Biology:17β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
| 17β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 1.1.1.51 | ||||||||
| CAS number | 9015-81-0 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
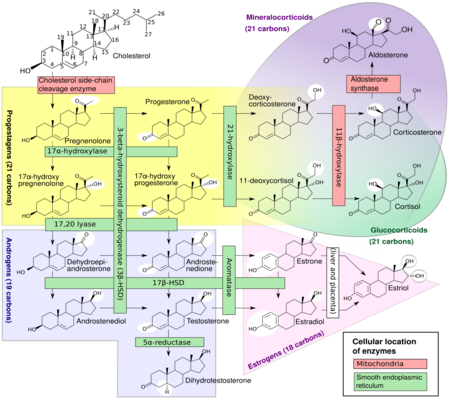
17β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases (17β-HSD, HSD17B) (EC 1.1.1.51), also 17-ketosteroid reductases (17-KSR), are a group of alcohol oxidoreductases which catalyze the reduction of 17-ketosteroids and the dehydrogenation of 17β-hydroxysteroids in steroidogenesis and steroid metabolism.[1][2][3][4][5] This includes interconversion of DHEA and androstenediol, androstenedione and testosterone, and estrone and estradiol.[6][7]
The major reactions catalyzed by 17β-HSD (e.g., the conversion of androstenedione to testosterone) are in fact hydrogenation (reduction) rather than dehydrogenation (oxidation) reactions.
Reactions
17β-HSDs have been known to catalyze the following redox reactions of sex steroids:
- 20α-Hydroxyprogesterone ↔ Progesterone
- DHEA ↔ Androstenediol
- Androstenedione ↔ Testosterone
- Dihydrotestosterone ↔ 5α-Androstanedione / 3α-Androstanediol / 3β-Androstanediol
- Estrone ↔ Estradiol
- 16α-Hydroxyestrone ↔ Estriol
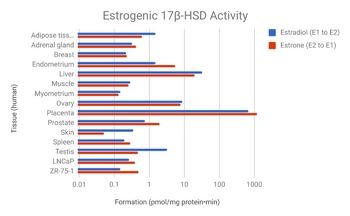
Activity distribution
Genes
Genes coding for 17β-HSD include:
- HSD17B1: Referred to as "estrogenic". Major subtype for activation of estrogens from weaker forms (estrone to estradiol and 16α-hydroxyestrone to estriol). Catalyzes the final step in the biosynthesis of estrogens. Highly selective for estrogens; 100-fold higher affinity for estranes over androstanes. However, also catalyzes the conversion of DHEA into androstenediol.[10] Recently, has been found to inactivate DHT into 3α- and 3β-androstanediol.[10][11] Expressed primarily in the ovaries and placenta but also at lower levels in the breast epithelium.[12][10] Major isoform of 17β-HSD in the granulosa cells of the ovaries.[13] Mutations and associated deficiency have not been reported in humans.[14] Knockout mice show altered ovarian sex steroid production, normal puberty, and severe subfertility due to defective luteinization and ovarian progesterone production.[15]
- HSD17B2: Describable as "antiestrogenic" and "antiandrogenic".[16] Major subtype for inactivation of estrogens and androgens into weaker forms (estradiol to estrone, testosterone to androstenedione, and androstenediol to DHEA). Also converts inactive 20α-hydroxyprogesterone into active progesterone. Preferential activity on androgens. Expressed widely in the body including in the liver, intestines, lungs, pancreas, kidneys, endometrium, prostate, breast epithelium, placenta, and bone.[10][17][12] Said to be responsible for 17β-HSD activity in the endometrium and placenta.[18] Mutations and associated congenital deficiency have not been reported in humans.[14] However, local deficiency in expression of HSD17B2 has been associated with endometriosis.[19]
