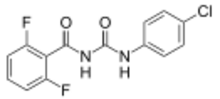
Chemistry:Diflubenzuron
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
N-[(4-Chlorophenyl)carbamoyl]-2,6-difluorobenzamide | |
| Other names
Dimilin
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties[1] | |
| C14H9ClF2N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 310.68 g·mol−1 |
| 0.08 mg/L | |
| Solubility in other solvents | DMSO: 12 g/100 g Acetone 0.615 g/100 g Methanol: 0.09 g/100 g |
| Pharmacology | |
| 1=ATCvet code} | QP53BC02 (WHO) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Diflubenzuron is an insecticide of the benzoylurea class.[2] It is used in forest management and on field crops[3] to selectively control insect pests, particularly forest tent caterpillar moths, boll weevils, gypsy moths, and other types of moths.[1] It is a widely used larvicide in India for control of mosquito larvae by public health authorities. Diflubenzuron is approved by the WHO Pesticide Evaluation Scheme.[1]
Mechanism of action
The mechanism of action of diflubenzuron involves inhibiting the production of chitin which is used by an insect to build its exoskeleton. It triggers insect larvae to molt early without a properly formed exoskeleton, resulting in the death of the larvae.
Environmental toxicity
Diflubenzuron has been evaluated by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), and it is classified as non-carcinogenic. 4-Chloroaniline, a metabolite of diflubenzuron which has been classified as a carcinogen, is produced after diflubenzuron has been ingested. The small amount converted to 4-chloroaniline after ingestion is not sufficient to cause cancer.[4]
Commercial uses
A commercial preparation containing diflubenzuron is sold under the trade name Adept and is used as an insect growth regulator designed to kill fungus gnat larvae in commercial greenhouses.[5][6] It is applied to infected soil and will kill fungus gnat larvae for 30–60 days from a single application. Although it is targeted at fungus gnat larvae, care should be taken in applying it as it is highly toxic to most aquatic invertebrates. It has no toxic effects on adult insects, only insect larvae are affected. Diflubenzuron can cause serious foliar injury to plants in the spurge family and certain types of begonia, particularly poinsettias, hibiscus and reiger begonia and should not be applied to these plant varieties.[5][6]
Diflubenzuron is used as a larvicide in the cattle farming industry. Sold under the name Vigilante, it is formulated as a bolus and is used to control fly populations.[7]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Diflubenzuron Pesticide Information Profile, Extension Toxicology Network
- ↑ Junquera, Pablo; Hosking, Barry; Gameiro, Marta; Macdonald, Alicia (2019). "Benzoylphenyl ureas as veterinary antiparasitics. An overview and outlook with emphasis on efficacy, usage and resistance". Parasite 26: 26. doi:10.1051/parasite/2019026. ISSN 1776-1042. PMID 31041897.

- ↑ Johnson, Douglas (2016). "Insecticide Recommendations for Soybeans - 2016". University of Kentucky: College of Agriculture, Food and Environment. http://pest.ca.uky.edu/EXT/Recs/ENT13-Soybeans.pdf.
- ↑ "Reregistration Eligibility Decision Diflubenzuron". https://www3.epa.gov/pesticides/chem_search/reg_actions/reregistration/fs_PC-108201_1-Aug-97.pdf.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "ADEPT Insect Growth Regulator". http://www.ohp.com/PIB/PDF/adept_130_pib.pdf.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "Adept label". http://www.ohp.com/Labels_MSDS/PDF/adept_label.pdf.
- ↑ Kydonieus, Agis F. (2017-10-02) (in en). Treatise on Controlled Drug Delivery: Fundamentals-optimization-applications. Routledge. ISBN 9781351406871. https://books.google.com/books?id=s0k4DwAAQBAJ&dq=%22vigilante+bolus%22&pg=PA231-IA43.
 |

