Software:Video games and Linux
This article may contain excessive or inappropriate references to self-published sources. (May 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
| Video games |
|---|
Linux-based operating systems can be used for playing video games. Because fewer games natively support the Linux kernel than Windows, various software has been made to run Windows games, software, and programs, such as Wine, Cedega, DXVK, and Proton, and managers such as Lutris and PlayOnLinux. The Linux gaming community has a presence on the internet with users who attempt to run games that are not officially supported on Linux.
History

Popular early titles included Netrek and the various XAsteroids, XBattle, XBill, XBoing, X-Bomber, XConq, XDigger, XEmeraldia, XEvil, XGalaga, XGammon, XLander, XLife, XMahjong, XMine, XSoldier, XPilot, XRobots, XRubiks, XShogi, XScavenger, XTris, XTron, XTic and XTux games using the X Window System.[1][2] Other games targeted or also supported the SVGAlib library allowing them to run without a windowing system,[3] such as LinCity, Maelstrom, Sasteroids,[4] and SABRE.[5] The General Graphics Interface was also used[6] for games like U.R.B.A.N The Cyborg Project[7] and Dave Gnukem[8] ported from MS-DOS. As the operating system itself grew and expanded, the amount of free and open-source games also increased in scale and complexity, with both clones of historically popular releases beginning with BZFlag, LinCity, and Freeciv,[9] as well as original creations such as Rocks'n'Diamonds, Cube, The Battle for Wesnoth, and Tux Racer.[10]
1994
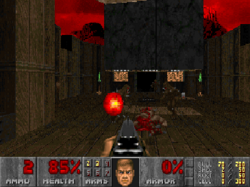
The beginning of Linux as a gaming platform for commercial video games is widely credited to have begun in 1994 when Dave D. Taylor ported the game Doom to Linux, as well as many other systems, during his spare time.[11][12] Shareware copies of the game were included on various Linux discs,[13] including those packed in with reference books.[14][15][16]
Ancient Domains of Mystery was also released for Linux in 1994 by Thomas Biskup, building on the roguelike legacy of games such as Moria and its descendent Angband, but more specifically Hack and NetHack.
1995
From there Taylor would also help found the development studio Crack dot Com, which released the video game Abuse,[17] with the game's Linux port even being distributed by Linux vendors Red Hat[18] and Caldera.[19] The studio's never finished Golgotha was also slated to be released by Red Hat in box.[20]
In 1991 DUX Software contracted Don Hopkins to port SimCity to Unix,[21] which he ported to Linux in 1995 and eventually released as open source for the OLPC XO Laptop.[22]
A website called The Linux Game Tome, also known as HappyPenguin after its URL, was begun by Tessa Lau in 1995 to catalogue games created for or ported to Linux from the SunSITE game directories as well as other classic X11 games for a collection of just over 100 titles.[23]
1996–1997
id Software, the original developers of Doom, also continued to release their products for Linux. Their game Quake was ported to Linux via X11 in 1996, once again by Dave D. Taylor working in his free time.[24][25] An SVGALib version was also later produced by Greg Alexander in 1997 using recently leaked source code, but was later mainlined by id.[26] Later id products continued to be ported by Zoid Kirsch[27] and Timothee Besset,[28] a practice that continued until the studio's acquisition by ZeniMax Media in 2009.[29] Initially, Zoid Kirsch was responsible for maintaining the Linux version of Quake and porting QuakeWorld to Linux.
Inner Worlds was released for and developed on Linux.[30] The UNIX Book of Games, a 1996 publication by Janice Winsor, described various games with an accompanying CD-ROM containing executables and source code for Linux and SCO Unix.[31]
1998
The Linux Game Tome was taken over by Bob Zimbinski in 1998 eventually growing to over 2000 entries, sponsored by retailer Penguin Computing and later LGP until it went down in 2013, although mirrors still exist.[32][33]
The site LinuxGames covered news and commentary from November 1998 until its host Atomicgamer went down in 2015.[34][35] It was established by Marvin Malkowski, head of the Telefragged gaming network, alongside Al Koskelin and Dustin Reyes;[36] Reyes died 8 August 2023.[37]
Zoid Kirsch from id Software ported Quake II to Linux. Two programmers from Origin ported Ultima Online to Linux and MP Entertainment released an adventure game Hopkins FBI for Linux[38][39]
On 9 November 1998, a new software firm called Loki Software was founded by Scott Draeker, a former lawyer who became interested in porting games to Linux after being introduced to the system through his work as a software licensing attorney.[40] Loki, although a commercial failure, is credited with the birth of the modern Linux game industry.[41] Loki developed several free software tools, such as the Loki installer (also known as Loki Setup),[42] and supported the development of the Simple DirectMedia Layer,[43] as well as starting the OpenAL audio library project.[44][45] These are still often credited as being the cornerstones of Linux game development.[46] They were also responsible for bringing nineteen high-profile games to the platform before its closure in 2002.
1999
Loki published Software:Civilization: Call to Power, Eric's Ultimate Solitaire, Heretic II, Heroes of Might and Magic III, Railroad Tycoon II: Gold Edition, Quake III: Arena, and Unreal Tournament for Linux.[47]
Loki's initial success also attracted other firms to invest in the Linux gaming market, such as Tribsoft, Hyperion Entertainment, Macmillan Digital Publishing USA, Titan Computer, Xatrix Entertainment, Philos Laboratories, and Vicarious Visions.[48]
The ports of Quake and Quake II were released physically by Macmillan Computer Publishing USA,[49] while Quake III was released for Linux by Loki Software.[50] Red Hat had previously passed on publishing Quake for Linux, since it was not open-source at the time.[51]
Philos Laboratories released a Linux version of Theocracy on the retail disk. Ryan "Ridah" Feltrin from Xatrix Entertainment released a Linux version of Software:Kingpin: Life of Crime.
BlackHoleSun Software released Krilo and Futureware 2001 released a trading simulation Würstelstand for Linux.[52]
The Indrema Entertainment System (also known as the L600) was also in development since 1999 as a Linux-based game console and digital media player,[53][54][55] but production halted in 2001 due to a lack of investment,[56][57] although the TuxBox project attempted a continuation.[58]
2000
Loki published Descent 3, Heavy Gear II, SimCity 3000, and Soldier of Fortune for Linux. They also released the expansion Descent 3: Mercenary as the downloadable Linux installer.[47]
Hyperion Entertainment ported Sin to Linux published by Titan Computer. Vicarious Visions ported the space-flight game Terminus to Linux. Mountain King Studios released a port of Software:Raptor: Call of the Shadows and CipSoft published the Linux client of Tibia.[59]
Boutell.com ported Software:Exile III: Ruined World to Linux, which was a game created by Spiderweb Software.
During this time Michael Simms founded Tux Games, one of the first online Linux game retailers,[60] later followed by Fun 4 Tux,[61] Wupra,[62] ixsoft, and LinuxPusher.[63]
The period also saw a number of commercial compilations released,[64] such as 100 Great Linux Games by Global Star Software,[65] Linux Games by Walnut Creek CDROM,[66][67] Linux Games++ by Pacific Hitech,[68][69] Linux Cubed Series 8 LINUX Games by Omeron Systems,[70] Best Linux Games by SOT Finnish Software Engineering,[71][72][73] LinuxCenter Games Collection,[74] Linux Games & Entertainment for X Windows by Hemming,[75][76] Linux Spiele & Games by more software,[77] Linux Spiele by Franzis Verlag,[78] and play it! Linux: Die Spielesammlung by S.A.D. Software.[79]
Numerous Linux distributions and collections packed in Loki games and demos,[80] including Red Hat Linux,[81] Corel Linux and WordPerfect Office,[82][83] and the complete Eric's Ultimate Solitaire bundled with PowerPlant by TheKompany.[84] Easy Linux 2000 similarly bundled in a copy of the Linux version of Hopkins FBI.[85]
2001
Loki published Heavy Metal: F.A.K.K.², Software:Kohan: Immortal Sovereigns, Mindrover: The Europa Project, Software:Myth II: Soulblighter, Postal Plus, Rune, Rune: Halls of Valhalla, Sid Meier's Alpha Centauri, and Tribes 2 for Linux.[47]
Linux Game Publishing was founded in 2001 in response to the impending demise of Loki. Creature Labs ported Creatures: Internet Edition to Linux, which was published by LGP.
Hyperion Entertainment ported Shogo: Mobile Armor Division to Linux, and Tribsoft created a Linux version of Jagged Alliance 2, both published by Titan Computer.
Illwinter Game Design released Conquest of Elysium II and Dominions: Priests, Prophets & Pretenders for Linux. Introversion Software released Uplink for Linux.
BlackHoleSun Software released Bunnies, and worked on Atlantis: The Underwater City – Interactive Storybook published by Sterling Entertainment.[52]
GLAMUS GmbH released a Linux version of their game Mobility and Oliver Hamann released the driving game Odyssey by Car.[86]
The company TransGaming marketed as a monthly subscription its own proprietary fork of Wine called WineX in October 2001, later renamed Cedega in 2004 and discontinued in 2011, which aimed for greater compatibility with Microsoft Windows games.
A special Gaming Edition of Mandrake Linux 8.1 was released that featured WineX packed in with The Sims.[87] The fact that the fork of Wine did not release source back to the main project was also a point of contention, despite promises to release code after achieving a set number of subscribers.[88][89]
The release of ScummVM in 2001,[90] Dosbox in 2002,[91] as well as video game console emulators like MAME from 1997 and released as open source in 2016, helped make Linux a viable platform for retro gaming (facilitated by the RetroArch frontend since 2010).[92][93] This is especially the case for the GP2X series of handheld game consoles by GamePark Holdings in addition to the community driven Pandora and DragonBox Pyra. Dedicated emulation setups are also built on single-board computers like the Raspberry Pi released in 2012, which are most often Linux based including with Raspberry Pi OS.[94] Wine is also useful for running older Windows games,[95] including 16-bit and even some 32-bit applications that no longer work on modern 64-bit Windows.[96] The Sharp Zaurus personal data assistants adopted a Linux derived system called OpenZaurus, which attracted its own gaming scene.[97][98] This was also the case with the Agenda VR3, advertised as the first "pure Linux PDA".[99][100]
2002

After Loki's closure, the Linux game market experienced some changes.[101] Although some new firms, such as Linux Game Publishing and RuneSoft, would largely continue the role of a standard porting house,[102] the focus began to change with Linux game proponents encouraging game developers to port their game products themselves or through individual contractors.[103] Influential to this was Ryan C. Gordon, a former Loki employee who would over the next decade port several game titles to multiple platforms, including Linux.[104]
Ryan ported America's Army, Candy Cruncher, Serious Sam: The First Encounter, and Unreal Tournament 2003 to Linux.[105][106][107]
Linux Game Publishing had initially tried to pick up the support rights to many of Loki's titles, but in the end it was only able to acquire the rights to MindRover: The Europa Project. They released the updated version of Mindrover and its downloadable update for owners of the old Loki version.[108]
Return to Castle Wolfenstein was released for Linux and with the Linux port done in-house by Timothee Besset[109]
Chronic logic released Bridge Construction Set and Triptych for Linux.
Sunspire Studios released in retail commercial expansion of the game titled Tux Racer.[110]
2003
Ryan ported Devastation, Medal of Honor Allied Assault, and Serious Sam: The Second Encounter to Linux.[107]
LGP took interest in publishing Pyrogon games on physical CDs and they released Candy Cruncher.[111] Mathieu Pinard from Tribsoft got LGP in contact with Cyberlore to save the Linux port of Majesty because Titan Computer get out of Linux publishing. This turn of events helped LGP to release a Majesty for Linux after Pinard closed his company in 2002.[112]
Timothee Bessett from id Software ported Wolfenstein: Enemy Territory to Linux.[113]
Around this time many companies, starting with id Software, also began to release legacy source code leading to a proliferation of source ports of older games to Linux and other systems.[114] This also helped expand the already existing free and open-source gaming scene, especially with regards to the creation of free first person shooters.[115] In addition, numerous game engine recreations have been produced to varying levels of accuracy using reverse engineering or underlying engine code supporting the original game files including on Linux and other niche systems.[116][117]
2004
Ryan ported Unreal Tournament 2004 to Linux for Epic Games[118] and Timothee Bessett from id Software ported Doom 3 to Linux.[113]
David Hedbor, founder and main programmer of Eon Games ported NingPo MahJong and Hyperspace Delivery Boy! to Linux, which later were published by LGP.[119]
2005–2007
Ryan ported Postal²: Share the Pain to Linux published by LGP.[120]
CodeWeavers offered an enhanced version of Wine called CrossOver Games.[121][122] The reliance on such compatibility layers remains controversial with concerns that it hinders growth in native development,[123][124] although this approach was defended based on Loki's demise.[125][126] PlayOnLinux, established in 2007, provides a community alternative,[127] with various guides being written on how to get games to run through Wine.[128]
2008–2011
Relative sales of first Humble Indie Bundle across systems[129]
The Linux gaming market also started to experience some growth towards the end of the decade with the rise of independent video game development,[130] with many "indie" developers favouring support for multiple platforms.[131] The Humble Indie Bundle initiatives inaugurated in 2010 helped to formally demonstrate this trend,[132] with Linux users representing a sizable population of their purchase base, and as being the most consistently financially generous in spending.[133][134] The Humble Indie Bundle V in 2012 faced controversy for featuring a Wine-based release of Limbo prepared by CodeWeavers,[135] while a native version was later released in 2014.[136] Humble eventually began offering Windows-only games in their bundles and on their store.[137][138]
In 2009, the small indie game company Entourev LLC published Voltley to Linux which is the first commercial exclusive game for this operating system.[139][140] In the same year, LGP released Shadowgrounds which was the first commercial game for Linux using the Nvidia PhysX middleware.[141] The GamingOnLinux website was launched on 4 July 2009, and eventually succeeded LinuxGames as the main source of news and commentary.[142]
The release of a Linux version of Desura in 2011,[143] a digital distribution platform with a primary focus on small independent developers, was heralded by several commentators as an important step to greater acknowledgement of Linux as a gaming platform.[130][144][145] Shortly before this, Canonical launched the Ubuntu Software Center which also sold digital games.[146] The digital store Gameolith also launched in 2011 focused principally on Linux before expanding in 2012 and closing in 2014.[147][148]
2012–2016
In July 2012, game developer and content distributor Valve announced a port of their Source engine for Linux as well as stating their intention to release their Steam digital distribution service for Linux.[149][150][151] The potential availability of a Linux Steam client had already attracted other developers to consider porting their titles to Linux,[145][152][153][154] including previously Mac OS only porting houses such as Aspyr Media and Feral Interactive.[155]
In November 2012, Unity Technologies ported their Unity engine and game creation system to Linux starting with version 4. All of the games created with the Unity engine can now be ported to Linux easily.[156]
In September 2013, Valve announced that they were releasing a gaming oriented Linux based operating system called SteamOS with Valve saying they had "come to the conclusion that the environment best suited to delivering value to customers is an operating system built around Steam itself."[145][157] This was used for their Steam Machine platform released on 10 November 2015, and discontinued in 2018.[158]
In March 2014, GOG.com announced they would begin to support Linux titles on their DRM free store starting the same year, after previously stating they would not be able due to too many distributions.[159] GOG.com began their initial roll out on 24 July 2014, by offering 50 Linux supporting titles, including several new to the platform.Cite error: Closing </ref> missing for <ref> tag The free software Lutris started in 2010,[160] GameHub from 2019,[161] MiniGalaxy from 2020,[162] and the Heroic Games Launcher from 2021,[163] offer support for GOG as well as the Epic Games Store, Ubisoft Connect and Origin.