- HSD17B3: Referred to as "androgenic". Major subtype in males for activation of androgens from weaker forms (androstenedione to testosterone and DHEA to androstenediol). Also activates estrogens from weaker forms to a lesser extent (estrone to estradiol). This is essential for testicular but not ovarian production of testosterone. Not expressed in the ovaries, where another 17β-HSD subtype, likely HSD17B5, is expressed instead. Mutations are associated with 17β-HSD type III deficiency. Males with this condition have pseudohermaphroditism, while females are normal with normal androgen and estrogen levels.[17][12]
- HSD17B4: Also known as D-bifunctional protein (DBP). Involved in fatty acid β-oxidation and steroid metabolism (specifically estrone to estradiol, for instance in the uterus).[20] Mutations are associated with DBP deficiency and Perrault syndrome (ovarian dysgenesis and deafness).[20]
- HSD17B5: Also known as aldo-keto reductase 1C3 (AKR1C3). Has 3α-HSD and 20α-HSD activity in addition to 17β-HSD activity. Expressed in the adrenal cortex and may act as the "androgenic" 17β-HSD in ovarian thecal cells. Also expressed in the prostate gland, mammary gland, and Leydig cells.[12]
- HSD17B6: Has 3α-HSD activity and catalyzes conversion of the weak androgen androstanediol into the powerful androgen dihydrotestosterone in the prostate gland. Also involved into a backdoor pathway from 17α-hydroxyprogesterone to dihydrotestosterone by 3α-reduction of a metabolic intermediary, 17α-hydroxydihydroprogesterone, into another intermediary, 17α-hydroxyallopregnanolone.[21] May be involved in the pathophysiology of PCOS.[12]
- HSD17B7: Is involved in cholesterol metabolism but is also thought to activate estrogens (estrone to estradiol) and inactivate androgens (dihydrotestosterone to androstanediol).[12] Expressed in the ovaries, breasts, placenta, testes, prostate gland, and liver.[12]
- HSD17B8: Inactivates estradiol, testosterone, and dihydrotestosterone, though can also convert estrone into estradiol. Expressed in the ovaries, testes, liver, pancreas, kidneys, and other tissues.[22][23]
- HSD17B9: Also known as retinol dehydrogenase 5 (RDH5). Involved in retinoid metabolism.[24] Mutations are associated with fundus albipunctatus.[25]
- HSD17B10: Also known as 2-methyl-3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase (MHBD). Substrates include steroids, neurosteroids, fatty acids, bile acids, isoleucine, and xenobiotics.[26][27] Mutations are associated with 17β-HSD type X deficiency (also known as HSD10 disease or MHBD deficiency) and mental retardation, X-linked, syndromic 10 (MRXS10), which are characterized by neurodegeneration and mental retardation, respectively.[26][27]
- HSD17B11
- HSD17B12
- HSD17B13
- HSD17B14
At least 7 of the 14 isoforms of 17β-HSD are involved in interconversion of 17-ketosteroids and 17β-hydroxysteroids.[12]
Overview
| # | Gene name | Synonyms | Family | Size (AA) | Gene location | Cellular location | Substrate specificities | Preferred cofactor | Catalytic preference | Tissue distribution | Expression profile | Pathology |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | HSD17B1 | SDR | 328 | 17q21.2 | Cytosol | Estrogens | NADH, NADPH | Reduction | Ovary, endometrium, breast, brain, prostate, placenta | Strongly restricted | Breast cancer, prostate cancer, endometriosis | |
