Chemistry:Venlafaxine
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˌvɛnləˈfæksiːn/ VEN-lə-FAK-seen |
| Trade names | Effexor, Efexor, Venbysi XR, others[1] |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a694020 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 42±15%[2] |
| Protein binding | 27±2% (parent compound), 30±12% (active metabolite, desvenlafaxine)[4] |
| Metabolism | Extensively metabolised by the liver,[2][4] primarily via CYP2D6[6] |
| Metabolites | O-desmethylvenlafaxine (ODV), see desvenlafaxine |
| Elimination half-life | 5±2 h (parent compound for immediate release preparations), 15±6 h (parent compound for extended release preparations), 11±2 h (active metabolite)[2][4] |
| Excretion | Kidney (87%; 5% as unchanged drug; 29% as desvenlafaxine and 53% as other metabolites)[2][4] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H27NO2 |
| Molar mass | 277.408 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Venlafaxine, sold under the brand name Effexor among others, is an antidepressant medication of the serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) class.[4][7] It is used to treat major depressive disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder.[7] Studies have shown that Venlafaxine improves quality of life.[8] It may also be used for chronic pain.[9] It is taken by mouth.[7] It is also available as the salt venlafaxine besylate in an extended-release formulation (Venbysi XR).[5]
Common side effects include loss of appetite, constipation, dry mouth, dizziness, sweating, insomnia, drowsiness and sexual problems.[7] Severe side effects include an increased risk of suicide, mania, and serotonin syndrome.[7] Antidepressant withdrawal syndrome may occur if stopped.[7] There are concerns that use during the later part of pregnancy can harm the baby.[7] How it works is not entirely clear, but it seems to be related to the potentiation of the activity of some neurotransmitters in the brain.[7]
Venlafaxine was approved for medical use in the United States in 1993.[7] It is available as a generic medication.[7] In 2021, it was the 44th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States with more than 15 million prescriptions.[10][11]
Medical uses
Venlafaxine is used primarily for the treatment of depression, general anxiety disorder, social phobia, panic disorder, and vasomotor symptoms.[12]
Venlafaxine has been used off label for the treatment of diabetic neuropathy[13] and migraine prevention.[14] It may work on pain via effects on the opioid receptor.[15] It has also been found to reduce the severity of 'hot flashes' in menopausal women and men on hormonal therapy for the treatment of prostate cancer.[16][17]
Due to its action on both the serotoninergic and adrenergic systems, venlafaxine is also used as a treatment to reduce episodes of cataplexy, a form of muscle weakness, in patients with the sleep disorder narcolepsy.[18] Some open-label and three double-blind studies have suggested the efficacy of venlafaxine in the treatment of attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).[19] Clinical trials have found possible efficacy in those with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).[20] Case reports, open trials and blinded comparisons with established medications have suggested the efficacy of venlafaxine in the treatment of obsessive–compulsive disorder.[21]
Depression
A comparative meta-analysis of 21 major antidepressants found that venlafaxine, agomelatine, amitriptyline, escitalopram, mirtazapine, paroxetine, and vortioxetine were more effective than other antidepressants, although the quality of many comparisons was assessed as low or very low.[22][23]
Venlafaxine was similar in efficacy to the atypical antidepressant bupropion; however, the remission rate was lower for venlafaxine.[24] In a double-blind study, patients who did not respond to an SSRI were switched to either venlafaxine or another SSRI (citalopram); similar improvement was observed in both groups.[25]
Studies have not established its efficacy for use by children.[26] In children and adolescents with depression, venlafaxine increases the risk of suicidal thoughts or attempts.[27][28][29][30][31][32]
Higher doses (e.g. 225 mg and 375 mg per day) of venlafaxine are more effective than lower doses (e.g. 75 mg per day), but also cause more side effects.[33]
Studies have shown that the extended release is superior to the immediate release form of venlafaxine.[34]
A meta-analysis has shown that efficacy of venlafaxine is not correlated with baseline severity of depression.[34]
Contraindications
Venlafaxine is not recommended in patients hypersensitive to it, nor should it be taken by anyone who is allergic to the inactive ingredients, which include gelatin, cellulose, ethylcellulose, iron oxide, titanium dioxide and hypromellose. It should not be used in conjunction with a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI), as it can cause potentially fatal serotonin syndrome.[2][4][35] Venlafaxine might interact with tramadol or other opioids, trazodone, so caution is needed while mixing multiple serotonergic agents together.[36]
Adverse effects
