb.2004.69.55. PMID 16117633.
- ↑ "LIT1, an imprinted antisense RNA in the human KvLQT1 locus identified by screening for differentially expressed transcripts using monochromosomal hybrids". Human Molecular Genetics 8 (7): 1209–1217. July 1999. doi:10.1093/hmg/8.7.1209. PMID 10369866.
- ↑ "Elongation of the Kcnq1ot1 transcript is required for genomic imprinting of neighboring genes". Genes & Development 20 (10): 1268–1282. May 2006. doi:10.1101/gad.1416906. PMID 16702402.
- ↑ 123.0 123.1 "Imprinting along the Kcnq1 domain on mouse chromosome 7 involves repressive histone methylation and recruitment of Polycomb group complexes". Nature Genetics 36 (12): 1296–1300. December 2004. doi:10.1038/ng1467. PMID 15516932.
- ↑ "The non-coding Air RNA is required for silencing autosomal imprinted genes". Nature 415 (6873): 810–813. February 2002. doi:10.1038/415810a. PMID 11845212. Bibcode: 2002Natur.415..810S.
- ↑ "Bidirectional action of the Igf2r imprint control element on upstream and downstream imprinted genes". Genes & Development 15 (18): 2361–2366. September 2001. doi:10.1101/gad.206201. PMID 11562346.
- ↑ "Allele-specific histone lysine methylation marks regulatory regions at imprinted mouse genes". The EMBO Journal 21 (23): 6560–6570. December 2002. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdf655. PMID 12456662.
- ↑ 127.0 127.1 "X inactivation Xplained". Current Opinion in Genetics & Development 17 (5): 387–393. October 2007. doi:10.1016/j.gde.2007.08.001. PMID 17869504.
- ↑ "The region 3′ to Xist mediates X chromosome counting and H3 Lys-4 dimethylation within the Xist gene". The EMBO Journal 23 (3): 594–604. February 2004. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600071. PMID 14749728.
- ↑ "Histone macroH2A1 is concentrated in the inactive X chromosome of female mammals". Nature 393 (6685): 599–601. June 1998. doi:10.1038/31275. PMID 9634239. Bibcode: 1998Natur.393..599C.
- ↑ "Telomere length, stem cells and aging". Nature Chemical Biology 3 (10): 640–649. October 2007. doi:10.1038/nchembio.2007.38. PMID 17876321.
- ↑ 131.0 131.1 "Developmentally regulated transcription of mammalian telomeres by DNA-dependent RNA polymerase II". Nature Cell Biology 10 (2): 228–236. February 2008. doi:10.1038/ncb1685. PMID 18157120.
- ↑ 132.0 132.1 "Telomeric repeat containing RNA and RNA surveillance factors at mammalian chromosome ends". Science 318 (5851): 798–801. November 2007. doi:10.1126/science.1147182. PMID 17916692. Bibcode: 2007Sci...318..798A.
- ↑ "Asynchronous replication, mono-allelic expression, and long range Cis-effects of ASAR6". PLOS Genetics 9 (4): e1003423. April 2013. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1003423. PMID 23593023.
- ↑ "ASAR15, A cis-acting locus that controls chromosome-wide replication timing and stability of human chromosome 15". PLOS Genetics 11 (1): e1004923. January 2015. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1004923. PMID 25569254.
- ↑ "Reciprocal monoallelic expression of ASAR lncRNA genes controls replication timing of human chromosome 6". RNA 26 (6): 724–738. June 2020. doi:10.1261/rna.073114.119. PMID 32144193.
- ↑ "The Role of RNA in DNA Breaks, Repair and Chromosomal Rearrangements". Biomolecules 11 (4): 550. April 2021. doi:10.3390/biom11040550. PMID 33918762.
- ↑ "LncBook: a curated knowledgebase of human long non-coding RNAs". Nucleic Acids Research 47 (Database issue): D128–D134. Jan 2019. doi:10.1093/nar/gky960. PMID 30329098.
- ↑ "BC200 RNA in normal human neocortex, non-Alzheimer dementia (NAD), and senile dementia of the Alzheimer type (AD)". Neurochemical Research 17 (6): 591–597. June 1992. doi:10.1007/bf00968788. PMID 1603265.
- ↑ "Primate brain-specific cytoplasmic transcript of the Alu repeat family". Molecular and Cellular Biology 7 (9): 3324–3327. September 1987. doi:10.1128/MCB.7.9.3324. PMID 2444875.
