Chemistry:Uranium(III) iodide
From HandWiki
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| UI3 | |
| Molar mass | 618.74232 g/mol |
| Appearance | black solid |
| Density | 6.78 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | 766[2] °C (1,411 °F; 1,039 K) |
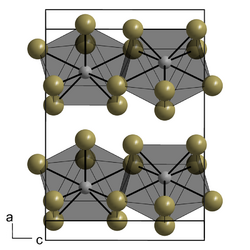
| Structure | |
| orthorhombic | |
| Ccmm, No. 63 | |
a = 432.8 pm, b = 1401.1 pm, c = 1000.5 pm
| |
Formula units (Z)
|
4 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |   
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H300, H330, H373, H411 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Uranium triiodide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula UI3. It is a black solid that is soluble in water.
Production
Uranium triiodide can be obtained from the direct reaction of its constituent elements:[3]
- 2 U + 3 I2 → 2 UI3
When the reaction is conducted in tetrahydrofuran (THF), the product is the blue complex UI3(THF)4.[4]
Properties
It crystallizes in the orthorhombic crystal system (plutonium tribromide-type) in the space group Ccmm with the lattice parameters a = 432.8 pm, b = 1401.1 pm, and c = 1000.5 pm and four formula units per unit cell.[1]
Uranium triiodide can be used as a Lewis acid catalyst for various Diels-Alder reactions carried out under mild conditions.[5]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Levy, J. H.; Taylor, J. C.; Wilson, P. W. (1975-03-01). "The structure of uranium(III) triiodide by neutron diffraction". Acta Crystallographica Section B Structural Crystallography and Crystal Chemistry 31 (3): 880–882. doi:10.1107/S0567740875003986. ISSN 0567-7408. https://scripts.iucr.org/cgi-bin/paper?S0567740875003986.
- ↑ Arnold F. Holleman, Nils Wiberg: Lehrbuch der Anorganischen Chemie, 102. Auflage, de Gruyter, Berlin 2007, ISBN:978-3-11-017770-1, S. 1969.
- ↑ Handbuch der präparativen anorganischen Chemie. 2 (3., umgearb. Aufl ed.). Stuttgart: Enke. 1978. ISBN 978-3-432-87813-3.
- ↑ David L. Clark; Alfred P. Sattelberger (1996). "Lewis Base Adducts of Uranium Triiodide and Tris[Bis(Trimethylsilyl)Amido]Uranium". Inorganic Syntheses. 31. 307–315. doi:10.1002/9780470132623.ch55. ISBN 978-0-470-13262-3.
- ↑ Collin, Jacqueline; Maria, Leonor; Santos, Isabel (Oct 2000). "Uranium iodides as catalysts for Diels–Alder reactions" (in en). Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical 160 (2): 263–267. doi:10.1016/S1381-1169(00)00257-0. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1381116900002570.
| HI | He | ||||||||||||||||
| LiI | BeI2 | BI3 | CI4 | NI3 | I2O4, I2O5, I4O9 |
IF, IF3, IF5, IF7 |
Ne | ||||||||||
| NaI | MgI2 | AlI3 | SiI4 | PI3, P2I4 |
S | ICl, ICl3 |
Ar | ||||||||||
| KI | CaI2 | Sc | TiI4 | VI3 | CrI3 | MnI2 | FeI2 | CoI2 | NiI2 | CuI | ZnI2 | Ga2I6 | GeI2, GeI4 |
AsI3 | Se | IBr | Kr |
| RbI | SrI2 | YI3 | ZrI4 | NbI5 | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | AgI | CdI2 | InI3 | SnI4, SnI2 |
SbI3 | TeI4 | I | Xe |
| CsI | BaI2 | HfI4 | TaI5 | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | AuI | Hg2I2, HgI2 |
TlI | PbI2 | BiI3 | Po | AtI | Rn | |
| Fr | RaI2 | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | |
| ↓ | |||||||||||||||||
| La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | SmI2 | Eu | Gd | TbI3 | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |||
| Ac | ThI4 | Pa | UI3, UI4 |
Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | EsI3 | Fm | Md | No | Lr | |||
 |