Venlafaxine can increase eye pressure, so those with glaucoma may require more frequent eye checks.[4]
A 2017 meta-analysis estimated venlafaxine discontinuation rate to 9.4%.[34]
Suicide
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) requires all antidepressants, including venlafaxine, to carry a black box warning with a generic warning about a possible suicide risk.[citation needed]
A 2014 meta analysis of 21 clinical trials of venlafaxine for the treatment of depression in adults found that compared to placebo, venlafaxine reduced the risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior.[37]
A study conducted in Finland followed more than 15,000 patients for 3.4 years. Venlafaxine increased suicide risk by 60% (statistically significant), as compared to no treatment. At the same time, fluoxetine (Prozac) halved the suicide risk.[38]
In another study, the data on more than 200,000 cases were obtained from the UK general practice research database. At baseline, patients prescribed venlafaxine had a greater number of risk factors for suicide (such as prior suicide attempts) than patients treated with other anti-depressants. The patients taking venlafaxine had significantly higher risk of suicide than the ones on fluoxetine or citalopram (Celexa). After adjusting for known risk factors, venlafaxine was associated with an increased risk of suicide relative to fluoxetine and dothiepin that was not statistically significant. A statistically significant greater risk for attempted suicide remained after adjustment, but the authors concluded that it could be due to residual confounding. The study was sponsored by Wyeth, which produces and markets venlafaxine.[39]
An analysis of clinical trials by the FDA statisticians showed the incidence of suicidal behaviour among the adults on venlafaxine to be not significantly different from fluoxetine or placebo.[40]
Venlafaxine is contraindicated in children, adolescents and young adults. In children and adolescents with depression, venlafaxine increases the risk of suicidal thoughts or attempts.[27][28][29][30][31][32]
Serotonin syndrome
The development of a potentially life-threatening serotonin syndrome (also classified as "serotonin toxicity")[41] may occur with venlafaxine treatment, particularly with concomitant use of serotonergic drugs, including but not limited to SSRIs and SNRIs, many hallucinogens such as tryptamines and phenethylamines (e.g., LSD/LSA, DMT, MDMA, mescaline), dextromethorphan (DXM), tramadol, tapentadol, pethidine (meperidine) and triptans and with drugs that impair metabolism of serotonin (including MAOIs).[citation needed] Serotonin syndrome symptoms may include mental status changes (e.g. agitation, hallucinations, coma), autonomic instability (e.g. tachycardia, labile blood pressure, hyperthermia), neuromuscular aberrations (e.g. hyperreflexia, incoordination), or gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g. nausea, vomiting, diarrhea). Venlafaxine-induced serotonin syndrome has also been reported when venlafaxine has been taken in isolation in overdose.[42] An abortive serotonin syndrome state, in which some but not all of the symptoms of the full serotonin syndrome are present, has been reported with venlafaxine at mid-range dosages (150 mg per day).[43] A case of a patient with serotonin syndrome induced by low-dose venlafaxine (37.5 mg per day) has also been reported.[44]
Pregnancy
There are few well-controlled studies of venlafaxine in pregnant women. A study released in May 2010 by the Canadian Medical Association Journal suggests use of venlafaxine doubles the risk of miscarriage.[45][46] Consequently, venlafaxine should only be used during pregnancy if clearly needed.[4] A large case-control study done as part of the National Birth Defects Prevention Study and published in 2012 found a significant association of venlafaxine use during pregnancy and several birth defects including anencephaly, cleft palate, septal heart defects and coarctation of the aorta.[47] Prospective studies have not shown any statistically significant congenital malformations.[48] There have, however, been some reports of self-limiting effects on newborn infants.[49] As with other serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SRIs), these effects are generally short-lived, lasting only 3 to 5 days,[50] and rarely resulting in severe complications.[51]
Drug interactions
Venlafaxine should be taken with caution when using St John's wort.[52] Venlafaxine may lower the seizure threshold, and coadministration with other drugs that lower the seizure threshold such as bupropion and tramadol should be done with caution and at low doses.[53]
Bipolar disorder
According to the ISBD Task Force report on antidepressant use in bipolar disorder,[54] during the course of treatment for depression with those suffering from bipolar I and II, venlafaxine "appears to carry a particularly high risk of inducing pathologically elevated states of mood and behavior." Because venlafaxine appears to be more likely than SSRIs and bupropion to induce mania and mixed episodes in these patients, provider discretion is advised through "carefully evaluating individual clinical cases and circumstances."
