Chemistry:Cephalosporin
| Cephalosporin | |
|---|---|
| Drug class | |
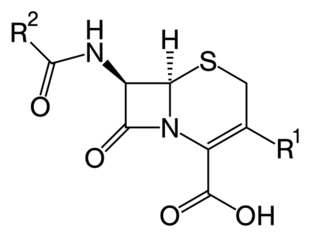 Core structure of the cephalosporins | |
| Class identifiers | |
| Use | Bacterial infection |
| ATC code | J01D |
| Biological target | Penicillin binding proteins |
| Clinical data | |
| Drugs.com | Drug Classes |
| External links | |
| MeSH | D002511 |
The cephalosporins (sg. /ˌsɛfələˈspɔːrɪn, ˌkɛ-, -loʊ-/[1][2]) are a class of β-lactam antibiotics originally derived from the fungus Acremonium, which was previously known as Cephalosporium.[3]
Together with cephamycins, they constitute a subgroup of β-lactam antibiotics called cephems. Cephalosporins were discovered in 1945, and first sold in 1964.[4]
Discovery
The aerobic mold which yielded cephalosporin C was found in the sea near a sewage outfall in Su Siccu, by Cagliari harbour in Sardinia, by the Italian pharmacologist Giuseppe Brotzu in July 1945.[5]
Structure
Cephalosporin contains a 6-membered dihydrothiazine ring. Substitutions at position 3 generally affect pharmacology; substitutions at position 7 affect antibacterial activity, but these cases are not always true.[6]
Medical uses
Cephalosporins can be indicated for the prophylaxis and treatment of infections caused by bacteria susceptible to this particular form of antibiotic. First-generation cephalosporins are active predominantly against Gram-positive bacteria, such as Staphylococcus and Streptococcus.[7] They are therefore used mostly for skin and soft tissue infections and the prevention of hospital-acquired surgical infections.[8] Successive generations of cephalosporins have increased activity against Gram-negative bacteria, albeit often with reduced activity against Gram-positive organisms.[citation needed]
The antibiotic may be used for patients who are allergic to penicillin due to the different β-lactam antibiotic structure. The drug is able to be excreted in the urine.[7]
Side effects
Common adverse drug reactions (ADRs) (≥ 1% of patients) associated with the cephalosporin therapy include: diarrhea, nausea, rash, electrolyte disturbances, and pain and inflammation at injection site. Infrequent ADRs (0.1–1% of patients) include vomiting, headache, dizziness, oral and vaginal candidiasis, pseudomembranous colitis, superinfection, eosinophilia, nephrotoxicity, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and fever.[citation needed]
Allergic hypersensitivity
The commonly quoted figure of 10% of patients with allergic hypersensitivity to penicillins and/or carbapenems also having cross-reactivity with cephalosporins originated from a 1975 study looking at the original cephalosporins,[9] and subsequent "safety first" policy meant this was widely quoted and assumed to apply to all members of the group.[10] Hence, it was commonly stated that they are contraindicated in patients with a history of severe, immediate allergic reactions (urticaria, anaphylaxis, interstitial nephritis, etc.) to penicillins, carbapenems, or cephalosporins.[11]
The contraindication, however, should be viewed in the light of recent epidemiological work suggesting, for many second-generation (or later) cephalosporins, the cross-reactivity rate with penicillin is much lower, having no significantly increased risk of reactivity over the first generation based on the studies examined.[10][12] The British National Formulary previously issued blanket warnings of 10% cross-reactivity, but, since the September 2008 edition, suggests, in the absence of suitable alternatives, oral cefixime or cefuroxime and injectable cefotaxime, ceftazidime, and ceftriaxone can be used with caution, but the use of cefaclor, cefadroxil, cefalexin, and cefradine should be avoided.[13] A 2012 literature review similarly finds that the risk is negligible with third- and fourth-generation cephalosporins. The risk with first-generation cephalosporins having similar R1 sidechains was also found to be overestimated, with the real value closer to 1%.[14]
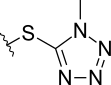
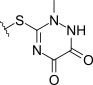
MTT side chain
