Chemistry:Dimefox
From HandWiki
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
N-[dimethylamino(fluoro)phosphoryl]-N-methylmethanamine
| |
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H12FN2OP | |
| Molar mass | 154.125 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colourless liquid |
| Density | 1.11 g·mL–1 |
| 14.8 g·L–1 | |
| Vapor pressure | 14663 mPa |
Henry's law
constant (kH) |
2.28·10–8 atm·m3·mol–1[2] |
| Pharmacology | |
| inhalation and dermal contact | |
| Legal status |
|
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Highly Toxic |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H300, H310 | |
| P262, P264, P270, P280, P301+310, P302+350, P310, P321, P322, P330, P361, P363, P405, P501 | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
2 mg/kg (oral, mice)[1] 1 mg/kg (oral, rats)[1] 3 mg/kg (intravenous, rabbits)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
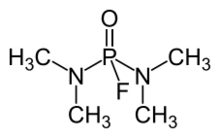
Dimefox, also known as TL-792 or T-2002, is a highly toxic organophosphate insecticide. In its pure form it is a colourless liquid with a fishy odour.[3] Dimefox was first produced in 1940 by the group of Gerhard Schrader in Germany. It was historically used as a pesticide, but has been deemed obsolete or discontinued for use by the World Health Organization due to being an inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase.[citation needed] It is not guaranteed that all commercial use of this compound ceased, but in most countries[which?] it is no longer registered for use as a pesticide.[4] It is considered an extremely hazardous substance as defined by the United States Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Chemical Warfare Agents, and Related Chemical Problems. Parts I-II. 1958. https://ntrl.ntis.gov/NTRL/dashboard/searchResults/titleDetail/PB158508.xhtml.
- ↑ "Dimefox". https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/summary/summary.cgi?cid=8264.
- ↑ "IUPAC FOOTPRINT Pesticides Properties Database". http://sitem.herts.ac.uk/aeru/iupac/236.htm.
- ↑ the WHO recommended classification of pesticides by hazard and guidelines to classification 2009, [1]
 |
