Biology:Aldosterone synthase
 Generic protein structure example |
Aldosterone synthase, also called steroid 18-hydroxylase, corticosterone 18-monooxygenase or P450C18, is a steroid hydroxylase cytochrome P450 enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of the mineralocorticoid aldosterone and other steroids. The enzyme catalyzes sequential hydroxylations of the steroid angular methyl group at C18 after initial 11β-hydroxylation (the enzyme has steroid 18-hydroxylase activity as well as steroid 11 beta-hydroxylase activity). It is encoded by the CYP11B2 gene in humans.
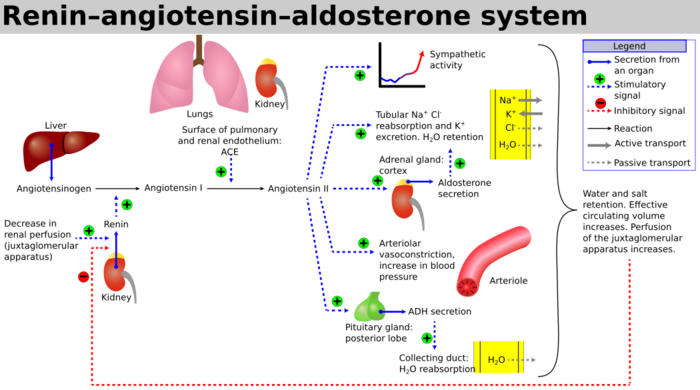
Aldosterone synthase is a protein which is only expressed in the zona glomerulosa[1] of the adrenal cortex and is primarily regulated by the renin–angiotensin system.[2] It is the sole enzyme capable of synthesizing aldosterone in humans and plays an important role in electrolyte balance and blood pressure.[3]
Genetics
Aldosterone synthase is encoded on chromosome 8q22[1] by the CYP11B2 gene.[1] The gene contains 9 exons and spans roughly 7000 base pairs of DNA.[1] CYP11B2 is closely related with CYP11B1. The two genes show 93% homology to each other and are both encoded on the same chromosome.[4] Research has shown that calcium ions activate transcription factors at CYP11B2 through well defined interactions at the 5'-flanking region of CYP11B2.[1]
Aldosterone synthase is a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes.[5] The cytochrome P450 proteins are monooxygenases that catalyze many reactions involved in drug metabolism and synthesis of cholesterol, steroids, and other lipids.
Function
Aldosterone synthase is the enzyme that has steroid 18-hydroxylase activity as well as steroid 11 beta-hydroxylase activity. The 18-hydroxylase activity consists in catalyzing sequential hydroxylations of the steroid angular methyl group at C18.
Whereas steroid 11β-hydroxylase (encoded by CYP11B1 gene) only catalyzes hydroxylation at position 11 beta (mainly of 11-deoxycorticosterone and 11-deoxycortisol), aldosterone synthase (encoded by CYP11B2 gene) catalyzes the synthesis of aldosterone from deoxycorticosterone, a process that successively requires hydroxylation at positions 11 beta and 18 and oxidation at position 18.[6]
Adrenocorticotropic hormone is assumed to play a role in the regulation of aldosterone synthase likely through stimulating the synthesis of 11-deoxycorticosterone which is the initial substrate of the enzymatic action in aldosterone synthase.[7]
Metabolism

Aldosterone synthase converts 11-deoxycorticosterone to corticosterone, to 18-hydroxycorticosterone, and finally to aldosterone:
-
11-deoxycorticosterone
-
18-hydroxycorticosterone
In human metabolism the biosynthesis of aldosterone largely depends on the metabolism of cholesterol. Cholesterol is metabolized in what is known as the early pathway of aldosterone synthesis[8] and is hydroxylated becoming (20R,22R)-dihydroxycholesterol which is then metabolized as a direct precursor to pregnenolone. Pregnenolone can then followed one of two pathways which involve the metabolism of progesterone or the testosterone and estradiol biosynthesis. Aldosterone is synthesized by following the metabolism of progesterone.
In the potential case where aldosterone synthase is not metabolically active the body accumulates 11-deoxycorticosterone. This increases salt retention leading to increased hypertension.[9]
Substrates
Aldosterone synthase shows different catalytic activity during metabolism of its substrates.[3] Here are some of the substrates, grouped by catalytic activity of the enzyme:
- strong:[3][10]
- 11-deoxycorticosterone to corticosterone[11] and aldosterone;[10]
- medium:[3][10]
- weak:[3][10]
- progesterone to 11β-hydroxyprogesterone,[10]
- testosterone to 18-hydroxytestosterone[14] and 11β-Hydroxytestosterone,[10]
- androstendione (to 11β-Hydroxyandrostendione[10] and 18-hydroxyandrostendione[verification needed]);
- very weak:[3]
- corticosterone,
- cortisol to 18-hydroxycortisol,[15]
- 18-Hydroxy-11-deoxycorticosterone,
- 21-hydroxypregnenolone.