In March and April 2014, two major developers Epic Games and Crytek announced Linux support for their next generation engines Unreal Engine 4 and CryEngine respectively.[164][165]
Towards the end of 2014, the game host itch.io announced that Linux would be supported with their developing open source game client.[166] This was fully launched simultaneously on Windows, Mac OS X and Linux on 15 December 2015.[167] The service had supported Linux since it was first unveiled on 3 March 2013, with creator Leaf Corcoran personally a Linux user.[168] The similar Game Jolt service also supports Linux and has an open source client released on 13 January 2016.[169][170] GamersGate also sells games for Linux.[171][172]
In 2015, started OpenXRay project — an improved version of the X-Ray Engine, the game engine used in the world-famous S.T.A.L.K.E.R, with Linux and macOS support.[173][174][175][176]
In July 2015, LinuxGames website shut down.[177]
2017–present

On 22 August 2018, Valve released their fork of Wine called Proton, aimed at gaming.[178] It features some improvements over the vanilla Wine such as Vulkan-based DirectX 11 implementation, Steam integration, better full screen and game controller support and improved performance for multi-threaded games.[179] It has since grown to include support for DirectX 9[180] and DirectX 12[181] over Vulkan. The itch.io app added its own Wine integration in June 2020,[182] while Lutris and PlayOnLinux are long-standing independent solutions for compatibility wrappers.[183][184]
As with Wine and Cedega in the past, concerns have been raised over whether Proton hinders native development more than it encourages use of the platform.[185][186] Prodeus dropped native support in favour of Proton shortly before final release[187] and Arcen Games cancelled planned native support for Heart of the Machine.[188] Valve has expressed no preference over Proton or native ports among developers.[189]
On 25 February 2022, Valve released Steam Deck, a handheld game console running SteamOS 3.0.[190][191] The deployment of Proton and other design decisions were based on the limited response to their previous Steam Machines.[192] Linux was also used as a base for several nostalgia consoles, including the Neo Geo X,[193] NES Classic Edition,[194] Super NES Classic Edition,[195] Sega Genesis Mini,[196] Intellivision Amico,[197] Lichee Pocket 4A,[198] and the Atari VCS.[199] It also powers the more general Polymega,[200] Anbernic RG351 and 5G552, as well as the Game Gadget,[201] Evercade, VS, EXP and Super Pocket retrogaming consoles by Blaze Entertainment.[202][203]
As of early 2023, the retro game store Zoom Platform was enhancing Linux support on their available titles.[204]
Commercial games for non-x86 instruction sets

Some companies ported games to Linux running on instruction sets other than x86, such as Alpha, PowerPC, SPARC, MIPS or ARM.
Loki Entertainment Software ported Software:Civilization: Call to Power, Eric's Ultimate Solitaire, Heroes of Might and Magic III, Software:Myth II: Soulblighter, Railroad Tycoon II Gold Edition and Sid Meier's Alpha Centauri with Alien Crossfire expansion pack to Linux PowerPC.[205] They also ported Civilization: Call to Power, Eric's Ultimate Solitaire, Sid Meier's Alpha Centauri with Alien Crossfire expansion pack to Linux Alpha and Civilization: Call to Power, Eric's Ultimate Solitaire to Linux SPARC.[206]
Linux Game Publishing published Candy Cruncher, Majesty Gold, NingPo MahJong and Soul Ride to Linux PowerPC. They also ported Candy Cruncher, Soul Ride to Linux SPARC and Soul Ride to Linux Alpha.[207][208]
Illwinter Game Design ported Software:Dominions: Priests, Prophets and Pretenders, Software:Dominions II: The Ascension Wars and Dominions 3 to Linux PowerPC, as well as Conquest of Elysium 3, Software:Dominions 4: Thrones of Ascension to Raspberry Pi.[209]
Hyperion Entertainment ported Sin to Linux PowerPC published by Titan Computer[210] and Gorky 17 to Linux PowerPC which later was published by LGP.[211]
Runesoft hired Gunnar von Boehn which ported Robin Hood – The Legend of Sherwood to Linux PowerPC.[212] Later Runesoft ported Airline Tycoon Deluxe to Raspberry Pi was running Debian GNU/Linux. Iain McLeod ported Spheres of Chaos to Linux on the PlayStation 2 consoles and later re-released it as a freeware game.
Market share
The Steam Hardware Survey reports that as of January 2024, 2% of users are using some form of Linux as their platform's primary operating system.[213] The Unity game engine used to[214] make their statistics available and in March 2016 reported that Linux users accounted for 0.4% of players.[215] In 2010, in the first Humble Bundle sales, Linux accounted for 18% of purchases.[216]
Supported hardware

Performance
In 2013, tests by Phoronix showed real-world performance of games on Linux with proprietary Nvidia and AMD drivers were mostly comparable to results on Windows 8.1.[217] Phoronix found similar results in 2015,[218] though Ars Technica described a 20% performance drop with Linux drivers.[219]
Software architecture
Linux kernel
The subsystems already mainlined and available in the Linux kernel are most probably performant enough so to not impede the gaming experience in any way, however additional software is available, such as e.g. the Brain Fuck Scheduler (a process scheduler) or the Budget Fair Queueing (BFQ) scheduler (an I/O scheduler).[220]
Similar to the way the Linux kernel can be, for example, adapted to run better on supercomputers, there are adaptations targeted at improving the performance of games. A project concerning itself with this issue is called Liquorix.[221][222]
Available software for video game designers
Game creation systems
Several game creation systems can be run on Linux, such as Game Editor, GDevelop, Construct and Stencyl, as well as beta versions of GameMaker.[223] A Linux version of Clickteam Fusion 3 was mentioned, but has yet to be released.[224] The Godot, Defold, and Solar2D game engines also supports creating games on Linux,[225] as do the commercial UnrealEd[226] and Unity Editor,[227][228] The visual programming environments Snap!, Scratch 1.X[229] and Tynker are Linux compatible. Enterbrain's RPG Maker MV was released for Linux.[230] In addition, open-source, cross-platform clones of the RPG Maker series exist such as Open RPG Maker, MKXP and EasyRPG,[231] as well as the similar OHRRPGCE and Solarus.[232] The Adventure Game Studio editor is not yet ported to Linux, although games made in it are compatible, and the Wintermute and SLUDGE[233] adventure game engines are available. ZGameEditor,[234] Novashell,[235] GB Studio,[236] and the ZZT inspired MegaZeux[237] are also options. Versions of Mugen were made available for Linux,[238] and open-source re-implementations such as IKEMEN Go are compatible.[239] The JavaScript based Ct.js[240] Pixelbox.js,[241] and Superpowers[242] are also options.
Level editors
Various level editors exist for Linux, such as wxqoole, GtkRadiant, TrenchBroom[243][244] and J.A.C.K.[245] for the id Tech engines and related, Eureka,[246] SLADE[247] and ReDoomEd[248] for the Doom engine, and the general purpose tile map editors LDtk,[249] Ogmo,[250] and Tiled.[251]
Debuggers
Several game development tools have been available for Linux, including GNU Debugger, LLDB, Valgrind, glslang and others. VOGL, a debugger for OpenGL was released on 12 March 2014.
Available interfaces and SDKs
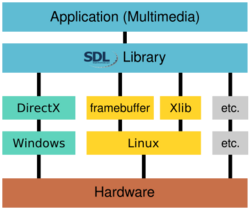
There are multiple interfaces and Software Development Kits available for Linux, and almost all of them are cross-platform. Most are free and open-source software subject to the terms of the zlib License, making it possible to static link against them from fully closed-source proprietary software. One difficulty due to this abundance of interfaces, is the difficulty for programmers to choose the best suitable audio API for their purpose. The main developer of the PulseAudio project, Lennart Poettering, commented on this issue.[252] Physics engines, audio libraries, that are available as modules for game engines, have been available for Linux for a long time.[time needed] The book Programming Linux Games covers a couple of the available APIs suited for video game development for Linux, while The Linux Programming Interface covers the Linux kernel interfaces in much greater detail.
| Library | License | in | Language bindings | Back-ends | Description | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Icon | Name | Official | 3rd-party | Linux | Windows | macOS | Other | |||
| Allegro | zlib License | C | Yes | Yes | Yes | Android, iOS | ||||
| ClanLib | zlib License | C++ | Python, Lua, Ruby | Yes | Yes | N/A | N/A | |||
| GLFW | zlib License | C | N/A | Ada, C#, Common Lisp, D, Go, Haskell, Java, Python, Rebol, Red, Ruby, Rust | Yes | Yes | Yes | a small C library to create and manage windows with OpenGL contexts, enumerate monitors and video modes, and handle input | ||
| Grapple | LGPL-2.1+ | C | Yes | Yes | Yes | free software package for adding multiplayer support | ||||
| Nvidia GameWorks | Proprietary | Unknown | WIP | Yes | N/A | N/A | As the result of their cooperation with Valve, Nvidia announced a Linux port of GameWorks.[253] As of June 2014, PhysX, and OptiX have been available for Linux for some time. | |||
| OpenPlay | APSL | C | Yes | Yes | Yes | N/A | networking library authored by Apple Inc. | |||
| Pygame | LGPL-2.1 | Python | Yes | Yes | Yes | build over SDL | ||||
| RakNet | 3-clause BSD | C++ | C++, C# | N/A | Yes | Yes | Yes | PlayStation 3, iOS, ... | game network engine for multi-player | |
| SDL | zlib License | C | C | C#, Pascal, Python, Gambas | EGL, Xlib, GLX? | GDI, Direct3D | Quartz, Core OpenGL? | PSP-stuff | a low-level cross-platform abstraction layer | |
| SFML | zlib License | C++ | C, D, Python, Ruby, OCaml, .Net, Go | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||
| wxWidgets | LGPL-like | C++ | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||||
Available middleware
Beside majority of the software which acts as an interface to various subsystems of the operating system, there is also software which can be simply described as middleware. A multitude of companies exist worldwide, whose main or only product is software that is meant to be licensed and integrated into a game engine. Their primary target is the video game industry, but the film industry also uses such software for special effects. Some very few well known examples are
- classical physics: Havok, Newton Game Dynamics and PhysX
- audio: Audiokinetic Wwise, FMOD
- other: SpeedTree
A significant share of the available middleware already runs natively on Linux, only a very few run exclusively on Linux.
Available IDEs and source code editors
Numerous source code editors and IDEs are available for Linux, among which are Visual Studio Code, Sublime Text, Software:Code::Blocks, Qt Creator, Emacs, or Vim.
Multi-monitor
A multi-monitor setup is supported on Linux at least by AMD Eyefinity & AMD Catalyst, Xinerama and RandR on both X11 and Wayland. Software:Serious Sam 3: BFE is one example of a game that runs natively on Linux and supports very high resolutions and is validated by AMD to support their Eyefinity.[254] Civilization V is another example, it even runs on a "Kaveri" desktop APU in 3x1 portrait mode.[255]
Voice over IP
The specifications of the Mumble protocol are freely available and there are BSD-licensed implementations for both servers and clients. The positional audio API of Mumble is supported by e.g. Software:Cube 2: Sauerbraten.
