Chemistry:Cefpodoxime
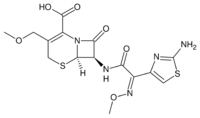 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Vantin, others |
| Other names | Cefpodoxime proxetil |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a698024 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 50% |
| Protein binding | 21% to 29% |
| Metabolism | Negligible. Cefpodoxime proxetil is metabolized to cefpodoxime by the liver |
| Elimination half-life | 2 hours |
| Excretion | Kidney, unchanged |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H17N5O6S2 |
| Molar mass | 427.45 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Cefpodoxime is an oral, third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic available in various generic preparations. It is active against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative organisms with notable exceptions including Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterococcus, and Bacteroides fragilis. It is typically used to treat acute otitis media, pharyngitis, sinusitis, and gonorrhea. It also finds use as oral continuation therapy when intravenous cephalosporins (such as ceftriaxone) are no longer necessary for continued treatment.
Cefpodoxime inhibits peptidoglycan synthesis in bacterial cell walls. It has an oral bioavailability of approximately 50%, which is increased when taken with food. It has an elimination half-life of 2-3 hours in adults, which is prolonged in renal failure. Approved indications include community acquired pneumonia, uncomplicated skin and skin structure infections, and uncomplicated urinary tract infections.
It was patented in 1980 and approved for medical use in 1989.[1]
Spectrum of bacterial susceptibility and resistance
Cefpodoxime has been used to treat gonorrhoea, tonsillitis, pneumonia, and bronchitis. The following minimum inhibitory concentrations have been reported:[2]
- Haemophilus influenzae: ≤0.03 – 1 μg/ml
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae: 0.004 – 0.06 μg/ml
- Streptococcus pyogenes: ≤0.004 – 2 μg/ml
Brand names
Zoetis markets cefpodoxime proxetil under the trade name Simplicef for veterinary use, Finecure,[3] India markets the products under trade name Cefpo.[4]
Vantin (by Pfizer)[5] in suspension or tablet form.
Toraxim (by Delta Pharma Ltd. Bangladesh)
Trucef (by Renata Limited, Bangladesh)
Tricef (by Alkaloid Skopje, North Macedonia)
Orelox (by Sanofi-Aventis)[6]
MAPDOX-CV: Cefpodoxime and Clavulanic acid combination
MONOTAX O (Cefpodoxime)/ MONOTAX CV (Cefpodoxime and Clavulanic acid combination) (by Zydus Healthcare Ltd.)
ACXIME 200/CV (by Allencia Biosciences, India)
POSTPOD-50 (Cefpodoxime 50mg/5ml) (by Laafon Galaxy Pharmaceuticals)[7]
References
- ↑ (in en) Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. 2006. p. 495. ISBN 9783527607495. https://books.google.com/books?id=FjKfqkaKkAAC&pg=PA495.
- ↑ "Cefpodoxime, Free Acid Susceptibility and Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Data". http://www.toku-e.com/Assets/MIC/Cefpodoxime%20Free%20acid.pdf.
- ↑ "Pharmaceuticals Manufacturer, Marketer, Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Company India". http://www.finecurepharma.com/.
- ↑ "Anti Biotics and Anti Bacterial". Finecurepharmaceuticalsltd. http://www.finecurepharma.com/cephalosporins.htm#cefu5.
- ↑ "Vantin – Drugs.com". https://www.drugs.com/international/vantin.html.
- ↑ "Orelox – Drugs.com". https://www.drugs.com/international/orelox.html.
- ↑ "Postpod dry syrup" (in en-US). https://www.laafon.com/product/postpod-dry-syrup/.
External links
- CID 6526396 from PubChem – cefpodoxime proxetil
- Vantin Tablets and Oral Suspension Torpod (Torrent) Full U.S. Prescribing Information (from manufacturer's website)
- Simplicef (from manufacturer's website)
- Intas Pharmaceuticals Ltd. » Animal Health :: Intas - a leading global pharmaceutical formulation development, manufacturing and marketing company
 |
