Chemistry:Ditolylguanidine
From HandWiki
Short description: Experimental drug
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
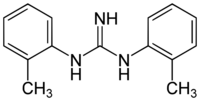
| Formula | C15H17N3 |
| Molar mass | 239.322 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Ditolylguanidine is a sigma receptor agonist.[1] It is somewhat[2] selective for sigma receptors, but non-selective between the two sigma receptor subtypes, binding to both σ1 and σ2 with equal affinity.[3] It has neuroprotective[4] and antidepressant effects,[5] and potentiates the effects of NMDA antagonists.[6]
See also
References
- ↑ "1,3-Di(2-[5-3Htolyl)guanidine: a selective ligand that labels sigma-type receptors for psychotomimetic opiates and antipsychotic drugs"]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 83 (22): 8784–8788. November 1986. doi:10.1073/pnas.83.22.8784. PMID 2877462. Bibcode: 1986PNAS...83.8784W.
- ↑ "1,3-Di-o-tolylguanidine | C15H17N3" (in en). PubChem. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/7333#section=BioAssay-Results.
- ↑ "Pharmacophore identification for sigma-1 (sigma1) receptor binding: application of the "deconstruction-reconstruction-elaboration" approach". Mini Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry 5 (10): 927–940. October 2005. doi:10.2174/138955705774329519. PMID 16250835.
- ↑ "Sigma-1 receptor activation prevents intracellular calcium dysregulation in cortical neurons during in vitro ischemia". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 319 (3): 1355–1365. December 2006. doi:10.1124/jpet.106.107557. PMID 16988055.
- ↑ "Sigma1 receptor antagonists attenuate antidepressant-like effect induced by co-administration of 1,3 di-o-tolylguanidine (DTG) and memantine in the forced swimming test in rats". Polish Journal of Pharmacology 55 (6): 1149–1152. 2003. PMID 14730114.
- ↑ "Protein kinase C-dependent potentiation of intracellular calcium influx by sigma1 receptor agonists in rat hippocampal neurons". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 307 (2): 705–712. November 2003. doi:10.1124/jpet.103.053447. PMID 12975497.
 |