Several cephalosporins are associated with hypoprothrombinemia and a disulfiram-like reaction with ethanol.[15][16] These include latamoxef (moxalactam), cefmenoxime, cefoperazone, cefamandole, cefmetazole, and cefotetan. This is thought to be due to the methylthiotetrazole side-chain of these cephalosporins, which blocks the enzyme vitamin K epoxide reductase (likely causing hypothrombinemia) and aldehyde dehydrogenase (causing alcohol intolerance).[17] Thus, consumption of alcohol after taking these cephalosporin orally or intravenously is contraindicated, and in severe cases can lead to death.[18] The methylthiodioxotriazine sidechain found in ceftriaxone has a similar effect. Cephalosporins without these structural elements are believed to be safe with alcohol.[19]
Mechanism of action
Cephalosporins are bactericidal and, like other β-lactam antibiotics, disrupt the synthesis of the peptidoglycan layer forming the bacterial cell wall. The peptidoglycan layer is important for cell wall structural integrity. The final transpeptidation step in the synthesis of the peptidoglycan is facilitated by penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs). PBPs bind to the D-Ala-D-Ala at the end of muropeptides (peptidoglycan precursors) to crosslink the peptidoglycan. Beta-lactam antibiotics mimic the D-Ala-D-Ala site, thereby irreversibly inhibiting PBP crosslinking of peptidoglycan.[20]
Resistance
Resistance to cephalosporin antibiotics can involve either reduced affinity of existing PBP components or the acquisition of a supplementary β-lactam-insensitive PBP. Compared to other β-lactam antibiotics (such as penicillins), they are less susceptible to β-lactamases. Currently, some Citrobacter freundii, Enterobacter cloacae, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and Escherichia coli strains are resistant to cephalosporins. Some Morganella morganii, Proteus vulgaris, Providencia rettgeri, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Serratia marcescens and Klebsiella pneumoniae strains have also developed resistance to cephalosporins to varying degrees.[21][22]
Classification
The cephalosporin nucleus can be modified to gain different properties. Cephalosporins are sometimes grouped into "generations" by their antimicrobial properties.[citation needed]
The first cephalosporins were designated first-generation cephalosporins, whereas, later, more extended-spectrum cephalosporins were classified as second-generation cephalosporins. Each newer generation has significantly greater Gram-negative antimicrobial properties than the preceding generation, in most cases with decreased activity against Gram-positive organisms. Fourth-generation cephalosporins, however, have true broad-spectrum activity.[23]
The classification of cephalosporins into "generations" is commonly practised, although the exact categorization is often imprecise. For example, the fourth generation of cephalosporins is not recognized as such in Japan.[citation needed] In Japan, cefaclor is classed as a first-generation cephalosporin, though in the United States it is a second-generation one; and cefbuperazone, cefminox, and cefotetan are classed as second-generation cephalosporins.
First generation
Cefalotin, cefazolin, cefalexin, cefapirin, cefradine, and cefadroxil are drugs belonging to this group.
Second generation
Cefoxitin, cefuroxime, cefaclor, cefprozil, and cefmetazole are classed as second-generation cephems.
Third generation
Ceftazidime, ceftriaxone, and cefotaxime are classed as third-generation cephalosporins. Flomoxef and latamoxef are in a new, related class called oxacephems.[24]
Fourth generation
Drugs included in this group are cefepime and cefpirome.
Further generations
Some state that cephalosporins can be divided into five or even six generations, although the usefulness of this organization system is of limited clinical relevance.[25]
Naming
Most first-generation cephalosporins were originally spelled "ceph-" in English-speaking countries. This continues to be the preferred spelling in the United States, Australia, and New Zealand, while European countries (including the United Kingdom) have adopted the International Nonproprietary Names, which are always spelled "cef-". Newer first-generation cephalosporins and all cephalosporins of later generations are spelled "cef-", even in the United States.[citation needed]
Activity
There exist bacteria which cannot be treated with cephalosporins of generations first through fourth:[26]
- Listeria spp.
