Chemistry:Dichlorodiphenyldichloroethane
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1-chloro-4-[2,2-dichloro-
| |
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,1′-(2,2-dichloroethane-1,1-diyl)bis(4-chlorobenzene) | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | DDD |
| 4-05-00-01884 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | DDD |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H10Cl4 | |
| Molar mass | 320.03 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless and crystalline |
| Density | 1.476 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 109.5 °C (229.1 °F; 382.6 K) |
| Boiling point | 350 °C (662 °F; 623 K) |
| 0.09 mg/L | |
| log P | 6.02 (octanol-water) |
| Vapor pressure | 1.35×10−6 mm Hg |
Henry's law
constant (kH) |
6.6×10−6 atm ∙ m3/mol |
Atmospheric OH rate constant
|
4.34×10−12 cm3/molecule ∙ s |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
DDE, DDT, mitotane, perthane |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
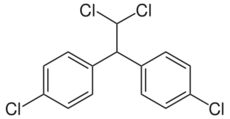
Dichlorodiphenyldichloroethane (DDD) is an organochlorine insecticide that is slightly irritating to the skin.[1] DDD is a metabolite of DDT.[2] DDD is colorless and crystalline;[3] it is closely related chemically and is similar in properties to DDT, but it is considered to be less toxic to animals than DDT.[4] The molecular formula for DDD is (ClC6H4)2CHCHCl2 or C14H10Cl4, whereas the formula for DDT is (ClC6H4)2CHCCl3 or C14H9Cl5.
DDD is in the “Group B2” classification, meaning that it is a probable human carcinogen. This is based on an increased incidence of lung tumors in male and female mice, liver tumors in male mice, and thyroid tumors in male rats. A further basis is that DDD is similar to and is a metabolite of DDT, another probable human carcinogen.[2]
DDD is no longer registered for agricultural use in the United States , but the general population continues to be exposed to it due to its long persistence time. The primary source of exposure is oral ingestion of food.[5]
1946 is the date of the earliest recorded use in English of the abbreviation “DDD” to stand for dichlorodiphenyldichloroethane, as far as could be determined.[3]

Mitotane
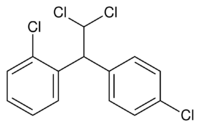
If one of the p-chlorines in DDD is switched to ortho-position, the result is the chemotherapeutic agent mitotane. This is an example of a positional isomer.
Table of names
The following are synonyms for DDD:
| Systematic Names | Superlist Names | Other Names |
|---|---|---|
| Benzene, 1,1'-(2,2- dichloroethylidene) bis(4-chloro- (9CI) |
4,4'-DDD | 1,1'-(2,2-Dichloroethylidene)bis (4-chlorobenzene) |
| Ethane, 1,1- dichloro-2,2-bis(p- chlorophenyl)- |
Benzene, 1,1'-(2,2- dichloroethylidene)bis(4-chloro- |
1,1-Bis(4-chlorophenyl)-2,2- dichloroethane |
| TDE | DDD | 1,1-Bis(p-chlorophenyl)-2,2- dichloroethane |
| p,p'-TDE | DDD, p,p'- | 1,1-Dichloor-2,2-bis(4-chloor fenyl)-ethaan (Dutch) |
| Dichlorodiphenyldichloroethane | 1,1-Dichlor-2,2-bis(4-chlor- phenyl)-aethan (German) | |
| RCRA waste number U060 | 1,1-Dichloro-2,2-bis(4- chlorophenyl)-ethane (French) | |
| TDE | 1,1-Dichloro-2,2-bis(4- chlorophenyl)ethane | |
| Tetrachlorodiphenylethane | 1,1-Dichloro-2,2-bis(p- chlorophenyl)ethane | |
| p,p'-TDE | 1,1-Dichloro-2,2-bis (parachlorophenyl)ethane | |
| 1,1-Dichloro-2,2-di(4- chlorophenyl)ethane | ||
| 1,1-Dicloro-2,2-bis(4-cloro-fenil)- etano (Italian) | ||
| 2,2-Bis(4-chlorophenyl)-1,1- dichloroethane | ||
| 2,2-Bis(p-chlorophenyl)-1,1- dichloroethane | ||
| 4,4' DDD | ||
| 4,4-DDD | ||
| 4,4'- Dichlorodiphenyldichloroethane | ||
| 4-05-00-01884 (Beilstein Handbook Reference) | ||
| AI3-04225 | ||
| Benzene, 1,1'-(2,2- dichloroethylidene)bis[4-chloro- | ||
| BRN 1914072 | ||
| CCRIS 573 | ||
| Caswell No. 307 | ||
| DDD analogue | ||
| DDD in whole water sample | ||
| Dichlorodiphenyl dichloroethane | ||
| Dichlorodiphenyldichlorethane | ||
| Dilene | ||
| EINECS 200-783-0 | ||
| ENT 4,225 | ||
| EPA Pesticide Chemical Code 029101 | ||
| Ethane, 1,1-dichloro-2,2-bis(p- chlorophenyl)- | ||
| HEPT | ||
| HSDB 285 | ||
| ME-1700 | ||
| Me-700 | ||
| NCI-C00475 | ||
| NSC 8941 | ||
| OMS 1078 | ||
| para-para DDD | ||
| para,para'-DDD | ||
| para,para'- Dichlorodiphenyldichloroethane | ||
| p,p-DDD | ||
| p,p'-DDD | ||
| p,p'-Dichlorodiphenyl-2,2-dichloroethylene | ||
| p,p'-Dichlorodiphenyldichloroethane | ||
| Rhothane | ||
| Rhothane D-3 | ||
| Rothane | ||
| Rothane WP-50 |
References
- “Chemicals: Dichlorodiphenyldichloroethane.” The Comparative Toxicogenomics Database. MDI Biological Laboratory, 11 Apr. 2007 <http://ctd.mdibl.org/detail.go?type=chem&acc=D003632>.