Wine
Wine is a compatibility layer that provides binary compatibility and makes it possible to run software, that was written and compiled for Microsoft Windows, on Linux. The Wine project hosts a user-submitted application database (known as Wine AppDB) that lists programs and games along with ratings and reviews which detail how well they run with Wine. Wine AppDB also has a commenting system, which often includes instructions on how to modify a system to run a certain game which cannot run on a normal or default configuration. Many games are rated as running flawlessly, and there are also many other games that can be run with varying degrees of success. The use of Wine for gaming has proved controversial in the Linux community as some feel it is preventing, or at least hindering, the further growth of native gaming on the platform.[256][257]
Emulators
There are numerous emulators for Linux. There are also APIs, virtual machines, and machine emulators that provide binary compatibility:
- Anbox and Waydroid for the Android operating system;
- Basilisk II for the 68040 Mac;
- DOSBox and DOSEMU for MS-DOS and compatibles;
- DeSmuME and melonDS for the Nintendo DS;
- Dolphin for the GameCube, Wii, and the Triforce;
- FCEUX, Nestopia and TuxNES for the Nintendo Entertainment System;
- Flashpoint for Adobe Flash;
- Frotz for Z-Machine text adventures;
- Fuse for the Sinclair ZX Spectrum;
- Hatari for the Atari ST, STe, TT and Falcon;
- gnuboy for the Nintendo Game Boy and Game Boy Color;
- MAME for arcade games (and previously MESS for multiple hardware platforms);
- Mednafen and Xe emulating multiple hardware platforms including some of the above;
- Mupen64Plus and the no longer actively developed original Mupen64 for the Nintendo 64;
- PCSX-Reloaded, pSX and the Linux port of ePSXe for the PlayStation;
- Neko Project for the NEC PC-9801;
- PCSX2 for the PlayStation 2;
- PPSSPP for the PlayStation Portable;
- ScummVM for LucasArts and various other adventure games;
- SheepShaver for the PowerPC Macintosh;
- Snes9x, higan and ZSNES for the Super NES;
- Stella for the Atari 2600;
- UAE for the Amiga;
- VICE for the Commodore 64, 128, VIC-20, Plus/4 and PET;
- VisualBoyAdvance, mGBA and Boycott Advance for the Game Boy Advance;
- Mini vMac and the no longer actively developed original vMac for the 680x0 Macintosh;
Linux homebrew on consoles
Linux has been ported to several game consoles, including the Xbox, PlayStation 2, PlayStation 3, PlayStation 4,[258] GameCube,[259] and Wii which allows game developers without an expensive game development kit to access console hardware. Several gaming peripherals also work with Linux.[260][261]
Types of Linux gaming
Linux gaming can be divided into a number of sub-categories.[262][263][264]
Libre gaming
Libre gaming is a form of Linux gaming that emphasizes libre software, which often includes levels and assets as well as code.[265][self-published source?][266][irrelevant citation]
Native gaming
Native gaming is a form of Linux gaming that emphasizes using only native games or ports and not using emulators or compatibility layers.[256][124][267][268]
DRM-free gaming
DRM-free gaming is a form of Linux gaming that emphasizes boycotting DRM technologies. This can include buying games from GOG.com, certain Humble Bundles or itch.io and avoiding Steam and similar services.[269][270]
Terminal gaming
Terminal gaming is the playing of text-based games from within a console,[271] often programmed within Bash or using libraries such as ncurses.[272][273]
Retro gaming
Retrogaming is the playing of older games[274] using emulators such as MAME or Dosbox,[275] compatibility layers such as Wine and Proton,[276] engine reimplementations and source ports,[277] or even older Linux distributions (including live CDs and live USB, or virtual machines),[278][279] original binaries,[41] and period hardware.[280]
Live gaming
A number of games can be played from live distributions such as Knoppix, allowing easy access for users unwilling to fully commit to Linux.[281] Certain live distros have specially targeted gamers, such as SuperGamer and Linux-Gamers.[282][283]
Browser gaming
Browser gaming is the act of playing online games through a web browser,[284] which has the advantage of largely being platform independent.[285][286] The same largely applies to social network games hosted on social media sites.[287] Older games were largely based on Adobe Flash,[288] while modern ones are mostly HTML5.[289]
Cloud gaming
Cloud gaming is the streaming of games from a central server onto a desktop client.[290] This is another way to play games on Linux that are not natively supported,[291][292] although some cloud services, such as the erstwhile Google Stadia,[293][294] are hosted on Linux[295][296] and Android servers.[297] GamingAnywhere is an open source implementation.[298]
On Windows
Although less exploited than the reverse,[299] as few programs are Linux exclusive,[300] support does exist for running Linux binaries from Windows.[301][302] The Windows Subsystem for Linux allows the running of both command line[303][304] and graphical Linux applications[305] from Windows 10 and Windows 11.[306] An earlier implementation is Cygwin,[307] started by Cygnus Solutions and later maintained by Red Hat,[308] although it has limited hardware access[309] and required adaptation.[310] The use of Wine can even allow for the running of Windows games on Linux from Windows. The LibTAS library for tool assisted speedruns currently recommends WSL to run on Windows.[311] Naughty Dog meanwhile have used Cygwin to run old command-line tools for use in their game development,[312] which is a broader use for the platform.[313] As with running Windows applications on Linux, there is controversy over whether running Linux applications on Windows will dilute interest in Linux as distinct platform,[314] though it has speciality uses.[315]
Android gaming
Originally derived from Linux, the Android mobile operating system has a distinct and popular gaming ecosystem.[316] It has also been used as the base for several game consoles, such as the Nvidia Shield Portable and the Ouya.[317] Popular games include Pokémon Go, Genshin Impact, Software:League of Legends: Wild Rift, Dead Cells and Software:Call of Duty: Mobile.[318] Certain games, such as Minecraft, Stardew Valley, and Papers Please, are available for both Android and desktop Linux.[319]
ChromeOS gaming
ChromeOS is another Linux derived operating system by Google for its Chromebooks,[320] and it too has a dedicated gaming ecosystem.[321][322] Partly owing to a lack of high end graphics hardware,[323][324] it is especially oriented towards cloud gaming[325] via services like GeForce Now and Xbox Cloud Gaming,[326][327] with models featuring Nvidia GPUs ultimately being cancelled.[328] Numerous games for Android have also been made compatible with ChromeOS,[329][330] as well as a standard Linux games,[331][332][333] Windows games via Wine or Proton,[334][335][336] and with browser games also being popular.[337] A version of Steam has been in development for ChromeOS,[338] with third party launchers also available such as the Heroic Games Launcher for the Epic Games Store.[339] Popular titles include Among Us, Genshin Impact, Alto's Odyssey, Roblox, and Fortnite.[340][341][342][343] Skepticism remains for using ChromeOS and Chromebooks as gaming machines.[344][345][346] In August 2025, Google announced that they will end Steam for Chromebook support in 2026.[347]
BSD gaming
Owing to a common Unix-like heritage and free software ethos, many games for Linux are also ported to BSD variants[348] or can be run using compatibility layers such as Linuxulator.[349] BSDi had partnered with Loki Software to ensure its Linux ports ran on FreeBSD.[350] The Mizutamari launcher exists to facilitate running Windows games through Wine,[351] which can still be used standalone.[352] A 2011 benchmark by Phoronix even found certain speed advantages over running games on Linux itself, comparing PC-BSD 8.2 to Ubuntu 11.04.[353] Most BSD systems come with the same pack in desktop games as Linux.[354] The permissive licensing of BSD has also lead to its inclusion in the system software of several game consoles, such as the Sony PlayStation line[355][356] and the Nintendo Switch.[357]
OpenHarmony gaming
HarmonyOS with custom kernel[358] and OpenHarmony-Oniro based operating systems distros[359] of these newer platforms has a dedicated gaming ecosystem with compatibilities with third-party Linux libraries by developers on Linux kernel subsystem such as musl-libc of C standard library that targets the Linux syscall and POSIX APIs compatibility for native compatible games as well as limited virtual machines such as Android-based sandboxed ones.[360][361]
Unix gaming
A further niche exists for running games, either through ports or lxrun,[362] on Solaris[363] and derivatives such as OpenIndiana,[364] Darwin distributions such as PureDarwin,[365] Coherent,[366] SerenityOS,[367][368] Redox OS,[369][370] ToaruOS,[371] Xv6,[372] Fiwix,[373] or on Minix[374] and Hurd based systems.[375] There has been some cross-pollination with purely proprietary Unix derivatives,[376] such as AIX,[377] QNX,[378] Domain/OS,[379] HP-UX,[380] IRIX (see here),[381][382] Xenix,[383] SCO Unix,[384] Unixware,[385] Tru64 UNIX,[386][387] LynxOS (which features inbuilt Linux compatibility[388]), Ultrix,[389] OpenVMS,[390][391] z/OS UNIX System Services,[392] and even A/UX.[393] The games Doom and Quake were developed by id Software on NeXTStep,[394] a forerunner of modern macOS,[395] before being ported to DOS and back to numerous other Unix variants.[396] This involved reaching out to numerous Unix vendors to supply machines to use in the build and testing process.[397]
Fandom

The fandom in the Linux video game community or free/open source video games is very small, almost all medium-sized or mature free video games have a forum or other means of communication.
However, in recent years, there have been no meetups for any of the games, although free video games have been present at free software community events, including FOSDEM, where the video game Luanti[398] usually has its own stand. There have also been online events such as onfoss.
On the other hand, many projects use the sale of merchandise with logos and other images from the video game on T-shirts and other products as one of their sources of funding.
See also
- Directories and lists
- Linux gaming software
- Other articles
- Linux for PlayStation 2
- Sega Lindbergh
References
- ↑ Armstrong, Ryan (18 November 2020). "Old X Games". https://zerker.ca/home/old-x-games.html.
- ↑ Wilson, Hamish (10 January 2022). "Building a Retro Linux Gaming Computer – Part 8: Shovelware with a Penguin". https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2022/01/building-a-retro-linux-gaming-computer-part-8-shovelware-with-a-penguin/.
- ↑ Link, Jay (30 September 1999). "Easy graphics: A beginner's guide to SVGAlib". https://www.developer.com/guides/easy-graphics-a-beginners-guide-to-svgalib/.
- ↑ Pitzel, Brad (12 February 1994). "Sasteroids v1.0 release (vga arcade game)". https://groups.google.com/g/comp.os.linux.announce/c/os3OUbGEbRk/m/G1Nz3lV0AiQJ.
- ↑ Ayers, Larry (1 July 1998). "Sabre: An Svgalib Flight Sim". https://linuxgazette.net/issue30/ayers3.html.
- ↑ Beck, Andreas (1 November 1996). "Linux-GGI Project". https://www.linuxjournal.com/article/160.
- ↑ Wilson, Hamish (12 March 2024). "Building a Retro Linux Gaming Computer Part 40: The Cyborg Project". https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2024/03/building-a-retro-linux-gaming-computer-part-40-the-cyborg-project/.
- ↑ "Software Announcements". 6 January 2000. https://lwn.net/2000/0106/bigpage.php3.
- ↑ Fox, Alexander (5 January 2018). "The Best Open Source Clones of Great Old Games". https://www.maketecheasier.com/best-open-source-clones-of-great-old-games/.
- ↑ Maskara, Swati (3 March 2021). "33 Best Open Source Games That Are Forever Free To Play". TechNorms. https://www.technorms.com/71807/best-open-source-games.
- ↑ Johnson, Michael K. (1 December 1994). "DOOM". Linux Journal. http://www.linuxjournal.com/article/1.
- ↑ Zimbinski, Bob (1 January 1999). "Getting Started with Quake". Linux Journal. http://www.linuxjournal.com/article/3180.
- ↑ Hellums, Duane (1 March 1999). "Red Hat LINUX Secrets, Second Edition". https://www.linuxjournal.com/article/3248. "It would be nice to see some extra CD goodies included, such as Doom and Quake which are freely available elsewhere."
- ↑ Tackett, Jack (1997). Special Edition. Using Linux. United States: Que Corporation. p. 287. ISBN 9780470485460. https://www.abebooks.com/servlet/BookDetailsPL?bi=31119018510&searchurl=an%3Djack%2Btackett%26sortby%3D17%26tn%3Dusing%2Blinux%2Bspecial%2Bedition&cm_sp=snippet-_-srp1-_-title2. "The X Windows version supplied on the accompanying Slackware CD-ROM in the /contrib directory is a complete hareware version. (The Red Hat distribution automatically installs the game during installation.) Although this version runs on 386 computers, it was built to run on high-end 486 systems. If you run DOOM on a 386 with a small amount of physical RAM, be prepared to be disappointed; the game will be too slow to be enjoyable. You need lots of horse-power to play DOOM under Linux."
- ↑ Barkakati, Naba (1996). Linux Secrets. United States: IDG Books Worldwide. p. 96. ISBN 9781568847986. https://books.google.com/books?id=HnqBQgAACAAJ. "This disk set contains a collection of well-known UNIX games (X is not required), such as Hangman, Dungeon, and Snake. The set also includes id Software's DOOM. (This game comes in two versions, one runs under X, and the other runs without X.) You may want to install this disk set just so you can try out DOOM."
- ↑ Parker, Tim (1996). Linux Unleashed. United States: Macmillan Computer Publishing. p. 981. ISBN 0672313723. https://books.google.com/books?id=IZ5kQgAACAAJ. "DOOM - This exciting, though controversially gory, game is now ported to Linux as well. Complete with sound support and exquisite graphics, this Linux port does its DOS counterpart justice."
- ↑ "So Long, Crack.com". loonygames. http://www.loonygames.com/content/1.10/guest/.
- ↑ "Partnership with Crack dot Com Brings Games to Linux" (Press release). Red Hat. 7 October 1997. Retrieved 31 July 2014.
- ↑ Anonymous (2000). Maximum Linux Security: A Hacker's Guide to Protecting Your Linux Server and Workstation, Volume 1. United States: Sams Publishing. p. 121. ISBN 9780672316708. https://books.google.com/books?id=WCfjE_TzmIAC. "A classic, and very easy-to-follow SUID attack is the on the file /usr/lib/games/abuse/ abuse.console—part of a game that was distributed with Open Linux 1.1 and Red Hat 2.1. Yes, you read that right: Even a game can be a security risk to the system."
- ↑ Jebens, Harley (26 April 2000). "Okay, Dave Taylor: Why Linux?". https://www.gamespot.com/articles/okay-dave-taylor-why-linux/1100-2467851/.
- ↑ Sawicki, Antoni (30 December 2022). "SimCity for Unix Liberated". https://virtuallyfun.com/2022/12/30/simcity-for-unix-liberated/.
- ↑ "History and Future of OLPC SimCity / Micropolis". http://www.donhopkins.com/drupal/.
- ↑ "[ANNC The Linux Game Tome on the Web"]. https://groups.google.com/g/comp.os.linux.misc/c/NzXFbdSJ1rY.
- ↑ "'Dave Taylor Interview – game developer'". blankmaninc.com. 27 October 2012. http://www.blankmaninc.com/david-taylor-interview.
- ↑ Mrochuk, Jeff (15 November 2000). "How To Install Quake 1". Linux.com. http://linux.omnipotent.net/article.php?article_id=11261.
- ↑ Wilson, Hamish (27 February 2023). "Building a Retro Linux Gaming Computer – Part 27: Lost Souls". https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2023/02/building-a-retro-linux-gaming-computer-part-27-lost-souls/.
- ↑ Raghavan, Barath; Katz, Jeremy; Moffitt, Jack (19 February 1999). "An interview with Dave "Zoid" Kirsch of linux quake fame". http://linuxpower.org/display_item.phtml?id=105.
- ↑ Reyes, Dustin (22 August 2004). "Interview with id Software's Timothee Besset". http://www.linuxgames.com/?dataloc=articles/ttimo/.
- ↑ Chalk, Andy (6 February 2013). "John Carmack Argues Against Native Linux Games". The Escapist. http://www.escapistmagazine.com/news/view/121945-John-Carmack-Argues-Against-Native-Linux-Games.
- ↑ Hitchens, Joe (19 September 2001). "Internet Based Software Development". Sleepless Software Inc. http://sleepless.com/iw/article.html.
- ↑ Dicks, Steve (December 1998). "REVIEW – The UNIX Book of Games". https://accu.org/bookreviews/1998/dicks_871/.
- ↑ Gasperson, Tina (16 December 2004). "Site review: Linux Game Tome". https://www.linux.com/news/site-review-linux-game-tome.
- ↑ Larabel, Michael (18 November 2010). "LGP Has Been Down For A Month And A Half". https://www.phoronix.com/news/ODc5OA.
- ↑ Stieben, Danny (6 February 2013). "Top 4 Websites To Discover Free Linux Games". Make Use Of. https://www.makeuseof.com/tag/top-4-websites-free-linux-games/.
- ↑ Wagh, Amol (14 September 2011). "Best Web Places to Find Amazing Free Linux Games". Digital Conqueror. https://digitalconqurer.com/general/best-web-places-to-find-amazing-free-linux-games/.
- ↑ Barr, Joe (1 July 1999). "You can tell a lot about an OS from its games". CNN. http://edition.cnn.com/TECH/computing/9907/01/linuxgame.idg/index.html.
- ↑ Dawe, Liam (14 August 2023). "Rest in peace Dustin 'Crusader' Reyes, a pioneer of Linux gaming news". https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2023/08/rest-in-peace-dustin-crusader-reyes-a-pioneer-of-linux-gaming-news/.
- ↑ "Ultima Online for Linux". http://reverser.hut.ru/old/linux.htm.
- ↑ Kuhnash, Jeremy (9 February 2000). "Hopkins FBI". Linux.com. http://linux.omnipotent.net/article.php?article_id=6937.
- ↑ "Interview: Scott Draeker and Sam Lantinga, Loki Entertainment". Linux Journal. 1 August 1999. http://www.linuxjournal.com/article/3521.
- ↑ 41.0 41.1 Lynch, Jim (7 September 2016). "Remembering Loki's Linux games from the '90s". https://www.infoworld.com/article/3117295/remembering-lokis-linux-games-from-the-90s.html.
- ↑ "Interview with Ryan Gordon: Postal2, Unreal & Mac Gaming – Macologist". http://www.macologist.org/viewtopic.php?t=607.
