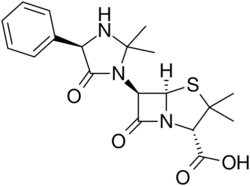
Chemistry:Hetacillin
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Hetacin, Versapen |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Veterinary Use |
| Routes of administration | Intramammary injection |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H23N3O4S |
| Molar mass | 389.47 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Hetacillin is a beta-lactam antibiotic that is part of the aminopenicillin family. It is a prodrug and has no antibacterial activity itself,[1] but quickly splits off acetone in the human body to form ampicillin,[2] which is active against a variety of bacteria.
Administration
Hetacillin can be administered orally. The potassium salt, hetacillin potassium, is administered by injection, either intravenously[3] or intramuscularly.[4] It is sold under the trade name Hetacin for intramammary injection in veterinary use.[5]
Hetacillin was withdrawn from the market for human use when the discovery was made that it had no advantages over ampicillin.[6]
Chemistry
Hetacillin is prepared from ampicillin and acetone. In aqueous solutions it is unstable, with a half life of 15 to 30 minutes at 37 °C (99 °F) and pH 7, quickly releasing acetone again.[7]
As opposed to ampicillin, hetacillin is only marginally broken down by the bacterial enzyme beta-lactamase, at least in vitro.[citation needed]
References
- ↑ "Hetacillin". Drugbank. http://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00739.
- ↑ "Laboratory and pharmacological studies in man with hetacillin and ampicillin". British Medical Journal 2 (5555): 804–8. June 1967. doi:10.1136/bmj.2.5555.804. PMID 5182358.
- ↑ "[Clinical effect of intravenous injection of potassium hetacillin (Versapen 'Bristol') on pre- and post-operative infections] (in Japanese)". The Japanese Journal of Antibiotics 23 (4): 400–2. August 1970. PMID 5312791.
- ↑ "[Therapeutic experience with intramuscular injection of hetacillin (Versapen 'Bristol') in infection in children] (in Japanese)". The Japanese Journal of Antibiotics 23 (5): 482–6. December 1970. PMID 5314634.
- ↑ Hetacin-K Intramammary Infusion for Veterinary Use
- ↑ "Hetacillin: A Chemical and Biological Comparison with Ampicillin". Chemotherapy 15 (6): 366–78. 1970. doi:10.1159/000220703. PMID 5514976.
- ↑ "Independent antibiotic actions of hetacillin and ampicillin revealed by fast methods". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 3 (1): 15–8. January 1973. doi:10.1128/aac.3.1.15. PMID 4597707.
 |