Liver injury
A rare but serious side effect of venlafaxine is liver injury. It appears to affect both male and female patients with a median age of 44. Cessation of venlafaxine is one of the appropriate measures of management. While the mechanism of venlafaxine-related liver injury remains unclear, findings suggest that it may be related to a CYP2D6 polymorphism.[55]
Other
In rare cases, drug-induced akathisia can occur after use in some people.[56]
Venlafaxine should be used with caution in hypertensive patients. Venlafaxine must be discontinued if significant hypertension persists.[57][58][59] It can also have undesirable cardiovascular effects.[60]
Overdose
Most patients overdosing with venlafaxine develop only mild symptoms. Plasma venlafaxine concentrations in overdose survivors have ranged from 6 to 24 mg/L, while postmortem blood levels in fatalities are often in the 10–90 mg/L range.[61] Published retrospective studies report that venlafaxine overdosage may be associated with an increased risk of fatal outcome compared to that observed with SSRI antidepressant products, but lower than that for tricyclic antidepressants. Healthcare professionals are advised to prescribe Effexor and Effexor XR in the smallest quantity of capsules consistent with good patient management to reduce the risk of overdose.[62] It is usually reserved as a second-line treatment for depression due to a combination of its superior efficacy to the first-line treatments like fluoxetine, paroxetine and citalopram and greater frequency of side effects like nausea, headache, insomnia, drowsiness, dry mouth, constipation, sexual dysfunction, sweating and nervousness.[22][63]
There is no specific antidote for venlafaxine, and management is generally supportive, providing treatment for the immediate symptoms. Administration of activated charcoal can prevent absorption of the drug. Monitoring of cardiac rhythm and vital signs is indicated. Seizures are managed with benzodiazepines or other anticonvulsants. Forced diuresis, hemodialysis, exchange transfusion, or hemoperfusion are unlikely to be of benefit in hastening the removal of venlafaxine, due to the drug's high volume of distribution.[64]
Withdrawal syndrome
People stopping venlafaxine commonly experience SSRI withdrawal symptoms such as dysphoria, headaches, nausea, irritability, emotional lability, sensation of electric shocks (commonly called "brain zaps"[65][66]), and sleep disturbance.[67] Venlafaxine has a higher rate of moderate to severe withdrawal symptoms relative to other antidepressants (similar to the SSRI paroxetine).[68]
The higher risk and increased severity of withdrawal symptoms relative to other antidepressants may be related to the short half-life of venlafaxine and its active metabolite.[69] After stopping venlafaxine, the levels of both serotonin and norepinephrine decrease, leading to the hypothesis that the withdrawal symptoms could result from an overly rapid reduction of neurotransmitter levels.[70]
Mechanism of action
Pharmacology
| Transporter | Ki [nM][71] | IC50 [nM][72] |
|---|---|---|
| SERT | 82 | 27 |
| NET | 2480 | 535 |
| DAT | 7647 | ND |
| Receptor | Ki [nM] [73][74] | Species |
|---|---|---|
| 5-HT2A | 2230 | Human |
| 5-HT2C | 2004 | Human |
| 5-HT6 | 2792 | Human |
| α1A | >1000 | Human |
Venlafaxine is usually categorized as a serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI), but it has also been referred to as a serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SNDRI).[75][76] It is described as 'synthetic phenethylamine bicyclic derivative with antidepressant activity'.[77][78] It works by blocking the transporter "reuptake" proteins for key neurotransmitters affecting mood, thereby leaving more active neurotransmitters in the synapse. The neurotransmitters affected are serotonin and norepinephrine. Additionally, in high doses it weakly inhibits the reuptake of dopamine,[79] since dopamine is inactivated by norepinephrine reuptake in the frontal cortex. The frontal cortex largely lacks dopamine transporters; therefore venlafaxine can increase dopamine neurotransmission in this part of the brain.[80][81]
Venlafaxine selectively inhibits the serotonin transporter at lower doses, but at a dose of 225 mg per day it additionally blocks the norepinephrine transporter.[82]
Venlafaxine indirectly affects opioid receptors as well as the α2-adrenergic receptor, and was shown to increase pain threshold in mice. These benefits with respect to pain were reversed with naloxone, an opioid antagonist, thus supporting an opioid mechanism.[83][84]
Pharmacokinetics
Venlafaxine is well absorbed, with at least 92% of an oral dose being absorbed into systemic circulation. It is extensively metabolized in the liver via the CYP2D6 isoenzyme to desvenlafaxine (O-desmethylvenlafaxine, now marketed as a separate medication named Pristiq[85]), which is just as potent an SNRI as the parent compound, meaning that the differences in metabolism between extensive and poor metabolisers are not clinically important in terms of efficacy. Side effects, however, are reported to be more severe in CYP2D6 poor metabolisers.[86][87] Steady-state concentrations of venlafaxine and its metabolite are attained in the blood within 3 days. Therapeutic effects are usually achieved within 3 to 4 weeks. No accumulation of venlafaxine has been observed during chronic administration in healthy subjects. The primary route of excretion of venlafaxine and its metabolites is via the kidneys.[4] The half-life of venlafaxine is relatively short, so patients are directed to adhere to a strict medication routine, avoiding missing a dose. Even a single missed dose can result in withdrawal symptoms.[88]
Venlafaxine is a substrate of P-glycoprotein (P-gp), which pumps it out of the brain. The gene encoding P-gp, ABCB1, has the SNP rs2032583, with alleles C and T. The majority of people (about 70% of Europeans and 90% of East Asians) have the TT variant.[89][unreliable source?] A 2007 study[90] found that carriers of at least one C allele (variant CC or CT) are 7.72 times more likely than non-carriers to achieve remission after 4 weeks of treatment with amitriptyline, citalopram, paroxetine or venlafaxine (all P-gp substrates). The study included patients with mood disorders other than major depression, such as bipolar II; the ratio is 9.4 if these other disorders are excluded. At the 6-week mark, 75% of C-carriers had remitted, compared to only 38% of non-carriers.[citation needed]
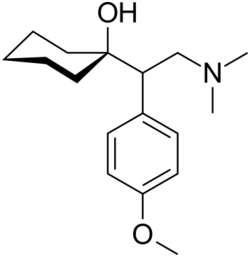
Chemistry
The IUPAC name of venlafaxine is 1-[2-(dimethylamino)-1-(4 methoxyphenyl)ethyl]cyclohexanol, though it is sometimes referred to as (±)-1-[a-[a-(dimethylamino)methyl]-p-methoxybenzyl]cyclohexanol. It consists of two enantiomers present in equal quantities (termed a racemic mixture), both of which have the empirical formula of C17H27NO2. It is usually sold as a mixture of the respective hydrochloride salts, (R/S)-1-[2-(dimethylamino)-1-(4 methoxyphenyl)ethyl]cyclohexanol hydrochloride, C17H28ClNO2, which is a white to off-white crystalline solid. Venlafaxine is structurally and pharmacologically related to the atypical opioid analgesic tramadol, and more distantly to the newly released opioid tapentadol, but not to any of the conventional antidepressant drugs, including tricyclic antidepressants, SSRIs, MAOIs, or RIMAs.[91]
Venlafaxine extended release is chemically the same as normal venlafaxine. The extended release (controlled release) version distributes the release of the drug into the gastrointestinal tract over a longer period than normal venlafaxine. This results in a lower peak plasma concentration. Studies have shown that the extended release formula has a lower incidence of nausea as a side effect, resulting in better compliance.[92]
Recreational use
Venlafaxine can be abused as recreational drug, with damages that can manifest within a month.[93] Hard data regarding prevalence of abuse are not easy to find. Abusers reported usage of extremely high dosage, 5 to 10 times of acceptable clinical dosage. The adverse side effects were strong cases of the listed side effects. As standard measure treatment is to be supervised by a doctor with relevant education, such as neurologist or psychiatrist.