- ↑ Lantinga, Sam (1 September 1999). "SDL: Making Linux fun". http://www-106.ibm.com/developerworks/library/l-making-linux-fun/.
- ↑ Kreimeier, Bernd (1 January 2001). "The Story of OpenAL". Linux Journal. http://www.linuxjournal.com/article/4400.
- ↑ Hills, James. "Loki and the Linux World Expo – GameSpy chats with Linux legend Scott Draeker about the future of Linux gaming". GameSpy. http://archive.gamespy.com/legacy/articles/loki_a.shtm.
- ↑ Foster-Johnson, Eric. "Does Ragnarok for Loki Spell Doom for Linux Games?". http://www.itworld.com/article/2785732/open-source-tools/does-ragnarok-for-loki-spell-doom-for-linux-games-.html.
- ↑ 47.0 47.1 47.2 Mielewczik, Michael. "Spielspass pur. Kommerzielle Linux-Spiele.". PC Magazin LINUX 2/2007: 80–83.
- ↑ Hills, James (1 March 2001). "Is Linux Gaming here to stay?". http://www.gamespy.com/articles/492/492050p1.html.
- ↑ "Macmillan Says 'Let the Linux Games Begin!'; Market Leader in Linux Software & Books Offers 'Quake' & 'Civilization'". 17 June 1999. https://www.thefreelibrary.com/Macmillan+Says+%27Let+the+Linux+Games+Begin%21%27%3B+Market+Leader+in+Linux...-a054913355.
- ↑ Shah, Rawn (9 March 2000). "Quake III Arena on Linux". http://www.cnn.com/2000/TECH/computing/03/09/quake3.linux.idg/index.html.
- ↑ CmdrTaco (5 November 1998). "Red Hat not Interested in Publishing Id Games". http://www.slashdot.org/articles/98/11/05/105224.shtml.
- ↑ 52.0 52.1 Wilson, Hamish (16 January 2023). "Building a Retro Linux Gaming Computer – Part 21: Fluffy Bunnies". https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2023/01/building-a-retro-linux-gaming-computer-part-21-fluffy-bunnies/.
- ↑ Gestalt (21 November 2000). "Indrema to bring Linux to the masses?". https://www.eurogamer.net/article-29793.
- ↑ Shankland, Stephen (2 January 2002). "Game start-up faces major rivals with Linux console". CNET. https://www.cnet.com/culture/game-start-up-faces-major-rivals-with-linux-console/.
- ↑ Manjoo, Farhad (13 March 2001). "Game Arrives Only in Dreams". Wired. https://www.wired.com/2001/03/game-arrives-only-in-dreams/. Retrieved 7 December 2023.
- ↑ Becker, David (2 January 2002). "Plans for Linux game console fizzle". CNET. https://www.cnet.com/culture/plans-for-linux-game-console-fizzle/.
- ↑ Smith, Tony (11 April 2001). "Linux games console fragged". The Register. https://www.theregister.com/2001/04/11/linux_games_console_fragged/.
- ↑ Gross, Grant (18 April 2001). "TuxBox: Rising from Indrema's ashes". https://www.linux.com/news/tuxbox-rising-indremas-ashes/.
- ↑ "The Linux Game Tome: Raptor – Call of the Shadows". http://happypenguin.org/show?Raptor%20-%20Call%20of%20the%20Shadows. on The Linux Game Tome
- ↑ "Linux Game Publishing Blog, LGP History pt 1: How LGP came to be". http://blog.linuxgamepublishing.com/2009/05/15/lgp-history-pt-1-how-lgp-came-to-be/.
- ↑ Dawe, Liam (30 June 2011). "Gameolith – The Linux Game Download Store". https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2011/06/gameolith-the-linuxacircreg-game-download-store/.
- ↑ Bush, Josh (11 September 2018). "Cheese talks to himself (about Proton and the history of modern Linux gaming)". http://cheesetalks.net/proton-linux-gaming-history.php.
- ↑ Larabel, Michael (1 April 2014). "Linux Game Publishing Remains Dormant". https://www.phoronix.com/news/MTY1MDQ.
- ↑ Wilson, Hamish (12 December 2023). "Building a Retro Linux Gaming Computer Part 36: Entertainment for X Windows". https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2023/12/building-a-retro-linux-gaming-computer-part-36-entertainment-for-x-windows/. "While still being the most elaborate, 100 Great Linux Games was far from the only shovelware set of games released for Linux, with several UNIX CD-ROM vendors such as Walnut Creek CDROM and Omeron Systems also seeking a piece of the action for themselves."
- ↑ Ajami, Amer (26 April 2000). "Take-Two Jumps on Linux". https://www.gamespot.com/articles/take-two-jumps-on-linux/1100-2446349/.
- ↑ "Linux Games". http://www.cdrom.com/titles/linux/lingame.phtml.
- ↑ "Walnut Creek CDROM Catalog". Walnut Creek CDROM. 17 December 2000. http://cd.textfiles.com/simtel/simtel0101/catalog.htm. "Linux Games (Linux) – Large collection of games, graphics, sound, and video applications, plus related development tools."
- ↑ "PC CD-ROM – Shareware & utlity". Zeta (Italy): 92. May 1997. https://archive.org/details/Zeta26/page/n91/mode/2up. Retrieved 4 April 2024.
- ↑ "PHT Products". 1998. http://pht.com/products/index.html. "Formerly known as 'Linux Games++', this is a collection of the best entertainment and multimedia programs for the Linux operating system. It also contains multimedia development tools to assist you in creating your own games and multimedia applications for Linux. This is the latest issue, volume 4, and features a new and improved user interface. The CD contains packages for i386, DEC Alpha, and PPC platforms. This product is only available through Walnut Creek CD-ROM."
- ↑ "Linux Cubed Series 8 LINUX Games". 11 December 1997. https://archive.org/details/linux-cubed-series-8-linux-games/.
- ↑ Thomas, Benjamin D. (2 April 2000). "Best Linux". https://www.linux.com/news/best-linux/.
- ↑ Knight, Will (5 February 2000). "CeBIT 2000: "Consumer" Linux from Finland". https://www.zdnet.com/home-and-office/networking/cebit-2000-quotconsumer-quot-linux-from-finland/.
- ↑ "Linux is Best". http://bestlinux.net/en/2000/games.shtml.
- ↑ Wilson, Hamish (8 August 2023). "Building a Retro Linux Gaming Computer Part 31: The Fear of Loss". https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2023/08/building-a-retro-linux-gaming-computer-part-31-the-fear-of-loss/. "I did discover that Phobia III was later packaged as part of the Russian made LinuxCenter Games Collection Vol.2 compilation, a selection of Linux gaming files that was sold on either four CD-ROMs or a single DVD, but this too appeared to have been scrubbed from the internet."
- ↑ Wilson, Hamish (12 December 2023). "Building a Retro Linux Gaming Computer Part 36: Entertainment for X Windows". https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2023/12/building-a-retro-linux-gaming-computer-part-36-entertainment-for-x-windows/.
- ↑ "Linux Products". http://www.hemming.de/english/Products/Linux/linux.html.
- ↑ "SPIELE-TEST: Linux – Spiele & Games". PC Player (Germany): 122. May 2000. https://archive.org/details/PC-Player-German-Magazine-2000-05. Retrieved 2 April 2023.
- ↑ "Linux Spiele". https://gamefaqs.gamespot.com/unixlinux/353404-linux-spiele.
- ↑ "play it! Linux: Die Spielesammlung …the funny side of Linux!". https://www.sockscap64.com/games/game/play-it-linux-die-spielesammlung-the-funny-side-of-linux/.
- ↑ "Loki Software Games Demos". 3 June 2022. https://www.halolinux.us/red-hat-7-2/loki-software-games-demos.html.
- ↑ "Red Hat brings out Linux 7.1". 19 April 2001. https://www.itweb.co.za/content/6GxRKMY8NKY7b3Wj.
- ↑ Menalo, Nikolina (18 May 2000). "Corel puts out the Word on Office 2000". https://www.itworldcanada.com/article/corel-puts-out-the-word-on-office-2000/34230.
- ↑ Knight, Will (9 December 1999). "Corel Linux Deluxe won't cross the pond". https://www.zdnet.com/home-and-office/networking/corel-linux-deluxe-wont-cross-the-pond/.
- ↑ Gilbert, Jim (1 December 2000). "PowerPlant Review". https://www.linuxjournal.com/article/4353.
- ↑ Schürmann, Tim (1 June 2001). "Komplettlösung Hopkins FBI". https://www.linux-community.de/ausgaben/linuxuser/2001/06/komplettloesung-hopkins-fbi/.
- ↑ Wilson, Hamish (4 June 2023). "Building a Retro Linux Gaming Computer Part 29: The Odyssey". https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2023/07/building-a-retro-linux-gaming-computer-part-29-the-odyssey/.
- ↑ Robertson, F. Grant (12 December 2001). "Review: Mandrake 8.1 Gaming Edition opens Linux to more games, more users". https://www.linux.com/news/review-mandrake-81-gaming-edition-opens-linux-more-games-more-users/.
- ↑ Gross, Grant (22 October 2001). "TransGaming, Mandrake team up to bring PC games directly to Linux". http://www.newsforge.com/article.pl?sid=01/10/22/0051250.
- ↑ Vaughan-Nichols, Steven J. (12 June 2008). "Finally, it's time for Wine". https://www.linux.com/news/finally-its-time-wine/. "According to White in a 2006 NewsForge interview, this forking caused Wine’s development to slow down for years. “Historically, the main interest for volunteer Wine developers was games; that was the primary focus for most of Wine’s early years (~1993–2000). When Transgaming started in 2001, they promised that they would release their DirectX improvements back to Wine. That cast a chill over games in Wine — why work on DirectX if all these improvements would ‘soon’ be coming back? Of course, no meaningful improvements have ever come back, which had the effect of creating a huge hole in what had been Wine’s very best facility.” By 2007, White says, “The Wine community had recovered from the hole created by Transgaming.”"
- ↑ Moss, Richard (16 January 2012). "Maniac Tentacle Mindbenders: How ScummVM's unpaid coders kept adventure gaming alive". Ars Technica. https://arstechnica.com/gaming/2012/01/maniac-tentacle-mindbenders-of-atlantis-how-scummvm-kept-adventure-gaming-alive/.
- ↑ Dawe, Liam (15 July 2019). "DOSBox-X and DOSBox Staging both had new releases lately". https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2021/07/dosbox-x-and-dosbox-staging-both-had-new-releases-lately/.
- ↑ Diener, Derrik (5 February 2018). "How To Play Arcade Games Using MAME On Linux". Addictivetips. https://www.addictivetips.com/ubuntu-linux-tips/play-arcade-games-on-linux-using-mame/.
- ↑ Dawe, Liam (15 July 2019). "RetroArch, the front-end app for emulators and more is heading to Steam". https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2019/07/retroarch-the-front-end-app-for-emulators-and-more-is-heading-to-steam/.
- ↑ Dawe, Liam (30 April 2020). "If you have the retro gaming itch RetroPie 4.6 is out with support for the Raspberry Pi 4". https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2019/07/retroarch-the-front-end-app-for-emulators-and-more-is-heading-to-steam/.
- ↑ Long, Moe (23 September 2016). "How to Play Retro Windows Games on Linux". https://www.makeuseof.com/tag/play-retro-windows-games-linux/.
- ↑ Warrington, Don (11 May 2020). "Is the Best Place to Run Old Windows Software... on Linux or a Mac?". https://vulcanhammer.info/2020/05/11/is-the-best-place-to-run-old-windows-software-on-linux-or-a-mac/.
- ↑ Aznar, Guylhem (2 July 2002). "Applications for the Sharp Zaurus". https://www.linuxjournal.com/article/5902. "An excellent way to start using the Zaurus is by playing games. The best way to play games on the Zaurus is to install an emulator."
- ↑ Kendrick, Bill. "Zaurus Software". http://www.newbreedsoftware.com/zaurus/.
- ↑ ""Agenda's agenda – a Linux-based "Open PDA""". Archived from the original on 13 May 2008. https://web.archive.org/web/20080513071354/http://www.linuxdevices.com/articles/AT4992223978.html., LinuxDevices.com, retrieved 17 July 2008
- ↑ "Games". http://agendawiki.com:80/cgi-bin/asr.pl?action=showcat&category=Games.
- ↑ Kepley, Travis (13 May 2010). "A brief history of commercial gaming on Linux (and how it's all about to change)". https://opensource.com/life/10/5/brief-history-commercial-gaming-linux.
- ↑ Olson, Dana (18 April 2003). "Gaming and Linux in 2003". http://www.linuxhardware.org/article.pl?sid=03/04/18/169209.
- ↑ Larabel, Michael (14 December 2010). "Alternative Games Is All About Linux Gaming". Phoronix. https://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=ODkwOA.
- ↑ Heggelund Hansen, Robin (10 March 2009). "Porting games to Linux". hardware.no. http://www.hardware.no/artikler/ryan_c_gordon_and_michael_simms/68450/2.
- ↑ "A mixed welcome for Unreal Tournament 2003 on Linux – LinuxWorld". http://linux.sys-con.com/node/32796.
- ↑ Mac, Linux America's Army – Blue's News
- ↑ 107.0 107.1 Serious Sam 2nd Encounter Q&A & Linux News – Blue's News
- ↑ LGP History pt 1: How LGP came to be Linux Game Publishing Blog, 15 May 2009 (Article by Michael Simms)
- ↑ Furness, James (15 November 2001). "On Wolf's Goldness". Blue's News. https://www.bluesnews.com/s/30526.
- ↑ "Tux Racer website". Sunspire Studios. http://tuxracer.com/.
- ↑ Linux Game Publishing and Pyrogon Announcement LinuxGames, 10 September 2002
- ↑ Majesty, Tribsoft, and LGP LinuxGames, 3 January 2002
- ↑ 113.0 113.1 id Software's Main Linux Game Developer Resigns Phoronix, 27 January 2012
- ↑ Crider, Michael (24 December 2017). "The Best Modern, Open Source Ports of Classic Games". https://www.howtogeek.com/335259/the-best-modern-open-source-ports-of-classic-games/.
- ↑ "Quake, Meet GPL; GPL, Meet Quake". Linux Journal. 1 December 2007. http://www.linuxjournal.com/article/9867.
- ↑ Bolding, Jonathan (4 September 2022). "Y'all know about these huge lists of free, open-source game clones, right?". https://www.pcgamer.com/yall-know-about-these-huge-lists-of-free-open-source-game-clones-right/.
- ↑ Kumar, Nitesh (2021). "Open Source Ports of Commercial Game Engines". https://linuxhint.com/open_source_prts_commercial_game_engines/.
- ↑ Interview with Ryan Gordon: Postal², Unreal & Mac Gaming[Usurped!] Macologist, 10 November. 2004
- ↑ Hyperspace Delivery Boy Port LinuxGames, 6 September 2002
- ↑ Interview with Ryan Gordon: Postal2, Unreal & Mac Gaming[Usurped!] Macologist, 10 November. 2004
- ↑ Rice, Christopher (28 December 2009). "Linux Gaming: Are We There Yet?". AnandTech. https://www.anandtech.com/show/2897.