- Atypicals (including Mycoplasma and Chlamydia)
- MRSA
- Enterococci
Fifth-generation cephalosporins (e.g. ceftaroline) are effective against MRSA, Listeria spp., and Enterococcus faecalis.[27][26]
Overview table
| rowspan=2 Script error: No such module "Vertical header". | Name | rowspan=2 Script error: No such module "Vertical header". | rowspan=2 Script error: No such module "Vertical header". | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Common | Alternate name or spelling | Brand | ||||
| (#) = noncephalosporins similar to generation # | H, human; V, veterinary; W, withdrawn; P, Pseudomonas; MR, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; An, anaerobe | |||||
| 1 | Cefalexin | cephalexin | Keflex | H V | Gram-positive: Activity against penicillinase-producing, methicillin-susceptible staphylococci and streptococci (though they are not the drugs of choice for such infections). No activity against methicillin-resistant staphylococci or enterococci.[citation needed]
Gram-negative: Activity against Proteus mirabilis, some Escherichia coli, and Klebsiella pneumoniae ("PEcK"), but have no activity against Bacteroides fragilis, Pseudomonas, Acinetobacter, Enterobacter, indole-positive Proteus, or Serratia.[citation needed] | |
| Cefadroxil | cefadroxyl | Duricef | H | |||
| Cefazolin | cephazolin | Ancef, Kefzol | H | |||
| Cefapirin | cephapirin | Cefadryl | V | |||
| Cefacetrile | cephacetrile | |||||
| Cefaloglycin | cephaloglycin | |||||
| Cefalonium | cephalonium | |||||
| Cefaloridine | cephaloradine | |||||
| Cefalotin | cephalothin | Keflin | ||||
| Cefatrizine | ||||||
| Cefazaflur | ||||||
| Cefazedone | ||||||
| Cefradine | cephradine | Velosef | ||||
| Cefroxadine | ||||||
| Ceftezole | ||||||
| 2 | Cefuroxime | Altacef, Zefu, Zinnat, Zinacef, Ceftin, Biofuroksym,[28] Xorimax | H | Gram-positive: Less than first-generation.[citation needed]
Gram-negative: Greater than first-generation: HEN Haemophilus influenzae, Enterobacter aerogenes and some Neisseria + the PEcK described above.[citation needed] | ||
| Cefprozil | cefproxil | Cefzil | H | |||
| Cefaclor | Ceclor, Distaclor, Keflor, Raniclor | H | ||||
| Cefonicid | Monocid | |||||
| Cefuzonam | ||||||
| Cefamandole | W | |||||
| (2) | Cefoxitin | Mefoxin | H | An | Cephamycins sometimes grouped with second-generation cephalosporins | |
| Cefotetan | Cefotan | H | An | |||
| Cefmetazole | Zefazone | An | ||||
| Cefminox | ||||||
| Cefbuperazone | ||||||
| Cefotiam | Pansporin | |||||
| Loracarbef | Lorabid | The carbacephem analog of cefaclor | ||||
| 3 | Cefdinir | Sefdin, Zinir, Omnicef, Kefnir | H | Gram-positive: Some members of this group (in particular, those available in an oral formulation, and those with antipseudomonal activity) have decreased activity against gram-positive organisms.
Activity against staphylococci and streptococci is less with the third-generation compounds than with the first- and second-generation compounds.[29] Gram-negative: Third-generation cephalosporins have a broad spectrum of activity and further increased activity against gram-negative organisms. They may be particularly useful in treating hospital-acquired infections, although increasing levels of extended-spectrum beta-lactamases are reducing the clinical utility of this class of antibiotics. They are also able to penetrate the central nervous system, making them useful against meningitis caused by pneumococci, meningococci, H. influenzae, and susceptible E. coli, Klebsiella, and penicillin-resistant N. gonorrhoeae. Since August 2012, the third-generation cephalosporin, ceftriaxone, is the only recommended treatment for gonorrhea in the United States (in addition to azithromycin or doxycycline for concurrent Chlamydia treatment). Cefixime is no longer recommended as a first-line treatment due to evidence of decreasing susceptibility.[30] | ||
| Ceftriaxone | Rocephin | H | ||||
| Ceftazidime | Meezat, Fortum, Fortaz | H | P | |||
| Cefixime | Fixx, Zifi, Suprax | H | ||||
| Cefpodoxime | Vantin, PECEF, Simplicef | H V | ||||
| Ceftiofur | Naxcel, Excenel | H V | ||||
| Cefotaxime | Claforan | H | ||||
| Ceftizoxime | Cefizox | H | ||||
| Cefditoren | Zostom-O | H | ||||
| Ceftibuten | Cedax | H | ||||
| Cefovecin | Convenia | V | ||||
| Cefdaloxime | ||||||
| Cefcapene | ||||||
| Cefetamet | ||||||
| Cefmenoxime | ||||||
| Cefodizime | ||||||
| Cefpimizole | ||||||
| Cefteram | ||||||
| Ceftiolene | ||||||
| Cefoperazone | Cefobid | W[31] | P | |||
| (3) | Latamoxef | moxalactam | W[31] | An oxacephem sometimes grouped with third-generation cephalosporins | ||
| 4 | Cefepime | Maxipime | H | P | Gram-positive: They are extended-spectrum agents with similar activity against Gram-positive organisms as first-generation cephalosporins.[citation needed]