Society and culture
Venlafaxine was originally marketed as Effexor in most of the world; generic venlafaxine has been available since around 2008 and extended release venlafaxine has been available since around 2010.[94]
As of January 2020, venlafaxine is marketed under many brand names worldwide, many with alternative extended release forms (not shown): Adefaxin, Alenthus, Altven, Alventa, Amfax, Anapresin, Ansifix, Arafaxina, Argofan, Arrow Venlafaxine, Axone, Axyven, Benolaxe, Blossom, Calmdown, Dalium, Defaxine, Depefex, Depretaxer, Deprevix, Deprexor, Deprixol, Depurol, Desinax, Dislaven, Dobupal, Duofaxin, Easyfor, Ectien, Eduxon, Efastad, Efaxin, Efaxine, Efectin, Efegen, Efevelon, Efevelone, Efexiva, Efexor, Effegad, Effexine, Effexor, Elafax, Elaxine, Elify, Enpress, Enlafax, Envelaf, Falven, Faxigen, Faxine, Faxiprol, Faxiven, Faxolet, Flavix, Flaxen, Fobiless, Ganavax, Idixor, Idoxen, Intefred, Illovex, Lafactin, Lafaxin, Lanvexin, Laroxin, Levest, Limbic, Linexel, Maxibral, Mazda, Melocin, Memomax, Mezine, Neoxacina, Neoxacina, Nervix, Norafexine, Norezor, Norpilen, Noviser, Nulev, Odiven, Olwexya, Oriven, Paxifar, Politid, Pracet, Prefaxine, Psiseven, Quilarex, Rafax, Senexon, Sentidol, Sentosa, Serosmine, Seroxine, Sesaren, Subelan, Sulinex, Sunveniz, Sunvex, Symfaxin, Tedema, Tifaxin, Tonpular, Trevilor, Tudor, Vafexin, Valosine, Vandral, Velaf, Velafax, Velahibin, Velaxin, Velaxor, Velept, Velpine, Venax, Venaxin, Venaxx, Vencarm, Vencontrol, Vendep, Venegis, Venex, Venexor, Venfalex, Venfax, Ven-Fax, Venfaxine, Venforin, Venforspine, Veniba, Veniz, Venjoy, Venla, Venlabax, Venlablue, Venlabrain, Venladep, Venladex, Venladoz, Venlaf, Venlafab, Venlafaxin, Venlafaxina, Venlafaxine, Venlagamma, Venlalic, Venlamax, Venlamylan, Venlaneo, Venlapine, Venla-Q, Venlasand, Venlatrin, Venlavitae, Venlax, Venlaxin, Venlaxine, Venlaxor, Venlazid, Venlectine, Venlifax, Venlift, Venlix, Venlobax, Venlofex, Venlor, Venorion, Venozap, Vensate, Ventab, Venxin, Venxor, Vextor, Venzip, Vexamode, Vfax, Viepax, ViePax, Voxafen, Zacalen, Zanfexa, Zaredrop, Zarelis, Zarelix, and Zenexor.[1]
The depressive suicidal black metal band Intig, consequently made by the same developers of Cry of Fear (a well-known video game that showcases the severe effects of depression and irrational recreational use of medical drugs), has a song titled "C17H27NO2".
Veterinary effects
Veterinary overdose in dogs is very well treated by Cyproheptadine HCl.[95](p1371)
Venlafaxine is highly toxic to Bacillariophyta and Chlorophyta phytoplankton.[96] Cats are drawn to the smell of Venlafaxine and tend to ingest the pills, which is highly toxic to them.[97]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Venlafaxine". Dallas, Texas: Drugsite Trust. January 2020. Brand Names. https://www.drugs.com/international/venlafaxine.html.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 "Efexor-XR (venlafaxine hydrochloride)" (PDF). https://www.ebs.tga.gov.au/ebs/picmi/picmirepository.nsf/pdf?OpenAgent&id=CP-2010-PI-04889-3.
