Chemistry:Europium hydride
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Europium(II) hydride
Europium dihydride | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| EuH2 | |
| Molar mass | 153.98 |
| Appearance | dark reddish powder[2] |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Europium(II) oxide Europium(II) hydroxide Europium(II) chloride |
Other cations
|
samarium hydride gadolinium hydride |
Related compounds
|
Europium(III) hydride[3] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
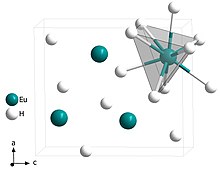
Europium hydride is the most common hydride of europium with a chemical formula EuH2. In this compound, europium atom is in the +2 oxidation state and the hydrogen atoms are -1.[4] It is a ferromagnetic semiconductor.[5]
Production
Europium hydride can be produced by directly reacting europium and hydrogen gas:[4]
- Eu + H2 → EuH2
Uses
EuH2 can be used as a source of Eu2+ to create metal-organic frameworks that have the Eu2+ ion.[2]
References
- ↑ SciFinder
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Rybak, Jens-Christoph; Hailmann, Michael; Matthes, Philipp R.; Zurawski, Alexander; Nitsch, Jörn; Steffen, Andreas; Heck, Joachim G.; Feldmann, Claus et al. (29 April 2013). "Metal–Organic Framework Luminescence in the Yellow Gap by Codoping of the Homoleptic Imidazolate ∞3[Ba(Im)2] with Divalent Europium". Journal of the American Chemical Society 135 (18): 6896–6902. doi:10.1021/ja3121718. PMID 23581546.
- ↑ Matsuoka, T.; Fujihisa, H.; Hirao, N.; Ohishi, Y.; Mitsui, T.; Masuda, R.; Seto, M.; Yoda, Y. et al. (5 July 2011). "Structural and valence changes of europium hydride induced by application of high-pressure H2". Physical Review Letters 107 (2): 025501. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.107.025501. PMID 21797616. Bibcode: 2011PhRvL.107b5501M. http://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.107.025501#fulltext. Retrieved 19 November 2016.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 洪广言 (2014). "3.2.4 稀土氢化物" (in zh). 稀土化学导论. 现代化学基础丛书. 36. 北京: 科学出版社. pp. 57–59. ISBN 978-7-03-040581-4.
- ↑ Bischof, R.; Kaldis, E.; Wachter, P. (February 1983). "EuH2: A new ferromagnetic semiconductor". Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 31-34: 255–256. doi:10.1016/0304-8853(83)90239-1. Bibcode: 1983JMMM...31..255B.
 |