- ↑ Hoogland, Jeff (April 2010). "Codeweavers vs. Cedega, Commercial Wine Product Comparison". Linux Gazette. https://linuxgazette.net/173/hoogland.html.
- ↑ Vrabie, Stefan (31 July 2006). "Cedega and Linux: Let the Windows games begin". Linux.com. https://www.linux.com/news/cedega-and-linux-let-windows-games-begin/.
- ↑ 124.0 124.1 Lees, Jennie (4 December 2005). "Linux gaming made easy". Engadget. https://www.engadget.com/2005-12-04-linux-gaming-made-easy.html.
- ↑ Dave, Salvator (28 July 2004). "Linux Takes on Windows Gaming". Extreme Tech. https://www.extremetech.com/computing/56768-linux-takes-on-windows-gaming.
- ↑ Millard, Elizabeth (24 June 2004). "TransGaming Updates WineX for Linux Gaming". Ecommerce Times. https://www.ecommercetimes.com/story/transgaming-updates-winex-for-linux-gaming-34702.html.
- ↑ M, Angelo (2 February 2021). "PlayOnLinux vs Wine: The Differences". https://www.imaginelinux.com/playonlinux-vs-wine/.
- ↑ Husted, Steve (13 September 2004). "Opinion: Regarding the Linux Gaming". https://www.osnews.com/story/8245/opinion-regarding-the-linux-gaming/.
- ↑ 129.0 129.1 "Wolfire Stats" (TXT). http://www.wolfire.com/humble/stats.
- ↑ 130.0 130.1 "The State of Linux Gaming 2011". OSNews.com. 14 November 2011. http://www.osnews.com/story/25328/The_State_of_Linux_Gaming_2011. "In short: indie games are thriving on Linux. The Humble Bundles have not only helped publicize the games, but have also helped prove that there is an untapped market for games on Linux, and that Linux users have no problem paying to support the developers who support them."
- ↑ Rosen, Jeffrey (28 December 2008). "Why you should support Mac OS X and Linux". http://blog.wolfire.com/2008/12/why-you-should-support-mac-os-x-and-linux/.
- ↑ Kuchera, Ben (1 March 2011). "Humble Bundle creator on Ars' influence and why Linux is important". Ars Technica. https://arstechnica.com/gaming/news/2011/03/humble-bundle-creator-on-ars-influence-and-why-linux-is-important.ars.
- ↑ Orland, Kyle (28 February 2011). "GDC 2011: Humble Indie Bundle Creators Talk Inspiration, Execution". https://www.gamedeveloper.com/console/gdc-2011-humble-indie-bundle-creators-talk-inspiration-execution. "Linux users tended to be the most generous of these, leading Graham to suggest indie developers go after underserved markets. "If you support Mac and Linux as an independent developer you have a good chance of doubling your revenue," Graham said."
- ↑ Sneddon, Joey (21 December 2011). "Linux Users Continue To Pay Most for the @Humble Indie Bundle". OMG! Ubuntu!. http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2011/12/linux-users-continue-to-most-for-the-humble-indie-bundle/.
- ↑ Priestman, Chris (4 June 2012). "Linux Users Petition Against 'humble Bundle V' Due To Non-native Version of 'Limbo'". Indie Game Magazine. http://www.indiegamemag.com/linux-users-petition-against-humble-bundle-v-due-to-non-native-version-of-limbo/.
- ↑ Dawe, Liam (19 June 2014). "LIMBO Dark Platformer Fully Native Linux Version Released, No More Wine". GamingOnLinux. http://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/limbo-dark-platformer-fully-native-linux-version-released-no-more-wine.3922.
- ↑ Orland, Kyle (29 November 2012). "Humble THQ Bundle threatens to ruin the brand's reputation (Updated)". Ars Technica. https://arstechnica.com/gaming/2012/11/humble-thq-bundle-threatens-to-ruin-the-brands-reputation/.
- ↑ Machkovich, Sam (14 January 2022). "Humble subscription service is dumping Mac, Linux access in 18 days". Ars Technica. https://arstechnica.com/gaming/2022/01/humble-subscription-service-is-dumping-mac-linux-access-in-18-days/.
- ↑ "Voltely product page". Entourev LLC. http://www.entourevllc.com/product.php?id=0001.
- ↑ "Native Linux Games". Linuxexperten.com. https://www.linuxexperten.com/content/linux-native-games.
- ↑ Larabel, Michael (29 January 2009). "LGP Is Now Porting Shadowgrounds: Survivor". Phoronix. https://www.phoronix.com/news/NzAyMw.
- ↑ "An Interview with Liam Dawe, Owner of GamingOnLinux". Linux Gaming Central. 20 April 2022. https://linuxgamingcentral.com/posts/interview-with-liam-from-gol/.
- ↑ "Desura games now also for Linux". 18 November 2011. http://www.h-online.com/open/news/item/Desura-games-now-also-for-Linux-1381658.html.
- ↑ "cheese talks to himself – Desura Beta". twolofbees.com. 11 October 2011. http://www.twolofbees.com/cheesetalks/desura.php.
- ↑ 145.0 145.1 145.2 "The state of Linux gaming in the SteamOS era". Ars Technica. 26 February 2015. https://arstechnica.com/gaming/2015/02/the-state-of-linux-gaming-in-the-steamos-era/1/.
- ↑ Zinoune, M. (27 November 2011). "Will it be Desura's Linux client Vs USC?". Unixmen. http://www.unixmen.com/will-it-be-desuras-linux-client-vs-usc/.
- ↑ Dawe, Liam (21 August 2011). "Interview with Jonathan Prior of Gameolith.com". https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2011/08/interview-with-jonathan-prior-of-gameolithcom/.
- ↑ Larabel, Michael (11 July 2011). "A New Linux Game Store Is Launching Next Week". https://www.phoronix.com/news/OTYyMg.
- ↑ Albanesius, Chloe (17 July 2012). "Valve Moves Forward With Steam for Linux | News & Opinion". PCMag.com. https://www.pcmag.com/article2/0,2817,2407237,00.asp.
- ↑ "Steam'd Penguins". Valve. 16 July 2012. http://blogs.valvesoftware.com/linux/steamd-penguins/.
- ↑ Lein, Tracey (16 July 2012). "'Left 4 Dead 2' to be first Valve game on Linux". The Verve. https://www.theverge.com/gaming/2012/7/16/3163717/left-4-dead-2-to-be-first-valve-game-on-linux.
- ↑ Hillier, Brenna (24 July 2012). "Serious Sam 3: BFE headed to Steam Ubuntu". VG247. http://www.vg247.com/2012/07/25/serious-sam-3-bfe-headed-to-steam-ubuntu/.
- ↑ Larbel, Michael (25 May 2010). "Valve's Linux Play May Lead More Games To Follow Suit". Phoronix. https://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=ODI4NA.
- ↑ Larbel, Michael (18 November 2010). "Egosoft Wants To Bring Games To Steam On Linux". Phoronix. https://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=MTIzMTY.
- ↑ "Editorial: Linux Gaming Will Be Fine Even Without Steam Machines Succeeding". GamingOnLinux. 20 February 2015. https://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/editorial-linux-gaming-will-be-fine-even-without-steam-machines-succeeding.4992.
- ↑ "Unity 4.0 Launches". Marketwire. 14 November 2012. http://www.marketwire.com/press-release/unity-40-launches-1726144.htm.
- ↑ Makuch, Eddie (23 September 2013). "Valve reveals SteamOS". GameSpot. http://uk.gamespot.com/news/valve-reveals-steamos-6414851.
- ↑ Crecente, Brian (4 June 2015). "The first official Steam Machines hit Oct. 16, on store shelves Nov. 10". Polygon. https://www.polygon.com/2015/6/4/8727269/steam-machine-launch-date.
- ↑ Dawe, Liam (18 March 2014). "GOG.com Are Going To Support Linux, Confirmed!". GamingOnLinux. http://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/gogcom-are-going-to-support-linux-confirmed.3288.
- ↑ "Lutris v0.5.12 out now fixing Origin, Epic Store, Ubisoft Connect, GOG". GamingOnLinux. 5 December 2022. https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2022/12/lutris-v0512-out-now-fixing-origin-epic-store-ubisoft-connect-gog/.
- ↑ "GameHub is another open source game launcher, giving Lutris some competition". GamingOnLinux. 18 March 2019. https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2019/03/gamehub-is-another-open-source-game-launcher-giving-lutris-some-competition/.
- ↑ "Minigalaxy the simple GOG client for Linux has a big 1.0 release". GamingOnLinux. 30 November 2020. https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2020/11/minigalaxy-the-simple-gog-client-for-linux-has-a-big-10-release/.
- ↑ "Heroic Games Launcher is a new unofficial Epic Games Store for Linux". GamingOnLinux. 5 January 2021. https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2021/01/heroic-games-launcher-is-a-new-unofficial-epic-games-store-for-linux/.
- ↑ "Unreal Engine 4.1 Update Preview". 3 April 2014. https://www.unrealengine.com/blog/41-update-preview.
- ↑ "CRYENGINE adds Linux Support as Crytek Prepare to Offer New Possibilities at GDC". 11 March 2014. http://www.crytek.com/news/conference-attendees-can-also-see-a-brand-new-mobile-game-extra-engine-updates-and-much-more-at-crytek-s-booth.
- ↑ Dawe, Liam (29 December 2014). "The Itch Games Store Are Working On An Open Source Client" (in en). https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2014/12/the-itch-games-store-are-working-on-an-open-source-client/.
- ↑ Corcoran, Leaf (14 December 2015). "Say hello to the itch.io app: itch". http://blog.itch.io/post/135196264464/say-hello-to-the-itchio-app-itch.
- ↑ Orphanides, K.G. (8 August 2018). "Crossing Platforms: a Talk with the Developers Building Games for Linux". https://www.linuxjournal.com/content/crossing-platforms-talk-developers-building-games-linux.
- ↑ Prakash, Abhishek (19 January 2023). "Fantastic Linux Games and Where to Find Them". https://itsfoss.com/download-linux-games/.
- ↑ Kerr, Chris (13 January 2016). "Indie marketplace Game Jolt releases open source desktop client". https://www.gamedeveloper.com/console/indie-marketplace-game-jolt-releases-open-source-desktop-client.
- ↑ Lee, Joel (30 August 2015). "Where to Download the Best Linux Games Without Any Hassle". https://www.makeuseof.com/tag/6-digital-distribution-services-linux-gamers/.
- ↑ Sohail, Mohd (23 December 2016). "Popular Gaming Platforms For Linux". https://www.linuxandubuntu.com/home/some-of-the-popular-gaming-platforms-for-linux.
- ↑ "OpenXRay, an enhanced game engine for S.T.A.L.K.E.R.: Call of Pripyat shows off Linux progress" (in en). 30 November 2018. https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2018/11/openxray-an-enhanced-game-engine-for-stalker-call-of-pripyat-shows-off-linux-progress/.
- ↑ Cartwright, John. "Stalker game running on Linux with Open Xray. – Securitron Linux blog." (in en-US). https://www.securitronlinux.com/it/stalker-game-running-on-linux-with-open-xray/.
- ↑ "Новая версия открытого движка OpenXRay (S.T.A.L.K.E.R.: Call of Pripyat) версии 730" (in ru). 10 July 2020. https://www.linux.org.ru/news/games/15803435.
- ↑ Isaac (2 December 2018). "OpenXRay: an improved graphics engine for STALKER: Call of Pripyat" (in en). https://blog.desdelinux.net/en/openxray-an-improved-graphics-engine-for-stalker-call-of-pripyat/.
- ↑ Dawe, Liam (16 July 2015). "End Of An Era, LinuxGames Website Looks To Be Shutting Down". GamingOnLinux. https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2015/07/end-of-an-era-linuxgames-website-looks-to-be-shutting-down/.
- ↑ Wong, Alistair (25 August 2018). "Steam Play Proton To Improve Game Support For Linux Users". https://www.siliconera.com/steam-play-proton-to-improve-game-support-for-linux-users/.
- ↑ "Steam for Linux :: Introducing a new version of Steam Play" (in en). 21 August 2018. https://steamcommunity.com/games/221410/announcements/detail/1696055855739350561.
- ↑ "Changelog · ValveSoftware/Proton Wiki" (in en). 31 July 2018. https://github.com/ValveSoftware/Proton/wiki/Changelog/664d37be002868c1b6ed27fc2b49adebcd8d1f49.
- ↑ "Changelog · ValveSoftware/Proton Wiki" (in en). 8 November 2018. https://github.com/ValveSoftware/Proton/wiki/Changelog/403c39180aef0b7a5c7cf8386d5bd3288e0b206d.
- ↑ Dawe, Liam (7 September 2020). "The itch.io app can now use a system installed Wine on Linux for Windows-only games" (in en). https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2020/09/the-itchio-app-can-now-use-a-system-installed-wine-on-linux-for-windows-only-games.
- ↑ Kenlon, Seth (25 October 2018). "Lutris: Linux game management made easy". https://opensource.com/article/18/10/lutris-open-gaming-platform.
- ↑ Saive, Ravi (18 July 2022). "PlayOnLinux – Run Windows Software and Games in Linux". https://www.tecmint.com/playonlinux-install-windows-software-in-linux/.
- ↑ Slater, Jack (19 July 2021). "Native Linux Games vs Windows API Compatibility Layers on the Steam Deck". https://nuclearmonster.com/2021/07/native-linux-games-vs-windows-api-compatibility-layers-on-the-steam-deck/.
- ↑ LateToTheParty (22 July 2021). "The Linux Gaming Conundrum: Proton vs. Native Linux Support". https://www.publish0x.com/late-to-the-show-and-games/the-linux-gaming-conundrum-proton-vs-native-linux-support-xnxqryr.
- ↑ Dawe, Liam (6 September 2022). "Prodeus cancels the Native Linux version, focusing on Proton compatibility (updated)" (in en). https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2022/09/prodeus-cancels-the-native-linux-version-focusing-on-proton-compatibility/.
- ↑ Dawe, Liam (14 August 2023). "Heart of the Machine from Arcen Games dropping Native Linux for Proton" (in en). https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2023/08/heart-of-the-machine-from-arcen-games-dropping-native-linux-for-proton/.
- ↑ Dawe, Liam (13 November 2021). "Valve answers the question: should developers do native Linux support or Proton?". https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2021/11/valve-answers-the-question-should-developers-do-native-linux-support-or-proton/.
- ↑ Dawe, Liam (25 February 2022). "The Steam Deck has released, here's my initial review" (in en). https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2022/02/steam-deck-initial-review/.
- ↑ Larabel, Michael (25 February 2022). "For Linux Enthusiasts Especially, The Steam Deck Is An Incredible & Fun Device" (in en). https://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=article&item=steam-deck-steamos-linux.
- ↑ Marks, Tom (30 July 2021). "Valve Explains How The Failure of Steam Machines Helped Build The Steam Deck". IGN. https://www.ign.com/articles/steam-deck-valve-explains-how-it-learned-from-past-mistakes.