- ↑ "Efexor XL 75 mg hard prolonged release capsules - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". 16 March 2020. https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/5474/smpc.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 4.8 4.9 "Effexor XR- venlafaxine hydrochloride capsule, extended release". https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=53c3e7ac-1852-4d70-d2b6-4fca819acf26.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "Venlafaxine tablet, extended release". 30 June 2022. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=e81a2daf-b8b2-7c05-b532-bc775700b100.
- ↑ Venlafaxine Therapy and CYP2D6 Genotype. National Center for Biotechnology Information (US). 2015. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK305561/#:~:text=Venlafaxine%20is%20metabolized%20into%20its,reduced%20or%20absent%20CYP2D6%20activity.. Retrieved 28 December 2018.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 7.7 7.8 7.9 "Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Monograph for Professionals". AHFS. https://www.drugs.com/monograph/venlafaxine-hydrochloride.html.
- ↑ Psychological and Pharmacological Treatments for Adults With Posttraumatic Stress Disorder: A Systematic Review Update (Report). Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ). 17 May 2018. doi:10.23970/ahrqepccer207. PMID 30204376. https://effectivehealthcare.ahrq.gov/topics/ptsd-adult-treatment-update/research-2018.
- ↑ "Antidepressants: Another weapon against chronic pain". https://www.mayoclinic.org/pain-medications/art-20045647.
- ↑ "The Top 300 of 2021". https://clincalc.com/DrugStats/Top300Drugs.aspx.
- ↑ "Venlafaxine - Drug Usage Statistics". https://clincalc.com/DrugStats/Drugs/Venlafaxine.
- ↑ "venlafaxine-hydrochloride". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. https://www.drugs.com/monograph/venlafaxine-hydrochloride.html.
- ↑ "Treatment of pain syndromes with venlafaxine". Pharmacotherapy 24 (5): 621–629. May 2004. doi:10.1592/phco.24.6.621.34748. PMID 15162896.
- ↑ "Venlafaxine". StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535363.
- ↑ The Opioid System as the Interface between the Brain's Cognitive and Motivational Systems. Academic Press. 2018. p. 73. ISBN 978-0-444-64168-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=sEFyDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA73. Retrieved 9 May 2020.
- ↑ Mayo Clinic staff (2005). "Beyond hormone therapy: Other medicines may help". Hot flashes: Ease the discomfort of menopause. Mayo Clinic. http://www.mayoclinic.com/invoke.cfm?id=HQ01409.
- ↑ "Venlafaxine hydrochloride for the treatment of hot flashes". The Annals of Pharmacotherapy 37 (11): 1703–1707. November 2003. doi:10.1345/aph.1C483. PMID 14565812.
- ↑ "Medications". Stanford University School of Medicine, Center for Narcolepsy. 7 February 2003. http://med.stanford.edu/school/Psychiatry/narcolepsy/medications.html.
- ↑ "Efficacy and adverse effects of venlafaxine in children and adolescents with ADHD: a systematic review of non-controlled and controlled trials". Reviews on Recent Clinical Trials 8 (1): 2–8. March 2013. doi:10.2174/1574887111308010002. PMID 23157376.
- ↑ "Extended-release formulation of venlafaxine in the treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder". Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics 7 (6): 603–615. June 2007. doi:10.1586/14737175.7.6.603. PMID 17563244.
- ↑ "The role of venlafaxine in the treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder". The Annals of Pharmacotherapy 39 (1): 136–140. January 2005. doi:10.1345/aph.1E362. PMID 15585743.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 "Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 12 new-generation antidepressants: a multiple-treatments meta-analysis". Lancet 373 (9665): 746–758. February 2009. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60046-5. PMID 19185342.
- ↑ "Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 21 antidepressant drugs for the acute treatment of adults with major depressive disorder: a systematic review and network meta-analysis". Lancet 391 (10128): 1357–1366. April 2018. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32802-7. PMID 29477251.
- ↑ "A double-blind comparison between bupropion XL and venlafaxine XR: sexual functioning, antidepressant efficacy, and tolerability". Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 26 (5): 482–488. October 2006. doi:10.1097/01.jcp.0000239790.83707.ab. PMID 16974189.
- ↑ "Venlafaxine extended release versus citalopram in patients with depression unresponsive to a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor". International Clinical Psychopharmacology 23 (3): 113–119. May 2008. doi:10.1097/YIC.0b013e3282f424c2. PMID 18408525.
- ↑ "Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor and venlafaxine use in children and adolescents with major depressive disorder: a systematic review of published randomized controlled trials". Canadian Journal of Psychiatry 49 (8): 557–563. August 2004. doi:10.1177/070674370404900807. PMID 15453105.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 "Antidepressants for children and teenagers: what works for anxiety and depression?" (in en). NIHR Evidence (National Institute for Health and Care Research). 3 November 2022. doi:10.3310/nihrevidence_53342. https://evidence.nihr.ac.uk/collection/antidepressants-for-children-and-teenagers-what-works-anxiety-depression/.
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 "Comparative efficacy and acceptability of antidepressants, psychotherapies, and their combination for acute treatment of children and adolescents with depressive disorder: a systematic review and network meta-analysis". The Lancet. Psychiatry 7 (7): 581–601. July 2020. doi:10.1016/S2215-0366(20)30137-1. PMID 32563306.
