Astronomy:VZ Camelopardalis
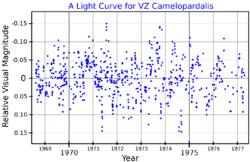 A visual band light curve for VZ Camelopardalis, plotted from data presented by Tabur et al. (2009)[1] | |
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Camelopardalis |
| Right ascension | 07h 31m 04.48017s[2] |
| Declination | +82° 24′ 41.2905″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 4.92[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Evolutionary stage | AGB[4] |
| Spectral type | M4IIIa[5] |
| B−V color index | +1.633±0.018[3] |
| Variable type | Lb?[6] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | +11.90±0.22[3] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −5.249[2] mas/yr Dec.: −42.174[2] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 6.4908 ± 0.2204[2] mas |
| Distance | 500 ± 20 ly (154 ± 5 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −1.00[3] |
| Details | |
| Radius | 88.93+7.92 −15.25[2] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 1252±48[2] L☉ |
| Temperature | 3,641+359 −152[2] K |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
VZ Camelopardalis is a single,[8] variable star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Camelopardalis. It has a reddish hue and is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude that fluctuates around 4.92.[3] The star is located at a distance of approximately 500 light years from the Sun based on parallax,[2] and is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +12 km/s.[3] It was considered a member of the Hyades Supercluster,[9] but in 1990 this was brought into question.[10]
This object is an aging red giant star on the asymptotic giant branch[4] with a stellar classification of M4IIIa.[5] Its variable nature was discovered by American astronomer J. Ashbrook in 1948.[11] This is a suspected slow irregular variable of sub-type Lb that varies in visual magnitude from 4.80 down to 4.96.[6] Long-term photometry measurements suggest there are at least four pulsation periods ranging from 27.1 to 39.0 days.[1] With the supply of hydrogen at its core exhausted the star has cooled and expanded until it has now reached 89 times the radius of the Sun. It is radiating 1,252 times the luminosity of the Sun from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 3,641 K.[2]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Tabur, V. et al. (December 2009), "Long-term photometry and periods for 261 nearby pulsating M giants", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 400 (4): 1945–1961, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.15588.x, Bibcode: 2009MNRAS.400.1945T.
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 Brown, A. G. A. (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 616: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012), "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation", Astronomy Letters 38 (5): 331, doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015, Bibcode: 2012AstL...38..331A.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Eggen, Olin J. (July 1992), "Asymptotic giant branch stars near the sun", Astronomical Journal 104 (1): 275–313, doi:10.1086/116239, Bibcode: 1992AJ....104..275E.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Yamashita, Y. (1967), "MK Spectral Types of Bright M-Type Stars", Publications of the Dominion Astrophysical Observatory 13: 47, Bibcode: 1967PDAO...13...47Y.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Samus, N. N. et al. (2017), "General Catalogue of Variable Stars", Astronomy Reports, 5.1 61 (1): 80–88, doi:10.1134/S1063772917010085, Bibcode: 2017ARep...61...80S.
- ↑ "VZ Cam". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=VZ+Cam.
- ↑ Eggleton, P. P.; Tokovinin, A. A. (September 2008), "A catalogue of multiplicity among bright stellar systems", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 389 (2): 869–879, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.13596.x, Bibcode: 2008MNRAS.389..869E.
- ↑ Eggen, O. J. (February 1985), "A systematic search for members of the Hyades supercluster. V. The red giants", Astronomical Journal 90: 333–340, doi:10.1086/113736, Bibcode: 1985AJ.....90..333E.
- ↑ Yamakawa, Fusatoshi; Uji-Iye, Kei-Ichi (August 1990), "A Candidate Star for Irregular Variability", Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan 42: L65–L67, Bibcode: 1990PASJ...42L..65Y.
- ↑ Eggen, Olin J.; Iben, Icko, Jr. (April 1991), "First Giant Branch and Asymptotic Giant Branch Stars in Nearby Aggregates", Astronomical Journal 101: 1377, doi:10.1086/115773, Bibcode: 1991AJ....101.1377E.
 |