- ↑ McFerran, Damien (11 September 2013). "Neo Geo X Gold & Mega Pack Volume 1". https://www.timeextension.com/news/2013/09/review_neo_geo_x_gold_and_mega_pack_volume_1. "It uses a Linux-based emulator running on a 1GHz Jz4770 system-on-chip"
- ↑ Humphries, Matthew (7 November 2016). "NES Classic Is a Quad-Core Linux Computer". https://www.pcmag.com/news/nes-classic-is-a-quad-core-linux-computer.
- ↑ Ackerman, Dan (9 October 2017). "Hackers crack SNES Classic to add more games and features". https://www.cnet.com/tech/gaming/hackers-crack-the-snes-classic-to-add-more-games-and-features/. "Fortunately, the SNES Classic, like its predecessor, is basically a Nintendo emulator built on a Linux foundation, so it's not impossible to hack."
- ↑ Machkovech, Sam (12 September 2019). "Sega Genesis Mini review: $80 delivers a ton of blast-processing fun". https://arstechnica.com/gaming/2019/09/sega-genesis-mini-review-genesis-does-what-ninten-did-and-thats-good-enough/. "Let this look at the taken-apart Sega Genesis Mini remind you that, like other recent retro consoles, the SGM relies on a Linux-driven SoC."
- ↑ Takahashi, Dean (21 June 2019). "Intellivision Entertainment prepares for its rebirth on 10–10–20". VentureBeat. https://venturebeat.com/2019/06/21/intellivision-entertainment-prepares-for-its-rebirth-on-10-10-20/. "But our OS is a hybrid, a Linux/Android hybrid that we’ve created in house. It’s very solid, but it’s very flexible, with Linux being the flexible part and Android being the solid part."
- ↑ Shilov, Anton (19 December 2023). "World's first RISC-V handheld gaming system announced — retro gaming platform uses Linux". https://www.tomshardware.com/pc-components/cpus/risc-v-handheld-gaming-system-announced-linux-as-the-basis-for-a-retro-gaming-platform.
- ↑ Portnoy, Sean (31 May 2018). "Atari VCS gaming console Linux mini-PC finally available to pre-order". https://www.zdnet.com/article/atari-vcs-gaming-console-linux-mini-pc-finally-available-to-pre-order/.
- ↑ Grant, Christopher (3 September 2021). "The Polymega is an all-in-one retro console worth your attention". https://www.polygon.com/2021/9/3/22653297/polymega-review-retro-game-console-emulation. "The Polymega is a software emulation-based console with a custom, Intel-backed motherboard running on Linux with a custom user interface."
- ↑ Welch, Thomas (28 November 2012). "Game Gadget Review". https://calmdowntom.com/2012/11/game-gadget-review/.
- ↑ Linneman, John (25 April 2020). "Evercade review: the cartridge-based retro handheld that works". https://www.eurogamer.net/digitalfoundry-2020-blaze-evercade-df-retro-hardware-review. "Inside, the Evercade features a 1.2GHz Cortex A7 SoC running a customized Linux setup."
- ↑ Petite, Steven (16 December 2022). "Evercade EXP Review". https://www.gamespot.com/articles/evercade-exp-review-retro-bliss-reborn/1100-6510138/. "The custom Linux operating system that the EXP runs borrows from the VS home console."
- ↑ Dawe, Liam (2 February 2023). "Zoom Platform, a store aimed at 'Generation X' adds more Linux support" (in en). https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2023/02/zoom-platform-a-store-aimed-at-generation-x-adds-more-linux-support/.
- ↑ "PPC games made by Loki software – related posts LinuxGames". http://www.linuxgames.com/?s=PPC+loki.
- ↑ "Loki Holiday Info and Deals LinuxGames". http://www.linuxgames.com/archives/5171.
- ↑ "Candy Cruncher Linux Sparc". 9 September 2005. http://www.linuxgamepublishing.com/info.php?id=10&.
- ↑ "Linux Game Publishing: Interview with Michael Simms". Linux Gazette. 6 March 2005. http://www.linuxgazette.com/node/10249.
- ↑ "Dominions II: The Ascension Wars 2.12". 8 June 2004. http://www.linuxgames.com/archives/6674.
- ↑ "Linux Version of SiN Almost Finished". amiga-news.de. 28 August 2008. https://www.amiga-news.de/en/news/AN-2000-08-00266-EN.html.
- ↑ "Gorky 17 dla Linuxa PPC". eXec.pl. 8 June 2006. https://www.exec.pl/wydarzenie.jsp?nid=2815&Gorky_17_dla_Linuxa_PPC.
- ↑ "Linux: PowerPC port of Robin Hood". amiga-news.de. 30 July 2006. https://www.amiga-news.de/en/news/AN-2006-07-00103-EN.html.
- ↑ "Steam Hardware & Software survey". July 2021. http://store.steampowered.com/hwsurvey/.
- ↑ "Where's the Unity stats page gone?" (in en-US). 24 January 2018. https://forum.unity.com/threads/wheres-the-unity-stats-page-gone.514106/.
- ↑ Platforms Top on 2016-03 Windows Players: 97.3%, OS X Players: 2.3%, Linux Players: 0.4%
- ↑ "Humble Budle data". http://www.wolfire.com/humble/stats.
- ↑ "Ubuntu Linux Gaming Performance Mostly On Par With Windows 8.1". Phoronix. 27 October 2013. https://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=article&item=gpus_windows81_ubuntu&num=1.
- ↑ "NVIDIA GeForce: Windows 10 vs. Ubuntu 15.04 Linux OpenGL Benchmarks Review – Phoronix". https://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=article&item=win10-nv-ubu1504&num=4.
- ↑ "SteamOS gaming performs significantly worse than Windows, Ars analysis shows". 13 November 2015. https://arstechnica.com/gaming/2015/11/ars-benchmarks-show-significant-performance-hit-for-steamos-gaming/.
- ↑ "Budget Fair Queueing I/O Scheduler". http://algo.ing.unimo.it/people/paolo/disk_sched/.
- ↑ "Phoronix: Liquorix-benchmarks". https://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=article&item=liquorix_311_kernel&num=1.
- ↑ "Liquorix homepage". http://liquorix.net/.
- ↑ Dawe, Liam (21 September 2021). "GameMaker Studio 2 update released to bring forth the Ubuntu Linux editor Beta". https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2021/09/gamemaker-studio-2-update-released-to-bring-forth-the-ubuntu-linux-editor-beta/.
- ↑ Dawe, Liam (27 September 2016). "Fusion 3, the next generation game engine and editor from Clickteam will support Linux". https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2016/09/fusion-3-the-next-generation-game-engine-and-editor-from-clickteam-will-support-linux/.
- ↑ Dawe, Liam (13 September 2023). "Here's some alternatives to the Unity game engine". https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2023/09/heres-some-alternatives-to-the-unity-game-engine/.
- ↑ Dawe, Liam (20 July 2022). "Unreal Engine 5 editor quietly gets a proper Linux version". https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2022/07/unreal-engine-5-editor-quietly-gets-a-proper-linux-version/.
- ↑ Best, Martin (30 May 2019). "Announcing the Unity Editor for Linux". https://blog.unity.com/technology/announcing-the-unity-editor-for-linux.
- ↑ Dawe, Liam (4 November 2020). "Unity Technologies committed to supporting the Linux Editor for the Unity game engine". https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2020/11/unity-editor-linux-2021/.
- ↑ "Scratch – Scratch Offline Editor". https://scratch.mit.edu/download.
- ↑ "RPG Maker MV Comes to Linux". 24 March 2017. https://gamefromscratch.com/rpg-maker-mv-comes-to-linux/.
- ↑ Larabel, Michael (8 January 2014). "MKXP: Open-Source, Linux Engine To RPG Maker XP". https://www.phoronix.com/news/MTU2Mzg.
- ↑ Dawe, Liam (6 March 2020). "Solarus is a free and open source cross-platform game engine for 2D action-RPGs". https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2020/03/solarus-is-a-free-and-open-source-cross-platform-game-engine-for-2d-action-rpgs/.
- ↑ Bush, Josh (9 July 2015). "Cheese talks to himself (about the SLUDGE engine)". https://cheesetalks.net/sludge.php.
- ↑ Schrier Shaenfeld, Karen (10 April 2016). Learning and Education Games: Volume Two: Bringing Games into Educational Contexts. Lulu.com. p. 265. ISBN 978-1329703568. https://books.google.com/books?id=DeKPDAAAQBAJ.
- ↑ "Open Source Game Creation Software: Working in 2D". 7 October 2009. https://www.brighthub.com/computing/linux/articles/51816/?expand_article=1.
- ↑ Dawe, Liam (26 August 2020). "Make retro Game Boy games with the open source GB Studio, now with colour in the 2.0 Beta". https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2020/08/make-retro-game-boy-games-with-the-open-source-gb-studio-now-with-colour-in-the-20-bet/.
- ↑ Wood, Evelyn (6 October 2016). "Succeeding MegaZeux". https://eev.ee/blog/2016/10/06/succeeding-megazeux/.
- ↑ Arrows, Kevin (28 April 2023). "How to Run Mugen Fighter Natively in a Linux Environment". https://appuals.com/run-mugen-fighter-natively-linux-environment/.
- ↑ Blizen, Arthur (20 January 2023). "IKEMEN Go Rollback Open Alpha Launches Today". https://dashfight.com/news/ikemen-go-rollback-open-alpha-launches-today-2332.
- ↑ Dawe, Liam (21 August 2019). "2D game editor ct.js goes open source and it's closing in on a new major release". https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2019/08/2d-game-editor-ctjs-goes-open-source-and-its-closing-in-on-a-new-major-release/.
- ↑ "Pixelbox.js Game Engine". 14 April 2020. https://gamefromscratch.com/pixelbox-js-game-engine/.
- ↑ Dawe, Liam (17 January 2016). "Superpowers, a HTML5 development environment for 2D & 3D games now open source". https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2016/01/superpowers-a-html5-development-environment-for-2d-3d-games-now-open-source/.
- ↑ Pearson, Craig (12 March 2013). "Make Quake With TrenchBroom". https://www.rockpapershotgun.com/make-quake-with-trenchbroom.
- ↑ Stone, Venn (1 March 2013). "TrenchBroom: Modern Cross Platform Map Editor For Quake 1". https://linuxgamecast.com/2013/03/trenchbroom-modern-cross-platform-map-editor-for-quake-1/.
- ↑ Merkit, Hasan (22 March 2022). "J.A.C.K. Hammer Editor". https://www.teteos.net/d/149-jack-hammer-editor.
- ↑ Wilson, Hamish (16 December 2012). "Eureka offers a new option for Doom mappers". https://www.gamingonlinux.com/articles/eureka-offers-a-new-option-for-doom-mappers.1535.
- ↑ "How to install Slade 3 on a Chromebook". 1 February 2021. https://www.linuxmadesimple.info/2021/02/how-to-install-slade-3-on-chromebook.html.
- ↑ Palacio, Daniel (26 January 2020). "'ReDoomEd', a port of the original Doom level editor, was released on Linux". https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2020/01/redoomed-a-port-of-the-original-doom-level-editor-was-released-on-linux/.
- ↑ Dawe, Liam (30 March 2022). "Free and open source level editor LDtk 1.0 is out now". https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2022/03/free-and-open-source-level-designer-ldtk-10-is-out-now/.
- ↑ "OGMO Level Editor". 18 November 2019. https://gamefromscratch.com/ogmo-level-editor/.
- ↑ McKenzie, Theodore (21 June 2021). "Tiled: A Flexible and Free-to-Use Level Editor". https://80.lv/articles/tiled-a-flexible-and-free-to-use-level-editor.
- ↑ Poettering, Lennart (24 September 2008). "A Guide Through The Linux Sound API Jungle". 0pointer.de/blog. http://0pointer.de/blog/projects/guide-to-sound-apis.html.
- ↑ "Introducing NVIDIA GameWorks™ | NVIDIA Developer Zone". Developer.nvidia.com. 2 March 2014. https://developer.nvidia.com/content/introducing-nvidia-gameworks.
- ↑ "AMD Eyefinity Validated and Ready Software". http://support.amd.com/en-us/recommended/eyefinity-software.
- ↑ "Multi-monitor: Civilization V on A10-7850K "Kaveri"". https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q0BN20BnRbg.
- ↑ 256.0 256.1 Hills, James. "Ports vs. Wine". GameSpy. http://www.gamespy.com/articles/may01/wine/.
- ↑ Larabel, Michael (3 July 2009). "An Interview With A Linux Game Porter". Phoronix. https://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=article&item=linux_gaming_frank&num=3.
- ↑ "Console Hacking 2015: Liner Notes". fail0verflow.com. 30 December 2015. https://fail0verflow.com/blog/2015/console-hacking-2015-liner-notes.html.
- ↑ "Gamecube Linux Wiki". Gc-linux.org. http://www.gc-linux.org/wiki/Main_Page.
- ↑ Larabel, Michael (5 October 2010). "A Gaming Mouse Vendor That Has Linux Drivers". Phoronix. https://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=ODY1Mw.
- ↑ Larabel, Michael (5 September 2011). "Roccat Linux Support Keeps Coming". Phoronix. https://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=OTg3NA.
- ↑ Bisson, Marilyn (19 October 2020). "Is Linux Good For Gaming?". https://blog.eldernode.com/is-linux-good-for-gaming/.
- ↑ Kenlon, Seth (7 February 2021). "3 ways to play video games on Linux". https://opensource.com/article/21/2/linux-gaming.
- ↑ Zinoune, M.. "Options for Linux Gamers". https://www.unixmen.com/options-for-linux-gamers/.
- ↑ Marchant, Layla. "The Gaming Trap". http://onpon4.github.io/articles/gaming-trap.html.
- ↑ Lunduke, Bryan (30 October 2015). "The Gaming Paradox: There just aren't enough Free and Open Source video games". https://www.networkworld.com/article/2999877/the-gaming-paradox-there-just-arent-enough-free-and-open-source-video-games.html.
- ↑ podiki (9 February 2022). "Proton vs Native: Is There Really A Difference?". https://boilingsteam.com/proton-vs-native-is-there-really-a-difference/.
- ↑ Gross, Grant (24 October 2001). "Loki's Draeker: Why run Windows games on Linux?". http://www.newsforge.com/article.pl?sid=01/10/23/013232.
- ↑ Dawe, Liam (22 August 2018). "GOG have gone on the offensive with their new 'FCK DRM' initiative". https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2018/08/gog-have-gone-on-the-offensive-with-their-new-fck-drm-initiative/.
- ↑ Dawe, Liam (2 July 2018). "The Humble DRM-Freedom Sale is live, plenty of Linux titles available". https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2018/07/the-humble-drm-freedom-sale-is-live-plenty-of-linux-titles-available/.
- ↑ Bisson, Marilyn (19 October 2020). "Is Linux Good For Gaming?". https://blog.eldernode.com/is-linux-good-for-gaming/. "You can also play through the terminal; Of course, it depends on your expectations and definition of the game! But if the goal is entertainment, the Linux terminal offers you funny and nostalgic choices."