Methyl oxidase deficiency
Lack of metabolically active aldosterone synthase leads to corticosterone methyl oxidase deficiency type I and II. The deficiency is characterized clinically by salt-wasting, failure to thrive, and growth retardation.[16] The in-active proteins are caused by the autosomal recessive inheritance of defective CYP11B2 genes in which genetic mutations destroy the enzymatic activity of aldosterone synthase.[16] Deficient aldosterone synthase activity results in impaired biosynthesis of aldosterone while corticosterone in the zona glomerulosa is excessively produced in both corticosterone methyl oxidase deficiency type I and II. The corticosterone methyl oxidase deficiencies both share this effect however type I causes an overall deficiency of 18-hydroxycorticosterone while type II overproduces it.[16]
Enzymatic inhibition
Inhibition of aldosterone synthase is currently being investigated as a medical treatment for hypertension, heart failure, and renal disorders.[17] Deactivation of enzymatic activity reduces aldosterone concentrations in plasma and tissues which decreases mineralocorticoid receptor-dependent and independent effects in cardiac vascular and renal target organs.[17] Inhibition has shown to decrease plasma and urinary aldosterone concentrations by 70 - 80%, rapid hypokalaemia correction, moderate decrease of blood pressure, and an increase plasma renin activity in patients who are on a low-sodium diet.[17] Ongoing medical research is focusing on the synthesis of second-generation aldosterone synthase inhibitors to create an ideally selective inhibitor as the current, orally delivered, LCl699 has shown to be non-specific to aldosterone synthase.[17]
See also
- Steroidogenic enzyme
- Hypoaldosteronism
- Glucocorticoid remediable aldosteronism
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 "The regulation of aldosterone synthase expression". Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology 217 (1–2): 67–74. March 2004. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2003.10.011. PMID 15134803.
- ↑ "Disorders of the aldosterone synthase and steroid 11beta-hydroxylase deficiencies". Hormone Research 51 (5): 211–22. 1999. doi:10.1159/000023374. PMID 10559665.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 "Structural insights into aldosterone synthase substrate specificity and targeted inhibition". Molecular Endocrinology 27 (2): 315–24. February 2013. doi:10.1210/me.2012-1287. PMID 23322723.
- ↑ "Characterization of two genes encoding human steroid 11 beta-hydroxylase (P-450(11) beta)". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 264 (35): 20961–7. December 1989. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)30030-4. PMID 2592361.
- ↑ "CYP11B2". http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/gene/CYP11B2.
- ↑ "Mutations in the human CYP11B2 (aldosterone synthase) gene causing corticosterone methyloxidase II deficiency". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 89 (11): 4996–5000. June 1992. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.11.4996. PMID 1594605. Bibcode: 1992PNAS...89.4996P.
- ↑ "Site of stimulation of aldosterone biosynthesis by angiotensin and potassium". The Journal of Clinical Investigation 51 (6): 1413–8. June 1972. doi:10.1172/JCI106937. PMID 4336939.
- ↑ "Aldosterone biosynthesis, regulation, and classical mechanism of action". Heart Failure Reviews 10 (1): 7–13. January 2005. doi:10.1007/s10741-005-2343-3. PMID 15947886.
- ↑ "CYP11B1". Genetics Home Reference. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Sep 2013. https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/gene/CYP11B1.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 10.6 10.7 "The in vitro metabolism of 11β-hydroxyprogesterone and 11-ketoprogesterone to 11-ketodihydrotestosterone in the backdoor pathway". The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 178: 203–212. April 2018. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2017.12.014. PMID 29277707.
- ↑ "The regulation of aldosterone synthase expression". Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology 217 (1–2): 67–74. March 2004. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2003.10.011. PMID 15134803.
- ↑ "DIAGNOSIS OF ENDOCRINE DISEASE: 18-Oxocortisol and 18-hydroxycortisol: is there clinical utility of these steroids?". European Journal of Endocrinology 178 (1): R1–R9. January 2018. doi:10.1530/EJE-17-0563. PMID 28904009.
- ↑ "Studies on the origin of circulating 18-hydroxycortisol and 18-oxocortisol in normal human subjects". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 89 (9): 4628–33. September 2004. doi:10.1210/jc.2004-0379. PMID 15356073.
- ↑ "Biosynthesis of 18-hydroxytestosterone in the human foetal liver". European Journal of Biochemistry 9 (3): 402–5. June 1969. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00622.x. PMID 4307594.
