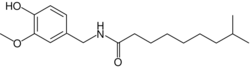
Dihydrocapsaicin
Names
Preferred IUPAC name
N -[(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-8-methylnonanamide
Other names
Dihydrocapsaicin, 6,7-Dihydrocapsaicin, 8-Methyl-N -vanillylnonanamide, Vanillylamide of 8-methylnonanoic acid, DHC, CCRIS 1589
Identifiers
2815150
ChEBI
ChEMBL
ChemSpider
EC Number
KEGG
RTECS number
UNII
InChI=1S/C18H29NO3/c1-14(2)8-6-4-5-7-9-18(21)19-13-15-10-11-16(20)17(12-15)22-3/h10-12,14,20H,4-9,13H2,1-3H3,(H,19,21)
N Key: XJQPQKLURWNAAH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
N InChI=1/C18H29NO3/c1-14(2)8-6-4-5-7-9-18(21)19-13-15-10-11-16(20)17(12-15)22-3/h10-12,14,20H,4-9,13H2,1-3H3,(H,19,21)
Key: XJQPQKLURWNAAH-UHFFFAOYAI
CC(C)CCCCCCC(=O)NCC1=CC(=C(C=C1)O)OC
Properties
C18 H29 NO3
Molar mass
307.43 g/mol
Appearance
White to off-white solid
Sparingly soluble
Hazards
GHS pictograms
GHS Signal word
Danger
H301 , H315 , H319 , H335
P261 , P264 , P270 , P271 , P280 , P301+310 , P302+352 , P304+340 , P305+351+338 , P312 , P321 , P330 , P332+313 , P337+313 , P362 , P403+233 , P405 , P501
NFPA 704
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their
standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
N verify what is Y N
Infobox references
Tracking categories (test):
Dihydrocapsaicin Heat Above peaktoxic ) Scoville scale 16,000,000[ 1]
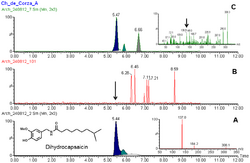
MS/MS spectra of standard dihydrocapsaicin (A) and from sample extract (B). Sample B confirms the compound was found in prehispanic pottery from Mexico. See here for details doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0079013.g005 Dihydrocapsaicin is a capsaicinoid and analog and congener of capsaicin in chili peppers (Capsicum irritant . It accounts for about 22% of the total capsaicinoid mixture[ 2] [ 1] dimethyl sulfoxide and 100% ethanol .
See also
References
↑ 1.0 1.1 "Capsicum — Production, Technology, Chemistry, and Quality. Part V. Impact on Physiology, Pharmacology, Nutrition, and Metabolism; Structure, Pungency, Pain, and Desensitization Sequences". Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition 29 (6): 435–474. 1991. doi :10.1080/10408399109527536 . PMID 2039598 . ↑ "Constitution and biosynthesis of capsaicin". J. Chem. Soc. C : 442. 1968. doi :10.1039/j39680000442 .
External links
TRPA
Activators
4-Hydroxynonenal 4-Oxo-2-nonenal 4,5-EET 12S-HpETE 15-Deoxy-Δ12,14 -prostaglandin J2 α-Sanshool (ginger , Sichuan and melegueta peppers )Acrolein Allicin (garlic )Allyl isothiocyanate (mustard , radish , horseradish , wasabi )AM404 Bradykinin Cannabichromene (cannabis )Cannabidiol (cannabis )Cannabigerol (cannabis )Cinnamaldehyde (cinnamon )CR gas (dibenzoxazepine; DBO) CS gas (2-chlorobenzal malononitrile) Curcumin (turmeric )Dehydroligustilide (celery )Diallyl disulfide Dicentrine (Lindera Farnesyl thiosalicylic acid Formalin Gingerols (ginger )Hepoxilin A3 Hepoxilin B3 Hydrogen peroxide Icilin Isothiocyanate Ligustilide (celery , Angelica acutiloba Linalool (Sichuan pepper , thyme )Methylglyoxal Methyl salicylate (wintergreen )N-Methylmaleimide Nicotine (tobacco )Oleocanthal (olive oil )Paclitaxel (Pacific yew )Paracetamol (acetaminophen) PF-4840154 Phenacyl chloride Polygodial (Dorrigo pepper )Shogaols (ginger , Sichuan and melegueta peppers )Tear gases Tetrahydrocannabinol (cannabis) Thiopropanal S-oxide (onion )Umbellulone (Umbellularia californica )WIN 55,212-2 Blockers
TRPC
TRPM
TRPML
TRPP
TRPV
Activators
2-APB 5',6'-EET 9-HODE 9-oxoODE 12S-HETE 12S-HpETE 13-HODE 13-oxoODE 20-HETE α-Sanshool (ginger , Sichuan and melegueta peppers )Allicin (garlic )AM404 Anandamide Bisandrographolide (Andrographis paniculata Camphor (camphor laurel , rosemary , camphorweed , African blue basil , camphor basil)< !--TRPV1 and TRPV3-->Cannabidiol (cannabis )Cannabidivarin (cannabis )Capsaicin (chili pepper )Carvacrol (oregano , thyme , pepperwort, wild bergamot, others)DHEA Diacyl glycerol Dihydrocapsaicin (chili pepper )Estradiol Eugenol (basil , clove )Evodiamine (Euodia ruticarpa Gingerols (ginger )GSK1016790A Heat Hepoxilin A3 Hepoxilin B3 Homocapsaicin (chili pepper )Homodihydrocapsaicin (chili pepper )Incensole (incense )Lysophosphatidic acid Low pH (acidic conditions)
Menthol (mint )N-Arachidonoyl dopamine N-Oleoyldopamine N-Oleoylethanolamide Nonivamide (PAVA) (PAVA spray )Nordihydrocapsaicin (chili pepper )Paclitaxel (Pacific yew )Paracetamol (acetaminophen) Phorbol esters (e.g., 4α-PDD )Piperine (black pepper , long pepper) Polygodial (Dorrigo pepper )Probenecid Protons RhTx Rutamarin (Ruta graveolens Resiniferatoxin (RTX) (Euphorbia resinifera /pooissonii Shogaols (ginger , Sichuan and melegueta peppers )Tetrahydrocannabivarin (cannabis )Thymol (thyme , oregano )Tinyatoxin (Euphorbia resinifera /pooissonii Tramadol Vanillin (vanilla )Zucapsaicin Blockers
Original source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dihydrocapsaicin. Read more