- ↑ Kili, Aaron (15 August 2016). "12 Amazing Terminal Based Games for Linux Enthusiasts". https://www.tecmint.com/best-linux-terminal-console-games/.
- ↑ Kumar, Nitesh (2021). "Best Command Line Games for Linux". https://linuxhint.com/command_line_games_for_linux/.
- ↑ Okoi, Divine (27 August 2018). "4 Best Ways to Play Retro Games on Linux". https://www.fossmint.com/play-retro-games-on-linux/.
- ↑ Cawley, Christian (28 June 2016). "7 Ways to Play Old Windows & DOS Games on Linux". https://www.makeuseof.com/tag/7-ways-play-old-windows-dos-games-linux/.
- ↑ "How to play Windows games under Linux". https://www.myabandonware.com/howto/wine.
- ↑ Chakraborty, Angsuman (20 August 2007). "How To Play Doom, Heretic, Hexen & Strife in Linux (Free)". http://tech.gaeatimes.com/index.php/archive/how-to-play-doom-heretic-hexen-strife-in-linux-free/.
- ↑ Armstrong, Ryan (27 December 2020). "Running Caldera OpenLinux 1.3 in QEMU". https://zerker.ca/home/openlinux13.html.
- ↑ Barnes, Hayden (7 September 2019). "The one in which I kind of get Corel Linux 1.2 to work 21 years later.". https://boxofcables.dev/corel-linux-1-2/.
- ↑ Wilson, Hamish (22 March 2021). "Building a Retro Linux Gaming Computer – Part 4: Installing Red Hat Linux 7.3". https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2021/03/building-a-retro-linux-gaming-computer-part-4-installing-red-hat-linux-73/.
- ↑ Wilson, Hamish (20 February 2023). "Building a Retro Linux Gaming Computer – Part 26: Coming to You Live". https://www.gamingonlinux.com/2023/02/building-a-retro-linux-gaming-computer-part-26-coming-to-you-live/.
- ↑ Powers, Shawn (14 January 2010). "SuperGamer, 8GB of Linux-Only Gameplay". https://www.linuxjournal.com/content/supergamer-8gb-linux-only-gameplay.
- ↑ Hernandez, Miguel (29 April 2010). "How-to Become a Linux Gamer". https://www.linuxjournal.com/content/how-become-linux-gamer.
- ↑ Abraham (24 December 2022). "Top 10 browser games you should be playing in 2022". https://www.fosslinux.com/91687/best-browser-games-playing.htm.
- ↑ Mutai, Josphat (5 January 2023). "From Valve to the Cloud: How Linux Gaming is Going to Evolve in 2022". https://computingforgeeks.com/how-linux-gaming-is-going-to-evolve/.
- ↑ Kuchera, Ben (14 October 2014). "Forget Windows, forget OS X, forget Linux: Humble Bundle is going truly multiplatform". https://www.polygon.com/2014/10/14/6975919/humble-bundle-browser-gaming.
- ↑ Zinoune, M.. "Options for Linux Gamers". https://www.unixmen.com/options-for-linux-gamers/. "The ever increasing popularity of social gaming is a definite threat to traditional forms of gaming. Social gaming comes in many forms, but an obvious example would be games that can be played on Facebook and other social networking websites where games and statistics can be viewed and shared online with a player’s friends. This form of gaming is very limited as the games that can be played via social networks are usually targeted towards casual gamers and not the hardcore PC type. I don’t see social gaming becoming an immediate threat to native gaming in the near future and will probably remain a casual space."
- ↑ Travis (9 October 2022). "How To Play Flash Games On Linux". https://www.systranbox.com/how-to-play-flash-games-on-linux/.
- ↑ ashar_oz (26 July 2017). "HTML5 Games Are Improving – Perfect For Ubuntu & Linux". https://www.ubuntubuzz.com/2017/07/html5-games-are-improving-perfect-for.html.
- ↑ markd (25 November 2020). "Cloud Gaming Services: Explained and Tested on Linux". https://boilingsteam.com/cloud-gaming-services-explained-and-tested-on-linux/.
- ↑ Dickson, Jamie; Boxer, Benjy. "Play Any PC Game On Your Linux Machine With Cloud Gaming Or Game Streaming". https://parsec.app/blog/play-any-pc-game-on-your-linux-machine-with-cloud-gaming-or-game-streaming-a64e9925462f.
- ↑ Kelestemur, Atalay (18 March 2023). "Why Linux is a more attractive gaming platform?". https://cloud7.news/opinion/why-linux-is-a-more-attractive-gaming-platform/.
- ↑ Sneddon, Joey (19 March 2019). "Stadia is Google's New Gaming Service Powered by Linux & Open-Source Tech". https://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2019/03/googles-new-game-service-is-based-on-linux-open-source-tech.
- ↑ Palumbo, Alessio (19 March 2019). "Stadia Is Google's Cloud Based Game Platform; Powered by AMD, Linux and Vulkan, Due in 2019". https://wccftech.com/stadia-is-googles-cloud-based-game-platform-powered-by-amd-linux-and-vulkan-due-in-2019/.
- ↑ bapt (22 June 2012). "Cloud Gaming, or a good reason to create Linux version of a game". https://drawcode.eu/blog/cloud-gaming-or-a-good-reason-to-create-linux-version-of-a-game/.
- ↑ Larabel, Michael (14 December 2021). "Amazon Is Hiring DXVK, Mesa & Proton Linux Developers For Luna Cloud Gaming in Mesa". https://www.phoronix.com/news/Amazon-Linux-Graphics-Jobs.
- ↑ Larabel, Michael (19 March 2023). "Canonical Gets Into Cloud Gaming & More With Anbox Cloud For Cloud-Based Android Apps/Gaming". https://www.phoronix.com/news/Canonical-Anbox-Cloud.
- ↑ "Open source cloud gaming, play remote games for free". 26 April 2022. https://www.helpwire.app/blog/open-source-cloud-gaming/.
- ↑ Davenport, Corbin (21 June 2019). "How to play Windows games in Linux". https://www.pcgamer.com/how-to-play-windows-games-in-linux/.
- ↑ "Hands on with WSLg: Running Linux GUI". 29 May 2021. https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/microsoft/hands-on-with-wslg-running-linux-gui-apps-in-windows-10/. "While Hedgewars is not a Linux-only game, I wanted to include it to show that even games can run under WSLg. While WSLg is likely not designed for gaming, the fact that you can play games using it shows the full depth of this new feature."
- ↑ Vaughan-Nichols, Steven (3 August 2020). "3 good ways to run Linux on Windows". https://www.hpe.com/us/en/insights/articles/3-good-ways-to-run-linux-on-windows-2007.html.
- ↑ Kiran, Amruth (7 November 2022). "How to Run Linux Software on Windows". https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/how-to-run-linux-software-on-windows/.
- ↑ Brown, Pete (22 July 2016). "Fun with the Windows Subsystem for Linux". https://blogs.windows.com/windowsdeveloper/2016/07/22/fun-with-the-windows-subsystem-for-linux/.
- ↑ Hanselman, Scott (12 January 2018). "Building 0verkill on Windows 10 Subsystem for Linux – 2D ASCII art deathmatch game". https://www.hanselman.com/blog/building-0verkill-on-windows-10-subsystem-for-linux-2d-ascii-art-deathmatch-game.
- ↑ Fenton, Tom (8 February 2017). "Running Graphical Programs on Windows Subsystem on Linux". https://virtualizationreview.com/articles/2017/02/08/graphical-programs-on-windows-subsystem-on-linux.aspx. "Blockout worked flawlessly, which surprised me as it is an extremely graphics-intensive application."
- ↑ Buckler, Craig (1 September 2022). "Windows Subsystem for Linux 2: The Complete Guide for Windows 10 & 11". https://www.sitepoint.com/wsl2/.
- ↑ Tozzi, Christopher (19 September 2017). "Why Microsoft's Windows Subsystem for Linux Is Not As Novel As It Sounds". https://www.channelfutures.com/open-source/why-microsofts-windows-subsystem-for-linux-is-not-as-novel-as-it-sounds-2.
- ↑ Hess, Ken (29 October 2020). "Creating a Linux-Windows hybrid system with Cygwin". Red Hat. https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/hybrid-system-cygwin.
- ↑ McIntyre-Bhatty, Hamish (21 May 2018). "Cygwin review part 1: Running Linux programs… on Windows?". https://www.hamishmb.com/cygwin-review-part-1/. "Can you run games? I have absolutely no idea, but I would guess the answer is no, because of the lack of hardware access. I did have a quick look for games like Neverball and Extreme Tux Racer, but they were nowhere to be found. When I follow this up, I’ll look a bit harder, and maybe try compiling them. Really, it’s kind of pointless, because you could just run the games in Windows."
- ↑ Finley, Klint (30 March 2016). "Why Microsoft Making Linux Apps Run on Windows Isn't Crazy". Wired. https://www.wired.com/2016/03/microsoft-making-linux-apps-run-windows-isnt-crazy/. Retrieved 18 March 2023.
- ↑ "LibTAS FAQ". https://clementgallet.github.io/libTAS/faq/. "If you have Windows 10, the easiest way is to use WSL 2 (Windows Subsystem for Linux) to run libTAS. Otherwise, you can install a Linux distribution (e.g. Ubuntu) on a virtual machine (e.g. using VirtualBox)."
- ↑ Nelva, Giuseppe (6 June 2014). "Naughty Dog Still Uses Old School Linux and Cygwin Command Line Tools; TLOU Panel Coming Next Week". https://www.dualshockers.com/naughty-dog-still-uses-old-school-linux-and-cygwin-command-line-tools-tlou-panel-coming-next-week/.
- ↑ "Using Cygwin for SDL Development". https://www.noquarterarcade.com/using-cygwin-for-sdl-development/.
- ↑ Delony, David (21 January 2022). "The Pros and Cons of Using Windows Subsystem for Linux". https://www.makeuseof.com/pros-cons-windows-subsystem-for-linux/.
- ↑ Bisson, Simon (23 April 2021). "Linux on Windows: This new upgrade allows you to run graphical apps simply and effectively". https://www.techrepublic.com/article/linux-on-windows-this-new-upgrade-allows-you-to-run-graphical-apps-simply-and-effectively/. "Mesa3D support should help developers using WSL 2 to port games to Linux, as well as allowing complex Unix CAD applications and other design tooling to use WSLg to work on Windows, without needing a full port. If you’re worried about application support, we’ve yet to find anything that didn’t work over WSLg. We’ve been able to run Ubuntu desktop tools, classic Unix games like Nethack’s X11 port, Linux games from Steam, a host of different editors and IDEs, the LibreOffice productivity suite, as well as Microsoft’s own Edge browser (using it to stream video and audio). The experience of using Linux applications on Windows is much like running Windows applications on macOS via Parallels."
- ↑ Montegriffo, Nicholas (30 October 2017). "A player's journey: How I learned to love Android gaming". https://www.nextpit.com/how-i-learned-to-love-android-gaming.
- ↑ Kian (20 December 2022). "The 4 Best Android Game Consoles Out Right Now". https://joyofandroid.com/best-android-game-consoles/.
- ↑ Hindy, Joe (1 April 2023). "15 best Android games available right now". https://www.androidauthority.com/best-android-games-316202/.
- ↑ Sholtz, Matthew (19 April 2023). "Best Android games in 2023: Top picks across every category". https://www.androidpolice.com/best-android-games/.
- ↑ "Are Chromebooks Good for Gaming?". https://www.google.com/chromebook/are-chromebooks-good-for-gaming/.
- ↑ Baker, Luke (30 January 2022). "Chromebook gaming: Everything you need to know". https://www.pocket-lint.com/laptops/news/159848-chromebook-gaming-everything-you-need-to-know/.
- ↑ Dalton, Matt (30 March 2022). "How Chrome OS is great for gaming Chromebooks can be easily picked up for gaming now". https://chromeready.com/8047/chrome-os-great-games/.
- ↑ Scott, Hilda (2 January 2023). "Best gaming Chromebooks 2024". https://www.laptopmag.com/news/best-chromebooks-for-gaming.
- ↑ Westover, Brian (22 November 2023). "The Best Chromebooks for Gaming in 2024". https://www.pcmag.com/picks/the-best-chromebooks-for-gaming.
- ↑ Takahashi, Dean (11 October 2022). "Google supports cloud-gaming Chromebook laptops for gamers". https://venturebeat.com/games/google-supports-cloud-gaming-chromebook-laptops-for-gamers/.
- ↑ Murray, Sean (18 August 2020). "GeForce NOW Comes To ChromeOS". https://www.thegamer.com/geforce-now-comes-to-chromeos/.
- ↑ Mehta, Ivan (11 October 2022). "Google introduces Chromebooks geared for cloud gaming". https://techcrunch.com/2022/10/11/google-introduces-chromebooks-geared-for-cloud-gaming/.
- ↑ Cunningham, Andrew (18 August 2023). ""Gaming Chromebooks" with Nvidia GPUs apparently killed with little fanfare". https://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2023/08/gaming-chromebooks-with-nvidia-gpus-apparently-killed-with-little-fanfare/.
- ↑ Lawler, Richard (2 September 2022). "A new ChromeOS gaming overlay puts touch-based Android games on your PC". https://www.theverge.com/2022/9/2/23333400/google-chromeos-touch-android-games-keyboard-controls.
- ↑ Nield, David (8 July 2023). "How to run games on a Chromebook". https://www.theverge.com/23786958/chromebook-chrome-gaming-how-to.
- ↑ Sneddon, Joey (2 July 2020). "Steam is Coming to Chromebooks with Ubuntu-based "Borealis" Feature". https://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2020/07/ubuntu-steam-chromebook-gaming.
- ↑ Duke, Kent (15 April 2021). "Your Chromebook will be getting a massive gaming performance boost soon". https://www.androidpolice.com/2021/04/15/vulkan-api-support-could-improve-linux-apps-and-games-performance-on-chromebooks/.
- ↑ Perrigo, Michael (22 April 2022). "How to play open-source retro games in your Chromebook's Linux terminal". https://chromeunboxed.com/how-to-play-games-in-your-chromebooks-linux-terminal/.
- ↑ Pereyra, Renato (24 January 2023). "Windows games on ChromeOS with Proton". https://chromeos.dev/en/posts/windows-games-on-chromeos.
- ↑ Patkar, Mihir (20 February 2018). "How to Install Windows Programs and Games on Chromebooks". https://www.makeuseof.com/tag/install-windows-programs-on-chromebooks/.
- ↑ Sattelberg, Will (6 August 2021). "Steam for Chromebooks could be right around the corner". https://www.androidpolice.com/2021/08/06/steam-for-chromebooks-could-be-right-around-the-corner/.
- ↑ Gordon, Whitson; Cohen, Jason (21 February 2024). "How to Play Games on Your Chromebook". https://www.pcmag.com/how-to/play-games-on-your-chromebook.
