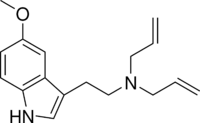
Chemistry:5-MeO-DALT
 | |
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H22N2O |
| Molar mass | 270.376 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
5-MeO-DALT or N,N-di allyl-5-methoxy tryptamine is a psychedelic tryptamine first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin.
Chemistry
The full name of the chemical is N-allyl-N-[2-(5-methoxy-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl] prop-2-en-1- amine. It is related to the compounds 5-MeO-DPT and DALT.
In April 2020, Chadeayne et al. solved the crystal structure of the freebase form of 5-MeO-DALT.[1]
Pharmacology
5-MeO-DALT binds to 5-HT1A, 5-HT1D, 5-HT1E, 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, 5-HT2C, 5-HT6, α2A, α2B, α2C, H1, κ-opioid, σ1 and σ2 receptors with Ki values lower than 10μM and also acts as a DAT and SERT monoamine reuptake inhibitor.[2]
| Binding site | pKi ± SEM at binding site |
| 5-HT1A | 7.70 ± 0.10 |
| 5-HT1B | 6.13 ± 0.04 |
| 5-HT1D | 7.00 ± 0.10 |
| 5-HT1E | 6.30 ± 0.05 |
| 5-HT2A | 6.66 ± 0.08 |
| 5-HT2B | 7.23 ± 0.05 |
| 5-HT2C | 6.34 ± 0.08 |
| 5-HT5A | 5.48 ± 0.04 |
| 5-HT6 | 6.81 ± 0.03 |
| 5-HT7 | 7.05 ± 0.07 |
| α2A | 6.67 ± 0.07 |
| α2B | 6.14 ± 0.04 |
| α2C | 5.83 ± 0.06 |
| H1 | 6.30 ± 0.06 |
| H3 | 5.77 ± 0.04 |
| κOR | 5.95 ± 0.07 |
| μOR | < 5.00 |
| σ1 | 6.52 ± 0.06 |
| σ2 | 6.60 ± 0.05 |
| DAT | 5.50 ± 0.20 |
| NET | < 5.00 |
| SERT | 6.30 ± 0.05 |
The metabolism and cytochrome P450 inhibition of 5-MeO-DALT has been described in scientific literature.[3][4]
History
The first material regarding the synthesis and effects of 5-MeO-DALT was sent from Alexander Shulgin to a research associate named Murple in May 2004, after which it was circulated online. In June 2004 5-MeO-DALT became available from internet research chemical vendors after being synthesized by commercial laboratories in China. In August 2004 the synthesis and effects of 5-MeO-DALT were published by Erowid.[5]
Dosage
Doses ranging from 12–20 mg were tested by Alexander Shulgin's research group.[6]
Therapeutic use
Numerous anecdotal reports[7] and a small-scale trial[8] indicate the potential of 5-MeO-DALT for the treatment of cluster headache, one of the most excruciating conditions known to medicine.[9] These observations are consistent with evidence of efficacy of other chemically-related indoleamines in the treatment of cluster headache.[10]
Side effects
There is no published literature on the toxicity of 5-MeO-DALT.
Legal Status
China
As of October 2015 5-MeO-DALT is a controlled substance in China.[11]
Japan
5-MeO-DALT became a controlled substance in Japan from April 2007, by amendment to the Pharmaceutical Affairs Law.[12]
United Kingdom
5-MeO-DALT became a Class A drug in the UK on January 7, 2015 after an update to the tryptamine blanket ban.
Singapore
5-MeO-DALT is listed in the Fifth Schedule of the Misuse of Drugs Act (MDA) and therefore illegal in Singapore as of May 2015.[13]
Sweden
Sveriges riksdag added 5-MeO-DALT to schedule I ("substances, plant materials and fungi which normally do not have medical use") as narcotics in Sweden as of May 1, 2012, published by Medical Products Agency in their regulation LVFS 2012:6 listed as 5-MeO-DALT N-allyl-N-[2-(5-metoxi-1H-indol-3-yl)etyl]-prop-2-en-1-amin.[14]
United States
5-MeO-DALT is not scheduled at the federal level in the United States ,[15] but it is likely that it could be considered an analog of 5-Meo-DiPT, which is a controlled substance in USA, or an analog of another tryptamine, in which case purchase, sale, or possession could be prosecuted under the Federal Analog Act.
