Chemistry:Chlorfenapyr
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
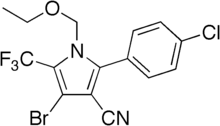
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-Bromo-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(ethoxymethyl)-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonitrile | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H11BrClF3N2O | |
| Molar mass | 407.62 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.543 g/ml tapped bulk density |
| Melting point | 100 to 101 °C (212 to 214 °F; 373 to 374 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |    
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H302, H320, H331, H371, H373, H410 | |
| P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P301+312, P304+340, P305+351+338, P309+311, P311, P314, P321, P330, P337+313, P391, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Chlorfenapyr is a pesticide, and specifically a pro-insecticide (meaning it is metabolized into an active insecticide after entering the host), derived from a class of microbially produced compounds known as halogenated pyrroles.
History and Applications
Chlorfenapyr was developed by American Cyanamid from the natural product dioxapyrrolomycin, which was isolated from Streptomyces fumanus.[1]
The United States Environmental Protection Agency initially denied registration in 2000 for use on cotton primarily because of concerns that the insecticide was toxic to birds and because effective alternatives were available.[2] However, it was registered by the EPA in January, 2001 for use on non-food crops in greenhouses.[3] In 2005, the EPA established a tolerance for residues of chlorfenapyr in or on all food commodities.
Chlorfenapyr is also used as a wool insect-proofing agent, and was introduced as an alternative to synthetic pyrethroids due to a lower toxicity to mammalian and aquatic life.[4]
In April 2016, in Pakistan, 31 people died when their food was spiked with chlorfenapyr.[5]
Mode of Action
Chlorfenapyr works by disrupting the production of adenosine triphosphate, specifically, "Oxidative removal of the N-ethoxymethyl group of chlorfenapyr by mixed function oxidases forms the compound CL 303268. CL 303268 uncouples oxidative phosphorylation at the mitochondria, resulting in disruption of production of ATP, cellular death, and ultimately organism mortality."
Notes
- ↑ Black, B.C.; Hollingworth, R.M.; Ahammadsahib, K.I.; Kukel, C.D.; Donovan, S. (October 1994). "Insecticidal Action and Mitochondrial Uncoupling Activity of AC-303,630 and Related Halogenated Pyrroles". Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology 50 (2): 115-128. doi:10.1006/pest.1994.1064.
- ↑ US EPA (2000). "Decision Memorandum: Denial of Registration of Chlorfenapyr for Use on Cotton". http://www.epa.gov/opprd001/chlorfenapyr/chlorfenapyr.pdf.
- ↑ US EPA (2001). "Pesticide Fact Sheet: Chlorfenapyr". http://www.epa.gov/pesticides/chem_search/reg_actions/registration/fs_PC-129093_01-Jan-01.pdf.
- ↑ Ingham, P. E.; McNeil, S. J.; Sunderland, M. R. (2012). "Functional finishes for wool – Eco considerations". Advanced Materials Research 441: 33–43. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.441.33.
- ↑ Fred Barbash (May 6, 2016). "31 people suddenly dropped dead in a Pakistani village. Now police claim to know the horrible reason why.". Washington Post. https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/morning-mix/wp/2016/05/06/he-wanted-to-teach-him-a-lesson-revenge-by-a-brother-in-pakistan-allegedly-leads-to-31-deaths-from-poisoned-sweets/.
External links
- Effects of Chlorfenapyr on Adult Birds
- Chlorfenapyr; Pesticide Tolerance
- Australian Pesticides and Veterinary Medicines Authority
 |