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 "New generation antidepressants for depression in children and adolescents: a network meta-analysis". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2021 (5): CD013674. May 2021. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD013674.pub2. PMID 34029378.
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 "Safety of 80 antidepressants, antipsychotics, anti-attention-deficit/hyperactivity medications and mood stabilizers in children and adolescents with psychiatric disorders: a large scale systematic meta-review of 78 adverse effects". World Psychiatry 19 (2): 214–232. June 2020. doi:10.1002/wps.20765. PMID 32394557.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 "Antidepressants in Children and Adolescents: Meta-Review of Efficacy, Tolerability and Suicidality in Acute Treatment". Frontiers in Psychiatry 11: 717. 2 September 2020. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00717. PMID 32982805.
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 "Efficacy and acceptability of pharmacological, psychosocial, and brain stimulation interventions in children and adolescents with mental disorders: an umbrella review". World Psychiatry 20 (2): 244–275. June 2021. doi:10.1002/wps.20881. PMID 34002501.
- ↑ "A randomized, placebo-controlled, dose-response trial of venlafaxine hydrochloride in the treatment of major depression". The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 59 (3): 116–122. March 1998. doi:10.4088/jcp.v59n0305. PMID 9541154.
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 34.2 "A meta-analysis of the efficacy of venlafaxine extended release 75-225 mg/day for the treatment of major depressive disorder". Current Medical Research and Opinion (Informa UK Limited) 33 (2): 317–326. February 2017. doi:10.1080/03007995.2016.1255185. PMID 27794623.
- ↑ The Maudsley Prescribing Guidelines in Psychiatry (illustrated ed.). John Wiley & Sons. 2012. ISBN 978-0-470-97948-8.
- ↑ "Lethal combination of tramadol and multiple drugs affecting serotonin". The American Journal of Forensic Medicine and Pathology 21 (4): 370–374. December 2000. doi:10.1097/00000433-200012000-00015. PMID 11111800. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11111800/. Retrieved 6 April 2022.
- ↑ "Suicidal thoughts and behavior with antidepressant treatment: reanalysis of the randomized placebo-controlled studies of fluoxetine and venlafaxine". Archives of General Psychiatry 69 (6): 580–587. June 2012. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.2048. PMID 22309973.
- ↑ "Antidepressants and the risk of suicide, attempted suicide, and overall mortality in a nationwide cohort". Archives of General Psychiatry 63 (12): 1358–1367. December 2006. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.63.12.1358. PMID 17146010.
- ↑ "Risk of suicide during treatment with venlafaxine, citalopram, fluoxetine, and dothiepin: retrospective cohort study". BMJ 334 (7587): 242. February 2007. doi:10.1136/bmj.39041.445104.BE. PMID 17164297.
- ↑ "Overview for December 13 Meeting of Psychopharmacologic Drugs Advisory Committee". Food and Drug Administration: Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. 16 November 2006. https://www.fda.gov/ohrms/dockets/ac/06/briefing/2006-4272b1-01-FDA.pdf.
- ↑ "The Hunter Serotonin Toxicity Criteria: simple and accurate diagnostic decision rules for serotonin toxicity". QJM 96 (9): 635–642. September 2003. doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcg109. PMID 12925718.
- ↑ "Isolated venlafaxine-induced serotonin syndrome". The Journal of Emergency Medicine 15 (4): 491–493. July–August 1997. doi:10.1016/S0736-4679(97)00078-4. PMID 9279702.
- ↑ "Hallucinations as a side effect of venlafaxine treatment". Psychiatry On-line. http://www.priory.com/psych/venhall.htm.
- ↑ "Serotonin syndrome induced by low-dose venlafaxine". The Annals of Pharmacotherapy 37 (2): 209–211. February 2003. doi:10.1345/aph.1C021. PMID 12549949.
- ↑ "Gestational exposure to antidepressants and the risk of spontaneous abortion: a review". Current Drug Delivery 7 (1): 76–92. January 2010. doi:10.2174/156720110790396508. PMID 19863482.
- ↑ "Use of antidepressants during pregnancy and the risk of spontaneous abortion". CMAJ 182 (10): 1031–1037. July 2010. doi:10.1503/cmaj.091208. PMID 20513781.
- ↑ "Association between reported venlafaxine use in early pregnancy and birth defects, national birth defects prevention study, 1997-2007". Birth Defects Research. Part A, Clinical and Molecular Teratology 97 (1): 28–35. January 2013. doi:10.1002/bdra.23096. PMID 23281074.
- ↑ "The safety of newer antidepressants in pregnancy and breastfeeding". Drug Safety 28 (2): 137–152. 2005. doi:10.2165/00002018-200528020-00005. PMID 15691224.
- ↑ "[Withdrawal symptoms in a neonate following exposure to venlafaxine during pregnancy]". Nederlands Tijdschrift voor Geneeskunde 147 (28): 1370–1372. July 2003. PMID 12892015.
- ↑ "Effects of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and venlafaxine during pregnancy in term and preterm neonates". Pediatrics 119 (1): 52–59. January 2007. doi:10.1542/peds.2006-2133. PMID 17200271.
