Chemistry:Sulbenicillin
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
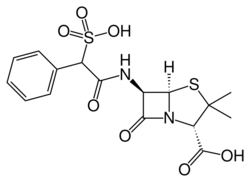
| Formula | C16H18N2O7S2 |
| Molar mass | 414.45 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Sulbenicillin (INN) is a penicillin antibiotic, notable for its combination use with dibekacin. [1] Penicillins, crucial in primary healthcare for potent bactericidal properties and wide distribution, include oral options for enhanced accessibility. Post-World War II, synthetic penicillins like sulbenicillin broadened efficacy, leading to new groups that diversified treatment. This evolution reflects a dynamic interplay between science and clinical needs, emphasizing enduring value in managing infectious diseases in primary care.
Structure and mechanism of action
Characterized by a distinctive beta-lactam ring, penicillins inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis, leading to cell destruction. This mechanism is effective against a broad spectrum of bacteria.[2]
References
- ↑ "Electron microscopy of Pseudomonas aeruginosa treated with sulbenicillin and dibekacin". Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 152 (2): 119–28. June 1987. doi:10.1620/tjem.152.119. PMID 3114912. https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/tjem1920/152/2/152_2_119/_article.
- ↑ PubChem. "CID 5317" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/5317.
 |
