Chemistry:Dysprosium(II) iodide
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| DyI2 | |
| Molar mass | 416.309 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | dark purple-black solid[1] |
| Melting point | 659 °C[1] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P264+265Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P319Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P321, P332+317Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P337+317Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P362+364Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
dysprosium(II) chloride dysprosium(II) bromide |
Related compounds
|
dysprosium(III) iodide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Dysprosium(II) iodide is an iodide of dysprosium with the chemical formula DyI2.
Preparation
Dysprosium(II) iodide can be produced by reducing dysprosium(III) iodide with metallic dysprosium under a vacuum at 800 to 900 °C:[1]
- Dy + 2 DyI
3 → 3 DyI
2
It can also be formed by the reaction of dysprosium and mercury(II) iodide:[1]
- Dy + HgI
2 → DyI
2 + Hg
It can also be formed by the direct reaction of dysprosium and iodine.[3]
- Dy + I
2 → DyI
2
Properties
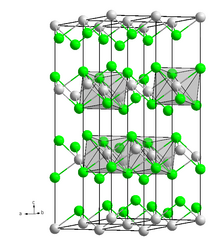
Dysprosium(II) iodide is a dark purple-black solid that is easily deliquescent and can only be stored in a dry inert gas or a vacuum. In the air, it will absorb moisture and become a hydrate, but they are unstable and will quickly convert into iodide oxides and release hydrogen gas. This process occurs faster in the presence of water. This compound has the same crystal structure as cadmium chloride.[1] It can form complexes with tetrahydrofuran, butanol and phenol.[3]
Uses
The reaction between dysprosium(II) iodide and silicon tetrachloride produces trichlorosilyl radicals, which can catalyze the trimerization of alkynes.[4][5]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Handbuch der präparativen anorganischen Chemie. 1 (3., umgearb. Aufl ed.). Stuttgart: Enke. 1975. ISBN 978-3-432-02328-1.
- ↑ "Dysprosium(II) iodide" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/71431174#section=Safety-and-Hazards.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Karl A. Jr. Gschneidner, Jean-Claude Bunzli, Vitalij K. Pecharsky (2009). Handbook on the Physics and Chemistry of Rare Earths. Elsevier. p. 247. ISBN 978-008093257-6.
- ↑ Sigma-Aldrich Co., product no. 652423.
- ↑ Zhu, Zhenyu; Wang, Chuanfeng; Xiang, Xu; Pi, Chengfu; Zhou, Xigeng (2006). "DyI2 initiated mild and highly selective silyl radical-catalyzed cyclotrimerization of terminal alkynes and polymerization of MMA". Chemical Communications (19): 2066–2068. doi:10.1039/b602883g. ISSN 1359-7345. PMID 16767277. http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/b602883g.
| HI | He | ||||||||||||||||
| LiI | BeI2 | BI3 | CI4 | NI3 | I2O4, I2O5, I4O9 |
IF, IF3, IF5, IF7 |
Ne | ||||||||||
| NaI | MgI2 | AlI3 | SiI4 | PI3, P2I4 |
S | ICl, ICl3 |
Ar | ||||||||||
| KI | CaI2 | Sc | TiI4 | VI3 | CrI3 | MnI2 | FeI2 | CoI2 | NiI2 | CuI | ZnI2 | Ga2I6 | GeI2, GeI4 |
AsI3 | Se | IBr | Kr |
| RbI | SrI2 | YI3 | ZrI4 | NbI5 | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | AgI | CdI2 | InI3 | SnI4, SnI2 |
SbI3 | TeI4 | I | Xe |
| CsI | BaI2 | HfI4 | TaI5 | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | AuI | Hg2I2, HgI2 |
TlI | PbI2 | BiI3 | Po | AtI | Rn | |
| Fr | RaI2 | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | |
| ↓ | |||||||||||||||||
| La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | SmI2 | Eu | Gd | TbI3 | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |||
| Ac | ThI4 | Pa | UI3, UI4 |
Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | EsI3 | Fm | Md | No | Lr | |||
 |