- ↑ "Neonatal signs after late in utero exposure to serotonin reuptake inhibitors: literature review and implications for clinical applications". JAMA 293 (19): 2372–2383. May 2005. doi:10.1001/jama.293.19.2372. PMID 15900008.
- ↑ 2006 Lippincott's Nursing Drug Guide. Philadelphia, Baltimore, New York, London, Buenos Aires, Hong Kong, Sydney, Tokyo: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2006. ISBN 978-1-58255-436-5. https://archive.org/details/2006lippincottsn0000karc.
- ↑ "Evolving epidemiology of drug-induced seizures reported to a Poison Control Center System". Journal of Medical Toxicology 3 (1): 15–19. March 2007. doi:10.1007/BF03161033. PMID 18072153.
- ↑ "The International Society for Bipolar Disorders (ISBD) task force report on antidepressant use in bipolar disorders". The American Journal of Psychiatry 170 (11): 1249–1262. November 2013. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2013.13020185. PMID 24030475.
- ↑ "Venlafaxine-induced cholestatic hepatitis: case report and review of literature". The American Journal of Surgical Pathology (Ovid Technologies (Wolters Kluwer Health)) 36 (11): 1724–1728. November 2012. doi:10.1097/pas.0b013e31826af296. PMID 23073329.
- ↑ "Venlafaxine Side Effects in Detail". https://www.drugs.com/sfx/venlafaxine-side-effects.html.
- ↑ "Hypertensive crisis associated with venlafaxine". The American Journal of Medicine 115 (8): 676–677. December 2003. doi:10.1016/S0002-9343(03)00472-8. PMID 14656626.
- ↑ "Effects of venlafaxine on blood pressure: a meta-analysis of original data from 3744 depressed patients". The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 59 (10): 502–508. October 1998. doi:10.4088/JCP.v59n1002. PMID 9818630.
- ↑ "Venlafaxine as single therapy associated with hypertensive encephalopathy". SpringerPlus 4 (1): 97. 26 February 2015. doi:10.1186/s40064-015-0883-0. PMID 25763307.
- ↑ "Cardiovascular changes associated with venlafaxine in the treatment of late-life depression". The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 14 (9): 796–802. September 2006. doi:10.1097/01.JGP.0000204328.50105.b3. PMID 16943176.
- ↑ Disposition of Toxic Drugs and Chemicals in Man (8th ed.). Foster City, CA: Biomedical Publications. 2008. pp. 1634–1637. ISBN 978-0-9626523-7-0.
- ↑ "Wyeth Letter to Health Care Providers". Wyeth Pharmaceuticals Inc. 2006. https://www.fda.gov/Safety/MedWatch/SafetyInformation/SafetyAlertsforHumanMedicalProducts/ucm150546.htm.
- ↑ "A review of the suitability of duloxetine and venlafaxine for use in patients with depression in primary care with a focus on cardiovascular safety, suicide and mortality due to antidepressant overdose". Therapeutic Advances in Psychopharmacology 3 (3): 151–161. June 2013. doi:10.1177/2045125312472890. PMID 24167687.
- ↑ "Serotonin syndrome and rhabdomyolysis in venlafaxine poisoning: a case report" (PDF). The Netherlands Journal of Medicine 63 (8): 316–318. September 2005. PMID 16186642. http://www.njmonline.nl/getpdf.php?id=432. Retrieved 6 November 2013.
- ↑ "Brain Zaps: An Underappreciated Symptom of Antidepressant Discontinuation". The Primary Care Companion for CNS Disorders 20 (6): 18m02311. December 2018. doi:10.4088/PCC.18m02311. PMID 30605268.
- ↑ "Antidepressant Discontinuation Syndrome: A Common but Underappreciated Clinical Problem". The Journal of the American Osteopathic Association 120 (3): 174–178. February 2020. doi:10.7556/jaoa.2020.030. PMID 32077900.
- ↑ "A case of interdose discontinuation symptoms with venlafaxine extended release". The Primary Care Companion for CNS Disorders 13 (5). 2011. doi:10.4088/PCC.11l01140. PMID 22295261.
- ↑ "SSRIs and SNRIs: A review of the Discontinuation Syndrome in Children and Adolescents". Journal of the Canadian Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry = Journal de l'Academie Canadienne de Psychiatrie de l'Enfant et de l'Adolescent 20 (1): 60–67. February 2011. PMID 21286371.
- ↑ "Antidepressant discontinuation syndromes". Drug Safety 24 (3): 183–197. March 2001. doi:10.2165/00002018-200124030-00003. PMID 11347722.
- ↑ "Venlafaxine and serious withdrawal symptoms: warning to drivers". MedGenMed 7 (3): 22. July 2005. PMID 16369248.
- ↑ "Comparative affinity of duloxetine and venlafaxine for serotonin and norepinephrine transporters in vitro and in vivo, human serotonin receptor subtypes, and other neuronal receptors". Neuropsychopharmacology 25 (6): 871–880. December 2001. doi:10.1016/S0893-133X(01)00298-6. PMID 11750180.
- ↑ "Heterocyclic cycloalkanol ethylamines as norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 20 (9): 2809–2812. May 2010. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.03.059. PMID 20378347.