- ↑ Hill, Paul (3 November 2022). "Steam enters beta on ChromeOS 108 following seven-month alpha period". https://www.neowin.net/news/steam-enters-beta-on-chromeos-108-following-seven-month-alpha-period/.
- ↑ Williams, Ian (19 September 2022). "Playing Epic Games on ChromeOS – A Heroic Games Launcher Tutorial". https://blog.crosexperts.com/playing-epic-games-on-chromeos-835477e4f3f0.
- ↑ Devine, Richard; Bacchus, Arif (6 January 2024). "Best ChromeOS games in 2023". https://www.xda-developers.com/best-games-chrome-os/.
- ↑ Casey, Henry T.; Washington, Shamar (26 December 2023). "Best Chromebook games 2024". https://www.laptopmag.com/articles/best-chromebook-games.
- ↑ Chakraborty, Suman (29 August 2023). "Top 10 Games to Play on Chromebook". https://techpp.com/2023/08/29/chromebook-games/.
- ↑ Dalton, Matt (16 September 2023). "Top 10 PC games to dive into on your ChromeOS". https://chromeready.com/22299/top-10-pc-games-to-dive-into-on-your-chromeos/.
- ↑ Gedeon, Kimberly (24 August 2023). "Steam on Chromebooks is a joke — 5 reasons it hasn't gotten an official release". https://www.laptopmag.com/news/steam-on-chromebooks-is-a-joke-5-reasons-it-hasnt-gotten-an-official-release.
- ↑ Guyton, Christian (10 December 2022). "So-called 'gaming Chromebooks' are a con – here's why". https://www.techradar.com/features/so-called-gaming-chromebooks-are-a-con-heres-why.
- ↑ Gariffo, Michael (1 December 2022). "Lenovo's IdeaPad Gaming Chromebook proves hardware isn't what's holding back cloud gaming". https://www.zdnet.com/home-and-office/home-entertainment/lenovo-ideapad-gaming-chromebook-review/.
- ↑ Li, Abner (7 August 2025). "Google ending Steam for Chromebook support in 2026". https://9to5google.com/2025/08/07/steam-chromebook-2026/.
- ↑ Rapenne, Solène (7 March 2021). "Top 12 best opensource games available on OpenBSD". https://dataswamp.org/~solene/2021-03-07-openbsd-best-games.html.
- ↑ Larabel, Michael (7 March 2021). "Running Steam's Linux Build On FreeBSD Is Becoming Increasingly Capable For Gaming". https://www.phoronix.com/news/Steam-FreeBSD-2021.
- ↑ Smith, JT (15 August 2000). "Loki and BSDi partner to certify Linux games for BSD". https://www.linux.com/news/loki-and-bsdi-partner-certify-linux-games-bsd/.
- ↑ Larabel, Michael (22 September 2019). "Homura Is A Windows Game Launcher For FreeBSD – Supports Steam, Origin, UPlay + More". https://www.phoronix.com/news/Homura-FreeBSD-Gaming.
- ↑ Larabel, Michael (14 December 2014). "Steam Gaming On PC-BSD". https://www.phoronix.com/news/MTg2MjQ.
- ↑ Larabel, Michael (7 September 2011). "FreeBSD: A Faster Platform For Linux Gaming Than Linux?". https://www.phoronix.com/review/linux_games_bsd/2.
- ↑ Lucas, Michael (22 March 2001). "FreeBSD Gaming". http://www.onlamp.com/pub/a/bsd/2001/03/22/Big_Scary_Daemons.html. "If you're running KDE or Gnome, you already have a few simple games installed. I'm not a fan of either desktop – both strike me as bloated and obtuse – but their games packages are a nice way to pick up a dozen simple favorites such as Solitaire, Asteroids, and Tetris."
- ↑ "Tweak It: PS3 GameOS" (in en-US). 17 July 2011. https://www.thesixthaxis.com/2011/07/17/tweak-it-ps3-gameos/.
- ↑ Anthony, Sebastian (24 June 2013). "PS4 runs Orbis OS, a modified version of FreeBSD that's similar to Linux". ExtremeTech. http://www.extremetech.com/gaming/159476-ps4-runs-orbis-os-a-modified-version-of-freebsd-thats-similar-to-linux.
- ↑ "What hackers know of the Nintendo Switch so far". 9 March 2017. http://wololo.net/2017/03/09/hackers-know-nintendo-switch-far/.
- ↑ Shabir, Swaira (25 July 2021). "Mini World: First Native HarmonyOS Game Now Available On AppGallery". https://www.technologytimes.pk/2021/07/25/mini-world-first-native-harmonyos-game-now-available-on-appgallery/.
- ↑ Bates, Kryzt (10 April 2023). "Developed based on the Cocos 2dx engine, the game "Happy Match" was successfully ported to OpenHarmony". https://www.gamingdeputy.com/developed-based-on-the-cocos-2dx-engine-the-game-happy-match-was-successfully-ported-to-openharmony/.
- ↑ openharmony/third_party_musl, OpenHarmony, 8 January 2022, https://github.com/openharmony/third_party_musl, retrieved 7 July 2024
- ↑ Blonia (28 June 2024), SleepEatCoding/VirtualAndroidForHMOSNext, https://github.com/SleepEatCoding/VirtualAndroidForHMOSNext, retrieved 7 July 2024
- ↑ Chalmers, Rachel (June 1999). "Sun Releases Tool To Make Linux Apps Run On Solaris". AUUGEN (Australia: AUUG): 29. https://books.google.com/books?id=3I_9M0DRtT4C. Retrieved 5 March 2023. "But the real strength of Linux over Solaris is the availability of games. Kay reveals, "If you've got a developer who's been doing heads-down coding for hours, they might want to take a break to use the latest greatest games," she chuckles. "If games are available on Linux now you can get them and use them on your new Solaris workstation. Managers like making sure that kind of thing is available to their creative end users."".
- ↑ "Fun in the Sun". http://sungames.com/.
- ↑ "Games". 30 October 2008. https://blogs.oracle.com/solaris/post/games.
- ↑ "Games". http://src.gnu-darwin.org/ports/games/.
- ↑ Dyer, Bill (28 December 2022). "Getting Nostalgic With the Historical Coherent Operating System". https://itsfoss.com/coherent-operating-system/. "For a small package, it was remarkably complete. Not only was it a standalone operating system, but came with a big box of goodies, such as a Bourne Shell, C compiler, assembler, debugger, DOS disk support, uucp, at least three editors, some games, mail, and around 200 of the most used and useful UNIX commands."
- ↑ "SerenityOS Ports – Games". https://ports.serenityos.net/#a-games.
- ↑ Straker, Adam (26 August 2022). "SerenityOS, the 90's Windows-like Unix system built from scratch by one man as a therapeutic project". https://www.gearrice.com/update/serenityos-the-90s-windows-like-unix-system-built-from-scratch-by-one-man-as-a-therapeutic-project/. "Among the ports already available we can find those of several popular video games such as Quake (I and II), Half-Life (since last January), Doom or VVVVVV, which complement own developments of the project’s collaborators"
- ↑ "Trying Out Redox". https://doc.redox-os.org/book/ch02-04-trying-out-redox.html.
- ↑ Larabel, Michael (13 February 2024). "The Current State & Plans For Porting Linux/BSD Software To Redox OS". https://www.phoronix.com/news/Redox-OS-Porting-Plans. "While not yet having accelerated graphics and their Wayland support is still some ways out, they have ported some games/emulators to Redox OS already like DOSBox, Neverball, OpenTTD, ScummVM, 2048, and others."
- ↑ gameblabla (8 November 2016). "ToaruOS – Unix-like "hobby" operating system". https://codewalr.us/index.php?topic=1700.0. "I ported Helicopters, one of my games, just to show you how easy you can port games to it."
- ↑ Saeki, Takaya (4 October 2020). "How we ran a Unix-like OS (Xv6) on our home-built CPU with our home-built C compiler". https://fuel.edby.coffee/posts/how-we-ported-xv6-os-to-a-home-built-cpu-with-a-home-built-c-compiler/. "However, some teams put more energy into doing fun such as running games or playing music by connecting a speaker with their CPU. Group 6, to which I belonged, was a group of such people who loved entertainment, and we decided to run an OS as our team goal."
- ↑ "Packages". https://www.fiwix.org/packages.html. "lxdoom-1.4.4"
- ↑ "Porting NetBSD Userland to MINIX 3". 28 October 2018. https://wiki.minix3.org/doku.php?id=developersguide:portingnetbsduserland.
- ↑ "Bug#679330: marked as done (ioquake3: Add support for GNU/Hurd)". 5 July 2012. https://alioth-lists.debian.net/pipermail/pkg-games-devel/2012-July/023651.html.
- ↑ Pendleton, Bob. "Game Programming with the Simple DirectMedia Layer". https://dl.acm.org/doi/fullHtml/10.5555/774727.774728. "SDL officially supports Linux, Windows, BeOS, Mac OS, Mac OS X, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, BSD/OS, Solaris and IRIX. SDL also works with Windows CE, AmigaOS, Atari, QNX, NetBSD, AIX, Tru64 UNIX and SymbianOS. However, those OSes are not yet officially supported. This means if you write your application using SDL, you can port it with minimal rework to all those OSes. SDL provides a portable way to write games and multimedia applications on every major OS currently in use."
- ↑ Holwerda, Thom (21 May 2022). "The nightmare of getting DOOM running on PowerPC AIX". https://www.osnews.com/story/134901/the-nightmare-of-getting-doom-running-on-powerpc-aix/.
- ↑ Williams, Al (3 May 2017). "Your Next Desktop… QNX?". https://hackaday.com/2017/05/03/your-next-desktop-qnx/. "The rest of the adventure went fairly well. He managed to build SDL and port over some games."
- ↑ "FORTRAN Computer Games". 18 November 2022. https://cyber.dabamos.de/programming/fortran/computer-games/. "Remake of Battle Zone (1986) by Justin S. Revenaugh for Apollo Domain/OS, using the GPR graphics library. The game was later ported as XBZONE to X11."
- ↑ "Games/Arcade". http://hpux.connect.org.uk/hppd/hpux/Games/Arcade/.
- ↑ "SGI – Freeware – Games". http://www.sgi.com/fun/freeware/games.html.
- ↑ "SuperTuxKart IRIX Screenshots". http://www.supertuxkart.de/stkirix.html.
- ↑ Knight, John (May 2021). "Exploring Microsoft's forgotten Unix distribution". https://www.linux-magazine.com/index.php/Issues/2021/246/Remembering-XENIX/(offset)/9. "Thankfully XENIX users weren't all business, and there are at least a few games available for the system. Although the IMG file from Archive.org wouldn't work, we found a working disk image from YouTube user MentionedBefore, who provides a link below his XENIX 2.3.1 VirtualBox tutorial. The disk comes with Worms (not the famous DOS game!), Rogue, Hack, and Trek, plus fortune and mathrec. (And there is a terminal-based version of Tetris somewhere out there!) Once installed, the executables for the games/amusements are found under /usr/games"
- ↑ "Caldera Skunkware X11 Games". 6 July 2001. https://www.sco.com/skunkware/x11/games/.
- ↑ Armstrong, James; Kent, Les (22 November 1993). "32-bit desktop operating systems". InfoWorld (United States: IDG Communications, Inc.): 75. https://books.google.com/books?id=ATsEAAAAMBAJ. Retrieved 5 March 2023. "Once a user is logged in, a window displays a number of icons that group some standard applications: Accessories, Applications, Preferences, Disks, Games, Shutdown, System Setup, Utilities, and Folder Maps. User can open any file or folder by double clicking on the appropriate icon.".
- ↑ "Open Source Software Collection for Tru64 UNIX V5.1A". 9 December 2014. https://wiki.classe.cornell.edu/Computing/Tru64Freeware.
- ↑ Magee, Mike (6 September 1999). "1.6GHz Alpha to be fastest Quake chip on planet". https://www.theregister.com/1999/09/06/1_6ghz_alpha/. "The beast is not designed for Windows – its OS preference a version of real time Tru64 using current OpenGL for the platform. Real time versions of Tru64 might be used in a high end arcade game console, with workstations using a more "normal" Tru64 Unix with OpenGL. Quake and Quake 2 are native on Alpha Linux platforms."
- ↑ Lehrbaum, Rick (8 May 2000). "Lynx + Linux = ... Lynux". https://www.zdnet.com/article/lynx-linux-lynux/.
- ↑ "ULTRIX – Reference Pages for Unsupported Software". Digital Equipment Corporation. June 1990. http://www.bitsavers.org/pdf/dec/vax/ultrix-32/4.0_Jun90/AA-MF05B-TE_Reference_Pages_for_Unsupported_Software_Jun90.pdf. "Section 6: Games – The reference pages in this section describe the games that are available in the unsupported software subset."
- ↑ Moreau, Patrick (2 January 2003). "Thematic Download Pages". http://decwarch.free.fr/decw.html.
- ↑ "Downloads: Games". https://www.openvmshobbyist.com/downloads.php?cat_id=3.
- ↑ Kippins, Aaron; Ropes, Charlie; Huntington, Brad (21 May 2020). "Minecraft on Z/OS". IBM Corporation. https://ecc.marist.edu/documents/355984/2180584/Kippins%2C+Aaron+Slides+Minecraft+on+Z.pdf/82ddfae0-eea8-4930-9741-4148e6dea6d2.
- ↑ Holwerda, Thom (9 June 2022). "Porting Doom to A/UX". https://www.osnews.com/story/134966/porting-doom-to-a-ux/.
- ↑ "Fiddling with NeXTSTEP". 29 December 2011. https://posts.boy.sh/fiddling-with-nextstep. "This screenshot shows Facebook, looking rather broken, and DOOM in the front. id Software used NeXT systems to create the famous first person shooter. Relying on the Objective-C based development environment to create most of the tools, like the level editor."
- ↑ Edwards, Benj (24 August 2020). "Before Mac OS X: What Was NeXTSTEP, and Why Did People Love It?". https://www.howtogeek.com/698532/before-mac-os-x-what-was-nextstep-and-why-did-people-love-it/.
- ↑ Sanglard, Fabien (10 December 2018). "Chapter 3: NeXT". Game Engine Black Book: DOOM. p. 103. ISBN 978-1099819773. https://books.google.com/books?id=wel6DwAAQBAJ.
- ↑ Hills, James (19 June 1999). "Interviews - Dave Taylor, Transmeta". https://www.talisman.org/~erlkonig/misc/ddt.shtml. "Anyway, so it felt almost natural to do weird things. Here was a company where hundreds of thousands of dollars changed hands depending on moods and stories, Nextstep was the development environment, and showing up to work and seeing something truly miraculous in John Carmack's office or the art room about once a week was the norm. So when I started calling various workstation vendors like IBM, Sun, SGI, and asking they send workstations in exchange for typing "make", no one was terribly surprised. It was just one more of the weekly miracles, and a lesser one at that. "Oh look. There's our game running in a window on 5 architectures and as many OS's. Huh.""
- ↑ https://blog.luanti.org/2025/03/09/FOSDEM2025/
 |