- “Data From SRC PhysProp Database.” SRC PhysProp Database. Syracuse Research Corporation. 11 Apr. 2007 <https://web.archive.org/web/20070927230912/http://esc.syrres.com/interkow/webprop.exe?CAS=72-54-8>.
- “DDD.” Hazardous Substances Data Bank. United States National Library of Medicine. 25 Apr. 2007 <https://web.archive.org/web/20120207033729/http://toxmap.nlm.nih.gov/toxmap/main/chemPage.jsp?chem=4,4-DICHLORODIPHENYLDICHLOROETHANE then click “Env. Fate / Exposure”>.
- “DDD—RN: 72-54-8.” ChemIDplus Lite Record. 9 Sept. 2004. United States National Library of Medicine Specialized Information Services. 11 Apr. 2007 <https://web.archive.org/web/20110717080344/http://chem2.sis.nlm.nih.gov/chemidplus/direct.jsp?regno=72-54-8>.
- Guralnik, David B., Editor in Chief. “DDD.” Webster’s New World Dictionary of the American Language. Second College Edition. New York, NY: Prentice Hall Press, 1986. ISBN:0-671-41809-2 (indexed), ISBN:0-671-41807-6 (plain edge), ISBN:0-671-41811-4 (pbk.), and ISBN:0-671-47035-3 (LeatherKraft).
- Mish, Frederick C., Editor in Chief. “DDD.” Webster’s Ninth New Collegiate Dictionary. 9th ed. Springfield, MA: Merriam-Webster Inc., 1985. ISBN:0-87779-508-8, ISBN:0-87779-509-6 (indexed), and ISBN:0-87779-510-X (deluxe).
- “p,p'-DDD.” Substance Registry System. 1 Feb. 2006. United States Environmental Protection Agency. 11 Apr. 2007 <https://web.archive.org/web/20061008163205/http://iaspub.epa.gov/srs/srs_proc_qry.navigate?P_SUB_ID=4937>.
- “p,p'-Dichlorodiphenyl dichloroethane (DDD) (CASRN 72-54-8).” Integrated Risk Information System. 25 Jan. 2007. United States Environmental Protection Agency. 23 Apr. 2007 <http://www.epa.gov/iris/subst/0347.htm>.
Notes
- ↑ Merck Index, 11th ed, p482
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 “p,p'-Dichlorodiphenyl dichloroethane (DDD) (CASRN 72-54-8).” Integrated Risk Information System. 25 Jan. 2007. United States Environmental Protection Agency. 23 Apr. 2007 <http://www.epa.gov/iris/subst/0347.htm>.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Mish, Frederick C., Editor in Chief. “DDD.” Webster’s Ninth New Collegiate Dictionary. 9th ed. Springfield, MA: Merriam-Webster Inc., 1985.
- ↑ Guralnik, David B., Editor in Chief. “DDD.” Webster’s New World Dictionary of the American Language. Second College Edition. New York, NY: Prentice Hall Press, 1986.
- ↑ “DDD.” Hazardous Substances Data Bank. United States National Library of Medicine. 25 Apr. 2007 <http://toxmap.nlm.nih.gov/toxmap/main/chemPage.jsp?chem=4,4-DICHLORODIPHENYLDICHLOROETHANE then click “Env. Fate / Exposure”>.
External links
- TOXMAP Chemical Page for DDD
- MSDS for rhothane (DDD) provided by the Physical and Theoretical Chemistry Laboratory of the University of Oxford
 |