- ↑ "Expression of CYP11B2 in Aldosterone-Producing Adrenocortical Adenoma: Regulatory Mechanisms and Clinical Significance". The Tohoku Journal of Experimental Medicine 240 (3): 183–190. November 2016. doi:10.1620/tjem.240.183. PMID 27853054.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 "Hereditary defect in biosynthesis of aldosterone: aldosterone synthase deficiency 1964-1997". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 82 (11): 3525–8. November 1997. doi:10.1210/jcem.82.11.4399. PMID 9360501.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 17.3 "Aldosterone synthase inhibition in humans". Nephrology, Dialysis, Transplantation 28 (1): 36–43. January 2013. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfs388. PMID 23045428.
Further reading
- "Twin genes and endocrine disease: CYP21 and CYP11B genes". Acta Endocrinologica 129 (2): 97–108. August 1993. doi:10.1530/acta.0.1290097. PMID 8372604.
- "Extra-adrenal mineralocorticoids and cardiovascular tissue". Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology 31 (6): 1175–84. June 1999. doi:10.1006/jmcc.1999.0963. PMID 10371693.
- "Familial varieties of primary aldosteronism". Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology & Physiology 28 (12): 1087–90. December 2001. doi:10.1046/j.1440-1681.2001.03574.x. PMID 11903322.
- "Genetic basis of cardiovascular disease--the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system as a paradigm". Journal of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System 1 (4): 316–24. December 2000. doi:10.3317/jraas.2000.060. PMID 11967817.
- "Hereditary hypertension caused by chimaeric gene duplications and ectopic expression of aldosterone synthase". Nature Genetics 2 (1): 66–74. September 1992. doi:10.1038/ng0992-66. PMID 1303253.
- "Congenitally defective aldosterone biosynthesis in humans: the involvement of point mutations of the P-450C18 gene (CYP11B2) in CMO II deficient patients". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 182 (2): 974–9. January 1992. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(92)91827-D. PMID 1346492.
- "Glucocorticoid-suppressible hyperaldosteronism results from hybrid genes created by unequal crossovers between CYP11B1 and CYP11B2". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 89 (17): 8327–31. September 1992. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.17.8327. PMID 1518866. Bibcode: 1992PNAS...89.8327P.
- "Mutations in the human CYP11B2 (aldosterone synthase) gene causing corticosterone methyloxidase II deficiency". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 89 (11): 4996–5000. June 1992. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.11.4996. PMID 1594605. Bibcode: 1992PNAS...89.4996P.
- "Role of steroid 11 beta-hydroxylase and steroid 18-hydroxylase in the biosynthesis of glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids in humans". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 89 (4): 1458–62. February 1992. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.4.1458. PMID 1741400. Bibcode: 1992PNAS...89.1458K.
- "The product of the CYP11B2 gene is required for aldosterone biosynthesis in the human adrenal cortex". Molecular Endocrinology 5 (10): 1513–22. October 1991. doi:10.1210/mend-5-10-1513. PMID 1775135.
- "Cloning and expression of a cDNA for human cytochrome P-450aldo as related to primary aldosteronism". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 173 (1): 309–16. November 1990. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(05)81058-7. PMID 2256920.
- "Characterization of two genes encoding human steroid 11 beta-hydroxylase (P-450(11) beta)". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 264 (35): 20961–7. December 1989. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)30030-4. PMID 2592361.
- "[Reconstruction and study of a multi-enzyme system by 11 beta-hydroxylase steroids]". Biokhimiia 50 (2): 243–57. February 1985. PMID 3872685.
- "Inborn errors of aldosterone biosynthesis in humans". Steroids 60 (1): 15–21. January 1995. doi:10.1016/0039-128X(94)00023-6. PMID 7792802.
- "Congenitally defective aldosterone biosynthesis in humans: inactivation of the P-450C18 gene (CYP11B2) due to nucleotide deletion in CMO I deficient patients". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 190 (3): 864–9. February 1993. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1993.1128. PMID 8439335.
- "Genetic variation in P450c11AS in Chilean patients with low renin hypertension". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 81 (12): 4347–51. December 1996. doi:10.1210/jcem.81.12.8954040. PMID 8954040.
- "CMO I deficiency caused by a point mutation in exon 8 of the human CYP11B2 gene encoding steroid 18-hydroxylase (P450C18)". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 234 (2): 382–5. May 1997. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1997.6651. PMID 9177280.
- "Human CYP11B2 (aldosterone synthase) maps to chromosome 8q24.3". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 83 (3): 1033–6. March 1998. doi:10.1210/jc.83.3.1033. PMID 9506770.
External links
- Aldosterone+synthase at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Human CPN2 genome location and CPN2 gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
- Human CYP11B2 genome location and CYP11B2 gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
 |