Chemistry:Hydroxy alpha sanshool
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
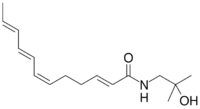
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2E,6Z,8E,10E)-N-(2-Hydroxy-2-methylpropyl)dodeca-2,6,8,10-tetraenamide | |
| Other names
Hydroxy-α-sanshool
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H25NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 263.381 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Hydroxy-alpha-sanshool is a molecule found in plants from the genus Zanthoxylum. It is believed to be responsible for the numbing and tingling sensation caused by eating food cooked with Sichuan peppercorns and Uzazi.
The term sanshool in the compound's name is derived from the Japanese term for the Japanese pepper, sanshō (山椒) (literally, mountain pepper), to which was appended the suffix -ol, indicating an alcohol.
Mechanism
This section is missing information about RA1 afferent fiber, 50Hz [PMID 24026819]. (October 2021) |
The chemical structure of hydroxy-alpha sanshool is similar to that of capsaicin, but the mechanism of action by which it induces nerve sensations has been a matter of debate. Although the compound is an agonist at the pain integration channels TRPV1 and TRPA1 like capsaicin, newer evidence suggests that the tandem pore domain potassium channels KCNK3, KCNK9, and KCNK18 are primarily responsible for sanshool's effects.[1]
Hydroxy-alpha sanshool excites D-hair afferent nerve fibers, a distinct subset of the sensitive light touch receptors in the skin, and targets novel populations of Aβ and C-fiber nerve fibers.[2]
Extraction
To isolate the molecule from the pepper in form of an extract, steam distillation can be used: Dried peels of the fruit are immersed in a mixture of lower alcohols (for example ethanol) and water with a mass percentage between 35-65% of the alcohol. The solution gets heated up in the process of steam distillation where the aqueous part evaporates and takes parts of the hydroxy-alpha- sanshool up, too. The distillate separates in two phases: the aqueous ethanol phase and the oil phase which contains the desired molecule.
Steam distillation extraction methods demonstrate yields of approximately 60%.[3]
See also
- Spilanthol
References
- ↑ "Pungent agents from Szechuan peppers excite sensory neurons by inhibiting two-pore potassium channels". Nat. Neurosci. 11 (7): 772–9. July 2008. doi:10.1038/nn.2143. PMID 18568022.
- ↑ Lennertz, Richard C; Tsunozaki, Makoto; Bautista, Diana M; Stucky, Cheryl L (24 Mar 2010). "Physiological basis of tingling paresthesia evoked by hydroxy-α-sanshool". J. Neurosci. (Society for Neuroscience) 30 (12): 4353–4361. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4666-09.2010. PMID 20335471.
- ↑ Schlander, David; Schleif, Chiara; Schnell, Maxim; Roumeliotis, Paul. Hydroxy-alpha-sanshool. Technische Universität Darmstadt. pp. 2. https://www.chemie.tu-darmstadt.de/media/ak_fessner/damocles_pdf/2019/Hydroxy-alpha-sanshool.pdf.