| 3 | HSD17B3 | SDR | 310 | 9q22.32 | ER | Androgens | NADPH | Reduction | Testis, ovary, blood, saliva, skin, adipose tissue, brain, bone | Strongly restricted | 17β-HSD3 deficiency, prostate cancer[32] | |
| 4 | HSD17B4 | DBP, MFP2 | SDR | 736 | 5q23.1 | PXS | Fatty acids, bile acids, estrogens, androgens | NAD+ | Oxidation | Liver, heart, prostate, testis, lung, skeletal muscle, kidney, pancreas, thymus, ovary, intestine, placenta, brain, spleen, colon, lymphocytes | Ubiquitous | DBP deficiency, Perrault syndrome, prostate cancer |
| 5 | AKR1C3 | HSD17B5, PGFS | AKR | 323 | 10p15.1 | Nucleus, cytosol | Androgens, progestogens, estrogens, prostaglandins | NADPH | Reduction | Prostate, mammary gland, liver, kidney, lung, heart, small intestine, colon, uterus, testis, brain, skeletal muscle, adipose tissue | Nearly ubiquitous | Breast cancer, prostate cancer |
| 6 | HSD17B6 | SDR | 317 | 12q13.3 | Endosomes | Retinoids, androgens, estrogens | NAD+ | Oxidation | Liver, testis, lung, spleen, brain, ovary, kidney, adrenal, prostate | Selectively distributed | ? | |
| 7 | HSD17B7 | SDR | 341 | 1q23.3 | PM, ER | Cholesterol, estrogens, androgens, progestogens | NADPH | Reduction | Ovary, corpus luteum, uterus, placenta, liver, breast, testis, brain, adrenal gland, small intestine, lung, thymus, prostate, adipose tissue, others | Widely distributed | Breast cancer | |
| 8 | HSD17B8 | SDR | 261 | 6p21.32 | MC | Fatty acids, estrogens, androgens | NAD+ | Oxidation | Prostate, placenta, kidney, brain, cerebellum, heart, lung, small intestine, ovary, testis, adrenal, stomach | Widely distributed | Polycystic kidney disease | |
| 9 | RDH5 | HSD17B9 | 318 | 12q13.2 | ER | Retinoids | NADH/NAD+ | Reduction / oxidation | Retina, liver, adipose tissue, blood, others | ? | Fundus albipunctatus | |
| 10 | HSD17B10 | MHBD | SDR | 261 | Xp11.2 | MC | Fatty acids, bile acids, estrogens, androgens, progestogens, corticosteroids | NAD+ | Oxidation | Liver, small intestine, colon, kidney, heart, brain, placenta, lung, ovary, testis, spleen, thymus, prostate, peripheral blood leukocytes | Nearly ubiquitous | 17β-HSD10 deficiency, MRXS10, Alzheimer's disease |
| 11 | HSD17B11 | SDR | 300 | 4q22.1 | ER, EP | Estrogens, androgens | NAD+ | Oxidation | Liver, pancreas, intestine, kidney, adrenal gland, heart, lung, testis, ovary, placenta, sebaceous gland | Nearly ubiquitous | ? | |
| 12 | HSD17B12 | SDR | 312 | 11p11.2 | ER | Fatty acids, estrogens, androgens | NADPH | Reduction | Heart, skeletal muscle, liver, kidney, adrenal gland, testis, placenta, cerebellum, pancreas, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, trachea, lung, thyroid, esophagus, prostate, aorta, urinary bladder, spleen, skin, brain, ovary, breast, uterus, vagina | Ubiquitous | ? | |
| 13 | HSD17B13 | SDR | 300 | 4q22.1 | ER, EP | ? | NAD+? | Oxidation? | Liver, bone marrow, lung, ovary, testis, kidney, skeletal muscle, brain, bladder, nasal epithelia | Strongly restricted | ? | |
| 14 | HSD17B14 | SDR | 270 | 19q13.33 | Cytosol | Estrogens, androgens, fatty acids | NAD+ | Oxidation | Liver, kidney, brain, gallbladder, breast, adrenal, placenta | Widely distributed | Breast cancer (prognostic) |
Clinical significance
Mutations in HSD17B3 are responsible for 17β-HSD type III deficiency.
