Chemistry:Cefamandole
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | former Mandol |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| MedlinePlus | a601206 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular, intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 75% |
| Elimination half-life | 48 minutes |
| Excretion | Mostly renal, as unchanged drug |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
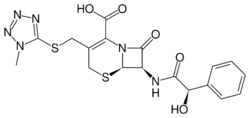
| Formula | C18H18N6O5S2 |
| Molar mass | 462.50 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Cefamandole (INN, also known as cephamandole) is a second-generation broad-spectrum cephalosporin antibiotic. The clinically used form of cefamandole is the formate ester cefamandole nafate, a prodrug which is administered parenterally. Cefamandole is no longer available in the United States.
The chemical structure of cefamandole, like that of several other cephalosporins, contains an N-methylthiotetrazole (NMTT or 1-MTT) side chain. As the antibiotic is broken down in the body, it releases free NMTT, which can cause hypoprothrombinemia (likely due to inhibition of the enzyme vitamin K epoxide reductase)(vitamin K supplement is recommended during therapy) and a reaction with ethanol similar to that produced by disulfiram (Antabuse), due to inhibition of aldehyde dehydrogenase.
Cefamandole has a broad spectrum of activity and can be used to treat bacterial infections of the skin, bones and joints, urinary tract, and lower respiratory tract. The following represents cefamandole MIC susceptibility data for a few medically significant microorganisms.
- Escherichia coli: 0.12 - 400 μg/ml
- Haemophilus influenzae: 0.06 - >16 μg/ml
- Staphylococcus aureus: 0.1 - 12.5 μg/ml[1]
CO2 is generated during the normal constitution of cefamandole and ceftazidime, potentially resulting in an explosive-like reaction in syringes.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ "Cefamandole sodium salt Susceptibility and 0.5 - 32 Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Data". The Antimicrobial Index. TOKU-E. 6 January 2020. http://www.toku-e.com/Assets/MIC/Cefamandole%20sodium%20salt.pdf.
- ↑ "Antibiotics, antifungals, and antivirals". Goldfrank's toxicologic emergencies. New York: McGraw-Hill. 2006. pp. 847. ISBN 0-07-143763-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=cvJuLqBxGUcC&pg=PA847. Retrieved 2009-07-03.
 |
