Chemistry:Titanium tetraiodide
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Titanium(IV) iodide
| |
| Other names
Titanium tetraiodide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| TiI4 | |
| Molar mass | 555.485 g/mol |
| Appearance | red-brown crystals |
| Density | 4.3 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 150 °C (302 °F; 423 K) |
| Boiling point | 377 °C (711 °F; 650 K) |
| hydrolysis | |
| Solubility in other solvents | soluble in CH2Cl2 CHCl3 CS2 |
| Structure | |
| cubic (a = 12.21 Å) | |
| tetrahedral | |
| 0 D | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | violent hydrolysis corrosive |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H314 | |
| P260, P264, P280, P301+330+331, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P321, P363, P405, P501 | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Titanium(IV) bromide Titanium(IV) chloride Titanium(IV) fluoride |
Other cations
|
Silicon tetraiodide Zirconium(IV) iodide Hafnium(IV) iodide |
Related compounds
|
Titanium(III) iodide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Titanium tetraiodide is an inorganic compound with the formula TiI4. It is a black volatile solid, first reported by Rudolph Weber in 1863.[2] It is an intermediate in the van Arkel–de Boer process for the purification of titanium.
Physical properties
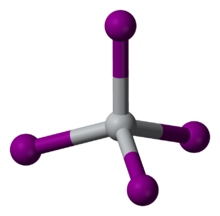
TiI4 is a rare molecular binary metal iodide, consisting of isolated molecules of tetrahedral Ti(IV) centers. The Ti-I distances are 261 pm.[3] Reflecting its molecular character, TiI4 can be distilled without decomposition at one atmosphere; this property is the basis of its use in the van Arkel–de Boer process. The difference in melting point between TiCl4 (m.p. -24 °C) and TiI4 (m.p. 150 °C) is comparable to the difference between the melting points of CCl4 (m.p. -23 °C) and CI4 (m.p. 168 °C), reflecting the stronger intermolecular van der Waals bonding in the iodides.
Two polymorphs of TiI4 exist, one of which is highly soluble in organic solvents. In the less soluble cubic form, the Ti-I distances are 261 pm.[3]
Production
Three methods are well known: 1) From the elements, typically using a tube furnace at 425 °C:[4]
- Ti + 2 I2 → TiI4
This reaction can be reversed to produce highly pure films of Ti metal.[5]
2) Exchange reaction from titanium tetrachloride and HI.
- TiCl4 + 4 HI → TiI4 + 4 HCl
3) Oxide-iodide exchange from aluminium iodide.
- 3 TiO2 + 4 AlI3 → 3 TiI4 + 2 Al2O3
Reactions
Like TiCl4 and TiBr4, TiI4 forms adducts with Lewis bases, and it can also be reduced. When the reduction is conducted in the presence of Ti metal, one obtains polymeric Ti(III) and Ti(II) derivatives such as CsTi2I7 and the chain CsTiI3, respectively.[6]
TiI4 exhibits extensive reactivity toward alkenes and alkynes resulting in organoiodine derivatives. It also effects pinacol couplings and other C-C bond-forming reactions.[7]
References
- ↑ "Titanium tetraiodide" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/111328#section=Safety-and-Hazards.
- ↑ Weber, R. (1863). "Ueber die isomeren Modificationen der Titansäure und über einige Titanverbindungen". Annalen der Physik 120 (10): 287–294. doi:10.1002/andp.18631961003. Bibcode: 1863AnP...196..287W. http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k15205n/f305.image.r=poggendorff.langFR.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Tornqvist, E. G. M.; Libby, W. F. (1979). "Crystal Structure, Solubility, and Electronic Spectrum of Titanium Tetraiodide". Inorganic Chemistry 18 (7): 1792–1796. doi:10.1021/ic50197a013.
- ↑ Lowry, R. N.; Fay, R. C. (1967). Titanium(IV) Iodide. Inorganic Syntheses. 10. pp. 1. doi:10.1002/9780470132418.ch1. ISBN 9780470132418.
- ↑ Blumenthal, W. B.; Smith, H. (1950). "Titanium tetraiodide, Preparation and Refining". Industrial and Engineering Chemistry 42 (2): 249. doi:10.1021/ie50482a016.
- ↑ Jongen, L.; Gloger, T.; Beekhuizen, J.; Meyer, G. (2005). "Divalent Titanium: The Halides ATiX3 (A = K, Rb, Cs; X = Cl, Br, I)". Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie 631 (2–3): 582. doi:10.1002/zaac.200400464.
- ↑ Shimizu, M.; Hachiya, I. (2014). "Chemoselective Reductions and Iodinations using Titanium Tetraiodide". Tetrahedron Letters 55 (17): 2781–2788. doi:10.1016/j.tetlet.2014.03.052.
| HI | He | ||||||||||||||||
| LiI | BeI2 | BI3 | CI4 | NI3 | I2O4, I2O5, I4O9 |
IF, IF3, IF5, IF7 |
Ne | ||||||||||
| NaI | MgI2 | AlI3 | SiI4 | PI3, P2I4 |
S | ICl, ICl3 |
Ar | ||||||||||
| KI | CaI2 | Sc | TiI4 | VI3 | CrI3 | MnI2 | FeI2 | CoI2 | NiI2 | CuI | ZnI2 | Ga2I6 | GeI2, GeI4 |
AsI3 | Se | IBr | Kr |
| RbI | SrI2 | YI3 | ZrI4 | NbI5 | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | AgI | CdI2 | InI3 | SnI4, SnI2 |
SbI3 | TeI4 | I | Xe |
| CsI | BaI2 | HfI4 | TaI5 | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | AuI | Hg2I2, HgI2 |
TlI | PbI2 | BiI3 | Po | AtI | Rn | |
| Fr | RaI2 | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | |
| ↓ | |||||||||||||||||
| La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | SmI2 | Eu | Gd | TbI3 | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |||
| Ac | ThI4 | Pa | UI3, UI4 |
Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | EsI3 | Fm | Md | No | Lr | |||
 |