- ↑ 140.0 140.1 "Regulation of apoptosis by a prostate-specific and prostate cancer-associated noncoding gene, PCGEM1". DNA and Cell Biology 25 (3): 135–141. March 2006. doi:10.1089/dna.2006.25.135. PMID 16569192.
- ↑ "PRNCR1: a long non-coding RNA with a pivotal oncogenic role in cancer". Human Genetics 141 (1): 15–29. January 2022. doi:10.1007/s00439-021-02396-8. PMID 34727260.
- ↑ "Long noncoding RNAs in patients with acute myocardial infarction". Circulation Research 115 (7): 668–677. September 2014. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.303836. PMID 25035150.
- ↑ "Identification and regulation of the long non-coding RNA Heat2 in heart failure". Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology 126: 13–22. January 2019. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2018.11.004. PMID 30445017.
- ↑ "A large noncoding RNA is a marker for murine hepatocellular carcinomas and a spectrum of human carcinomas". Oncogene 26 (6): 851–858. February 2007. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209846. PMID 16878148.
- ↑ "Antisense intronic non-coding RNA levels correlate to the degree of tumor differentiation in prostate cancer". Oncogene 23 (39): 6684–6692. August 2004. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1207880. PMID 15221013.
- ↑ "Accumulation of miR-155 and BIC RNA in human B cell lymphomas". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 102 (10): 3627–3632. March 2005. doi:10.1073/pnas.0500613102. PMID 15738415. Bibcode: 2005PNAS..102.3627E.
- ↑ "Expression of the putative proto-oncogene His-1 in normal and neoplastic tissues". The American Journal of Pathology 150 (4): 1297–1305. April 1997. PMID 9094986.
- ↑ "Identification and characterization of a novel, psoriasis susceptibility-related noncoding RNA gene, PRINS". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 280 (25): 24159–24167. June 2005. doi:10.1074/jbc.M501704200. PMID 15855153. http://doktori.bibl.u-szeged.hu/312/1/2005_sonkoly_eniko.pdf.
- ↑ "Identification of a novel non-coding RNA, MIAT, that confers risk of myocardial infarction". Journal of Human Genetics 51 (12): 1087–1099. 2006. doi:10.1007/s10038-006-0070-9. PMID 17066261.
- ↑ "A common allele on chromosome 9 associated with coronary heart disease". Science 316 (5830): 1488–1491. June 2007. doi:10.1126/science.1142447. PMID 17478681. Bibcode: 2007Sci...316.1488M.
- ↑ "Characterization of a germ-line deletion, including the entire INK4/ARF locus, in a melanoma-neural system tumor family: identification of ANRIL, an antisense noncoding RNA whose expression coclusters with ARF". Cancer Research 67 (8): 3963–3969. April 2007. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-2004. PMID 17440112.
- ↑ "Susceptibility to coronary artery disease and diabetes is encoded by distinct, tightly linked SNPs in the ANRIL locus on chromosome 9p". Human Molecular Genetics 17 (6): 806–814. March 2008. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddm352. PMID 18048406.
- ↑ 153.0 153.1 "Functional analysis of the chromosome 9p21.3 coronary artery disease risk locus". Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 29 (10): 1671–1677. October 2009. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.189522. PMID 19592466.
- ↑ "INK4/ARF transcript expression is associated with chromosome 9p21 variants linked to atherosclerosis". PLOS ONE 4 (4): e5027. April 2009. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0005027. PMID 19343170. Bibcode: 2009PLoSO...4.5027L.
- ↑ "SNPs in the promoter of a B cell-specific antisense transcript, SAS-ZFAT, determine susceptibility to autoimmune thyroid disease". Human Molecular Genetics 13 (19): 2221–2231. October 2004. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddh245. PMID 15294872.
- ↑ "Expression of a noncoding RNA is elevated in Alzheimer's disease and drives rapid feed-forward regulation of beta-secretase". Nature Medicine 14 (7): 723–730. July 2008. doi:10.1038/nm1784. PMID 18587408.
- ↑ "Transcription of antisense RNA leading to gene silencing and methylation as a novel cause of human genetic disease". Nature Genetics 34 (2): 157–165. June 2003. doi:10.1038/ng1157. PMID 12730694.
- ↑ "Long noncoding RNAs are involved in multiple immunological pathways in response to vaccination". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 116 (34): 17121–17126. August 2019. doi:10.1073/pnas.1822046116. PMID 31399544.
 |