Inhibitors of 17β-HSD type II are of interest for the potential treatment of osteoporosis.[33][34]
Some inhibitors of 17β-HSD type I have been identified, for example esters of cinnamic acid and various flavones (e.g. fisetin).[35]
See also
References
- ↑ "Anreicherung einer 17β-hydroxysteroid:NAD(P)-oxydoreduktase aus der Nebenniere der Ratte" (in German). Hoppe-Seyler's Zeitschrift für Physiologische Chemie 336: 63–8. 1964. doi:10.1515/bchm2.1964.336.1.63. PMID 14214322.
- ↑ "The conversion of progesterone to androgens by testes". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 232 (2): 1015–30. June 1958. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)77419-5. PMID 13549484.
- ↑ "Induction and purification of alpha- and beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 218 (2): 661–74. February 1956. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)65833-8. PMID 13295221.
- ↑ "3(17)beta-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase of Pseudomonas testosteroni. A convenient purification and demonstration of multiple molecular forms". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 252 (11): 3775–83. June 1977. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(17)40319-X. PMID 193845.
- ↑ "Purification and properties of a beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 205 (2): 823–37. December 1953. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)49226-5. PMID 13129261.
- ↑ "The key role of 17 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases in sex steroid biology". Steroids 62 (1): 148–58. January 1997. doi:10.1016/S0039-128X(96)00174-2. PMID 9029730.
- ↑ Brook, Charles G. D.; Truong, Daniel; Clayton, Peter; Carroll, William; Brown, Rosalind (2011). Brook's Clinical Pediatric Endocrinology. John Wiley & Sons. p. 288. ISBN 978-1-4443-1673-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=Y8nhO6D0k4cC&pg=PA288.
- ↑ "Distribution of 17 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase gene expression and activity in rat and human tissues". J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 41 (3–8): 597–603. March 1992. doi:10.1016/0960-0760(92)90390-5. PMID 1314080.
- ↑ Michael Oettel; Ekkehard Schillinger (6 December 2012). Estrogens and Antiestrogens I: Physiology and Mechanisms of Action of Estrogens and Antiestrogens. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 226. ISBN 978-3-642-58616-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=0BfrCAAAQBAJ&pg=PA226.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 "Estrogen and androgen-converting enzymes 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase and their involvement in cancer: with a special focus on 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1, 2, and breast cancer". Oncotarget 8 (18): 30552–30562. May 2017. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.15547. PMID 28430630.
- ↑ "17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 stimulates breast cancer by dihydrotestosterone inactivation in addition to estradiol production". Molecular Endocrinology 24 (4): 832–45. April 2010. doi:10.1210/me.2009-0468. PMID 20172961.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 12.4 12.5 12.6 12.7 Strauss, Jerome Frank; Barbieri, Robert L. (13 September 2013). Yen and Jaffe's Reproductive Endocrinology. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 82. ISBN 978-1-4557-2758-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=KZ95AAAAQBAJ&pg=PA82.
- ↑ "Physiology and molecular genetics of 17 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases". Steroids 62 (1): 143–7. January 1997. doi:10.1016/s0039-128x(96)00173-0. PMID 9029729.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Jameson, J. Larry (13 July 1998). Principles of Molecular Medicine. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 549. ISBN 978-1-59259-726-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=UhjyBwAAQBAJ&pg=PA549.
- ↑ "Hydroxysteroid (17β)-dehydrogenase 1-deficient female mice present with normal puberty onset but are severely subfertile due to a defect in luteinization and progesterone production". FASEB Journal 29 (9): 3806–16. September 2015. doi:10.1096/fj.14-269035. PMID 26018678.
- ↑ "High Expression of 17β-hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 2 is Associated with a Better Prognosis in Urothelial Carcinoma of the Urinary Tract". Journal of Cancer 7 (15): 2221–2230. 2016. doi:10.7150/jca.16777. PMID 27994658. "HSD17B2 has both anti-estrogenic and anti-androgenic functions.".
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 Melmed, Shlomo (2016). Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 904. ISBN 978-0-323-29738-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=YZ8_CwAAQBAJ&pg=PA904.