Florida
5-MeO-DALT is a Schedule I controlled substance in the state of Florida making it illegal to buy, sell, or possess in Florida.[16]
Louisiana
5-MeO-DALT is a Schedule I controlled substance in the state of Louisiana making it illegal to buy, sell, or possess in Louisiana.[17]
Notes
- ↑ "5-MeO-DALT: the freebase of N,N-diallyl-5-meth-oxy-tryptamine". IUCrData (International Union of Crystallography (IUCr)) 5 (Pt 4): x200498. April 2020. doi:10.1107/s2414314620004988. PMID 36338299.
- ↑ "Receptor binding profiles and quantitative structure-affinity relationships of some 5-substituted-N,N-diallyltryptamines". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters (Elsevier BV) 26 (3): 959–964. February 2016. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.12.053. PMID 26739781.
- ↑ "Metabolism of the new psychoactive substances N,N-diallyltryptamine (DALT) and 5-methoxy-DALT and their detectability in urine by GC-MS, LC-MSn, and LC-HR-MS-MS". Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry (Springer Science and Business Media LLC) 407 (25): 7831–7842. October 2015. doi:10.1007/s00216-015-8955-0. PMID 26297461. https://researchonline.ljmu.ac.uk/id/eprint/3406/1/ABC-01148-2015.R1.pdf.
- ↑ "Cytochrome P450 inhibition potential of new psychoactive substances of the tryptamine class". Toxicology Letters (Elsevier BV) 241: 82–94. January 2016. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2015.11.013. PMID 26599973. https://researchonline.ljmu.ac.uk/id/eprint/2402/1/ToxLett_17.15.49.pdf.
- ↑ "The Last Interview With Alexander Shulgin". 2010-05-02. https://www.vice.com/en/article/avjewz/the-last-interview-with-alexander-shulgin-423-v17n5.
- ↑ Sasha Shulgin - 5-MeO-DALT, 2C-B-FLY & 5-EtOs. Archived from the original on 2021-12-13. Retrieved 3 September 2015 – via YouTube.
- ↑ "Cluster Headache Patient Survey: 5-MeO-DALT". Figshare. 2015. doi:10.6084/M9.FIGSHARE.1372467.V3. https://figshare.com/articles/journal_contribution/1372467.
- ↑ "Treatment of Cluster Headache Symptoms using Synthetic Tryptamine N,N-Diallyl-5 Methoxytryptamine". Figshare. 2014. doi:10.6084/M9.FIGSHARE.1119697.V1. https://figshare.com/articles/journal_contribution/1119697.
- ↑ "Pharmacotherapy for Cluster Headache". CNS Drugs (Springer Science and Business Media LLC) 34 (2): 171–184. February 2020. doi:10.1007/s40263-019-00696-2. PMID 31997136.
- ↑ "Indoleamine Hallucinogens in Cluster Headache: Results of the Clusterbusters Medication Use Survey". Journal of Psychoactive Drugs (Informa UK Limited) 47 (5): 372–381. 2015-10-20. doi:10.1080/02791072.2015.1107664. PMID 26595349.
- ↑ "关于印发《非药用类麻醉药品和精神药品列管办法》的通知" (in Chinese). China Food and Drug Administration. 27 September 2015. http://www.sfda.gov.cn/WS01/CL0056/130753.html.
- ↑ "厚生労働省:平成18年度無承認無許可医薬品等買上調査の結果について" (in Japanese). http://www.mhlw.go.jp/houdou/2007/08/h0810-3.html.
- ↑ "CNB NEWS RELEASE". Central Narcotics Bureau (CNB). 30 April 2015. http://www.cnb.gov.sg/Libraries/CNB_Newsroom_Files/CNB_NR_-_30_Apr_2015.sflb.ashx.
- ↑ "Föreskrifter om ändring i Läkemedelsverkets föreskrifter (LVFS 2011:10) om förteckningar över narkotika" (in Swedish). 20 April 2012. https://lakemedelsverket.se/upload/lvfs/LVFS_2012_6.pdf.
- ↑ "§1308.11 Schedule I.". http://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/21cfr/cfr/1308/1308_11.htm.
- ↑ "Chapter 893 - DRUG ABUSE PREVENTION AND CONTROL". Florida Statutes. http://leg.state.fl.us/statutes/index.cfm?App_mode=Display_Statute&URL=0800-0899/0893/0893.html.
- ↑ "Louisiana State Legislature". http://legis.la.gov/Legis/Law.aspx?d=98877.
External links
 |