- ↑ "Comparative affinity of duloxetine and venlafaxine for serotonin and norepinephrine transporters in vitro and in vivo, human serotonin receptor subtypes, and other neuronal receptors". Neuropsychopharmacology 25 (6): 871–880. December 2001. doi:10.1016/S0893-133X(01)00298-6. PMID 11750180.
- ↑ "Screening the receptorome yields validated molecular targets for drug discovery". Current Pharmaceutical Design 12 (14): 1785–1795. 2006. doi:10.2174/138161206776873680. PMID 16712488.
- ↑ Clinical trial number NCT00001483 for "Acute Effectiveness of Additional Drugs to the Standard Treatment of Depression" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- ↑ "Postmortem tissue concentrations of venlafaxine". Forensic Science International 121 (1–2): 70–75. September 2001. doi:10.1016/S0379-0738(01)00455-8. PMID 11516890.
- ↑ "venlafaxine". National Cancer Institute. https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-drug/def/venlafaxine.
- ↑ "Venlafaxine". StatPearls. StatPearls. 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535363/. Retrieved 24 January 2022.
- ↑ "Venlafaxine extended-release: a review of its use in the management of major depression". CNS Drugs 15 (8): 643–669. 2001. doi:10.2165/00023210-200115080-00007. PMID 11524036.
- ↑ "Stahl's Essential Psychopharmacology – Cambridge University Press". Stahlonline.cambridge.org. http://stahlonline.cambridge.org/prescribers_drug.jsf?page=0521683505c95_p539-544.html.therapeutics&name=Venlafaxine&title=Therapeutics.
- ↑ "Role of norepinephrine in depression". The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 61 (Suppl 1): 5–12. 2000. PMID 10703757.[full citation needed]
- ↑ "Differential Potency of Venlafaxine, Paroxetine, and Atomoxetine to Inhibit Serotonin and Norepinephrine Reuptake in Patients With Major Depressive Disorder". The International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology 25 (4): 283–292. April 2022. doi:10.1093/ijnp/pyab086. PMID 34958348.
- ↑ Massachusetts General Hospital Comprehensive Clinical Psychiatry. Elsevier Health Sciences. 2015. p. 860. ISBN 9780323295079. https://books.google.com/books?id=deR1BwAAQBAJ&pg=PA860. Retrieved 9 May 2020.
- ↑ The Opioid System as the Interface between the Brain's Cognitive and Motivational Systems. Academic Press. 2018. p. 73. ISBN 9780444641687. https://books.google.com/books?id=sEFyDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA73. Retrieved 9 May 2020.
- ↑ "Desvenlafaxine in the treatment of major depressive disorder". Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy 12 (18): 2923–2928. December 2011. doi:10.1517/14656566.2011.636033. PMID 22098230.
- ↑ "CYP2D6 polymorphism and clinical effect of the antidepressant venlafaxine". Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics 31 (5): 493–502. October 2006. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2710.2006.00763.x. PMID 16958828.
- ↑ "Venlafaxine Therapy and CYP2D6 Genotype". Medical Genetics Summaries. National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). 2015. Bookshelf ID: NBK305561. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK305561/. Retrieved 7 February 2020.
- ↑ "Withdrawal reactions associated with venlafaxine". The Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry 32 (2): 291–294. April 1998. doi:10.3109/00048679809062742. PMID 9588310.
- ↑ "Rs2032583 -SNPedia". Snpedia.com. http://www.snpedia.com/index.php/Rs2032583.
- ↑ "Polymorphisms in the drug transporter gene ABCB1 predict antidepressant treatment response in depression". Neuron 57 (2): 203–209. January 2008. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2007.11.017. PMID 18215618.
- ↑ "Relative toxicity of venlafaxine and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in overdose compared to tricyclic antidepressants". QJM 96 (5): 369–374. May 2003. doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcg062. PMID 12702786.
- ↑ "Immediate-release versus controlled-release formulations: pharmacokinetics of newer antidepressants in relation to nausea". The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 64 (Suppl 18): 14–19. 2003. PMID 14700450.
- ↑ "Venlafaxine Abuse in a Patient With a History of Methylphenidate Abuse: A Case Report". Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 39 (2): 172–174. 2019. doi:10.1097/JCP.0000000000001011. PMID 30811375.
- ↑ "Drugstores accuse Pfizer, Teva of blocking Effexor generics". FiercePharma. 13 June 2012. http://www.fiercepharma.com/sales-and-marketing/drugstores-accuse-pfizer-teva-of-blocking-effexor-generics.
- ↑ Veterinary Toxicology : Basic and Clinical Principles (2 ed.). Amsterdam Boston: Academic Press. 2012. pp. xii+1438. ISBN 978-0-12-385926-6. OCLC 794491298.
- ↑ "Susceptibility of phytoplankton to the increasing presence of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) in the aquatic environment: A review". Aquatic Toxicology (Elsevier) 234: 105809. May 2021. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2021.105809. PMID 33780670. Bibcode: 2021AqTox.23405809C.
- ↑ "The Top 5 Cat Toxins" (in en). https://www.pethealthnetwork.com/cat-health/cat-toxins-poisons/top-5-cat-toxins.
Further reading
 |



