Chemistry:Lorglumide
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
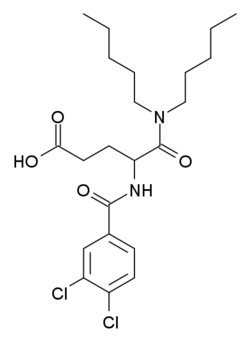
| Other names | 4-[(3,4-dichlorobenzoyl)amino]-5-(dipentylamino)-5-oxopentanoic acid |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H32Cl2N2O4 |
| Molar mass | 459.41 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Lorglumide (CR-1409) is a drug which inhibits gastrointestinal motility and reduces gastric secretions, acting as a cholecystokinin antagonist,[1] with fairly high selectivity for the CCKA subtype.[2] It has been suggested as a potential treatment for a variety of gastrointestinal problems including stomach ulcers, irritable bowel syndrome, dyspepsia, constipation and pancreatitis, as well as some forms of cancer, but animal and human testing has produced inconsistent results and no clear therapeutic role has been established, although it is widely used in scientific research.[3][4][5][6]
References
- ↑ "Pharmacological properties of lorglumide as a member of a new class of cholecystokinin antagonists". Arzneimittel-Forschung 37 (11): 1265–8. November 1987. PMID 3440035.
- ↑ "Selective CCK-A but not CCK-B receptor antagonists inhibit HT-29 cell proliferation: synergism with pharmacological levels of melatonin". Journal of Pineal Research 39 (3): 243–50. October 2005. doi:10.1111/j.1600-079X.2005.00239.x. PMID 16150104.
- ↑ "Recent advances in the chemistry of cholecystokinin receptor ligands (agonists and antagonists)". Current Medicinal Chemistry 6 (6): 433–55. June 1999. doi:10.2174/0929867306666220330183253. PMID 10213792.
- ↑ "Therapeutic and chemical developments of cholecystokinin receptor ligands". Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs 9 (1): 129–46. January 2000. doi:10.1517/13543784.9.1.129. PMID 11060666.
- ↑ "Cholecystokinin antagonists: pharmacological and therapeutic potential". Medicinal Research Reviews 23 (5): 559–605. September 2003. doi:10.1002/med.10042. PMID 12789687.
- ↑ "Progress in developing cholecystokinin (CCK)/gastrin receptor ligands that have therapeutic potential". Current Opinion in Pharmacology 7 (6): 583–92. December 2007. doi:10.1016/j.coph.2007.09.011. PMID 17997137.
 |