- ↑ Jameson, J. Larry; De Groot, Leslie J. (25 February 2015). Endocrinology: Adult and Pediatric E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 2078. ISBN 978-0-323-32195-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=xmLeBgAAQBAJ&pg=PA2078.
- ↑ "17Beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase-2 deficiency and progesterone resistance in endometriosis". Seminars in Reproductive Medicine 28 (1): 44–50. January 2010. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1242992. PMID 20108182.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 "Mutations in the DBP-deficiency protein HSD17B4 cause ovarian dysgenesis, hearing loss, and ataxia of Perrault Syndrome". American Journal of Human Genetics 87 (2): 282–8. August 2010. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.07.007. PMID 20673864.
- ↑ Masiutin, Maxim; Yadav, Maneesh (2023). "Alternative androgen pathways". WikiJournal of Medicine 10: X. doi:10.15347/WJM/2023.003.
- ↑ "Characterization of Ke 6, a new 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, and its expression in gonadal tissues". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 273 (35): 22664–71. August 1998. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.35.22664. PMID 9712896.
- ↑ "Physical mapping 220 kb centromeric of the human MHC and DNA sequence analysis of the 43-kb segment including the RING1, HKE6, and HKE4 genes". Genomics 42 (3): 422–35. June 1997. doi:10.1006/geno.1997.4745. PMID 9205114.
- ↑ "Structure and function of retinol dehydrogenases of the short chain dehydrogenase/reductase family". Molecular Aspects of Medicine 24 (6): 403–9. December 2003. doi:10.1016/s0098-2997(03)00036-0. PMID 14585311.
- ↑ "Fundus albipunctatus: review of the literature and report of a novel RDH5 gene mutation affecting the invariant tyrosine (p.Tyr175Phe)". Journal of Applied Genetics 56 (3): 317–27. August 2015. doi:10.1007/s13353-015-0281-x. PMID 25820994.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 "Hydroxysteroid (17β) dehydrogenase X in human health and disease". Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 343 (1–2): 1–6. 2011. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2011.06.011. PMID 21708223.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 "Roles of 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 10 in neurodegenerative disorders". J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 143: 460–72. 2014. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2014.07.001. PMID 25007702.
- ↑ Zhu, Yuan-Shan; Imperato-McGinley, Julianne L. (9 November 2016). "4.02: Disorders of Sexual Development in Males: Molecular Genetics, Epigenetics, Gender Identity, and Cognition". Hormones, Brain and Behavior. 4: Clinical Important Effects of Hormones on Brain and Behavior. Elsevier Science. pp. 69. ISBN 978-0-12-803608-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=NT8oCwAAQBAJ&pg=RA3-PA69.
- ↑ "Integrated view on 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases". Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 301 (1–2): 7–19. 2009. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2008.10.040. PMID 19027824.
- ↑ "The role of 17 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases". Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 218 (1–2): 7–20. 2004. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2003.12.006. PMID 15130507.
- ↑ "17β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases (17β-HSDs) as therapeutic targets: protein structures, functions, and recent progress in inhibitor development". J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 125 (1–2): 66–82. 2011. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2010.12.013. PMID 21193039.
- ↑ "Development of 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 3 as a target in hormone-dependent prostate cancer therapy". Steroids 121: 10–16. 2017. doi:10.1016/j.steroids.2017.02.003. PMID 28267564.
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedpmid26230882 - ↑ "Novel, potent and selective 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 inhibitors as potential therapeutics for osteoporosis with dual human and mouse activities". European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 83: 317–37. August 2014. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.06.036. PMID 24974351.
- ↑ "Flavonoids and cinnamic acid derivatives as inhibitors of 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1". Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology 301 (1–2): 229–34. March 2009. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2008.09.004. PMID 18835421. https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-00532074/document.
External links
- 3(or+17)beta-hydroxysteroid+dehydrogenase at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
 |