Gram-negative: Fourth-generation cephalosporins are zwitterions that can penetrate the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria.[32] They also have a greater resistance to β-lactamases than the third-generation cephalosporins. Many can cross the blood–brain barrier and are effective in meningitis. They are also used against Pseudomonas aeruginosa.[citation needed] Cefiderocol has been called a fourth-generation cephalosporin by only one source as of November 2019.[33] | |
| Cefiderocol | Fetroja | H | ||||
| Cefquinome | V | |||||
| Cefclidine | ||||||
| Cefluprenam | ||||||
| Cefoselis | ||||||
| Cefozopran | ||||||
| Cefpirome | Cefrom | |||||
| (4) | Flomoxef | An oxacephem sometimes grouped with fourth-generation cephalosporins | ||||
| 5 | Ceftaroline | H | MR | Ceftobiprole has been described as "fifth-generation" cephalosporin,[34][35] though acceptance for this terminology is not universal. Ceftobiprole has anti-pseudomonal activity and appears to be less susceptible to development of resistance. Ceftaroline has also been described as "fifth-generation" cephalosporin, but does not have the activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa or vancomycin-resistant enterococci that ceftobiprole has.[36] Ceftolozane is an option for the treatment of complicated intra-abdominal infections and complicated urinary tract infections. It is combined with the β-lactamase inhibitor tazobactam, as multi-drug resistant bacterial infections will generally show resistance to all β-lactam antibiotics unless this enzyme is inhibited.[37][38][39][40][41] | ||
| Ceftolozane | Zerbaxa | H | ||||
| Ceftobiprole | MR | |||||
| ? | Cefaloram | These cephems have progressed far enough to be named, but have not been assigned to a particular generation. Nitrocefin is a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate, and is used for detection of β-lactamases.[citation needed] | ||||
| Cefaparole | ||||||
| Cefcanel | ||||||
| Cefedrolor | ||||||
| Cefempidone | ||||||
| Cefetrizole | ||||||
| Cefivitril | ||||||
| Cefmatilen | ||||||
| Cefmepidium | ||||||
| Cefoxazole | ||||||
| Cefrotil | ||||||
| Cefsumide | ||||||
| Ceftioxide | ||||||
| Cefuracetime | ||||||
| Nitrocefin | ||||||
History
Cephalosporin compounds were first isolated from cultures of Acremonium strictum from a sewer in Sardinia in 1948 by Italian scientist Giuseppe Brotzu.[42] He noticed these cultures produced substances that were effective against Salmonella typhi, the cause of typhoid fever, which had β-lactamase. Guy Newton and Edward Abraham at the Sir William Dunn School of Pathology at the University of Oxford isolated cephalosporin C. The cephalosporin nucleus, 7-aminocephalosporanic acid (7-ACA), was derived from cephalosporin C and proved to be analogous to the penicillin nucleus 6-aminopenicillanic acid (6-APA), but it was not sufficiently potent for clinical use. Modification of the 7-ACA side chains resulted in the development of useful antibiotic agents, and the first agent, cefalotin (cephalothin), was launched by Eli Lilly and Company in 1964.[citation needed]
References
- ↑ "Cephalosporin". Merriam-Webster Dictionary. https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/cephalosporin.
- ↑ "cephalosporin – definition of cephalosporin in English from the Oxford dictionary". OxfordDictionaries.com. https://www.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/english/cephalosporin.
- ↑ "cephalosporin" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ↑ Oxford Handbook of Infectious Diseases and Microbiology. OUP Oxford. 2009. p. 56. ISBN 9780191039621. https://books.google.com/books?id=5W-WBQAAQBAJ&pg=PT56.
- ↑ , Wikidata Q29581637
- ↑ Prince, A. "Cephalosporins and vancomycin". Columbia University. http://www.columbia.edu/itc/hs/medical/pathophys/id/2004/lecture/notes/CephaloVanco_Prince.pdf.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "Cephalosporins – Infectious Diseases" (in en-US). https://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/infectious-diseases/bacteria-and-antibacterial-drugs/cephalosporins.
- ↑ Pandey, Neelanjana; Cascella, Marco (2020). "Beta Lactam Antibiotics". StatPearls. StatPearls. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK545311/.
- ↑ Dash, C. H. (1 September 1975). "Penicillin allergy and the cephalosporins". Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1 (suppl 3): 107–118. doi:10.1093/jac/1.suppl_3.107. PMID 1201975.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Pegler, Scott; Healy, Brendan (10 November 2007). "In patients allergic to penicillin, consider second and third generation cephalosporins for life threatening infections". The BMJ 335 (7627): 991. doi:10.1136/bmj.39372.829676.47. PMID 17991982.
- ↑ Rossi S, editor. Australian Medicines Handbook 2006. Adelaide: Australian Medicines Handbook; 2006.[page needed]
- ↑ Pichichero, Michael E (2006). "Cephalosporins can be prescribed safely for penicillin-allergic patients". The Journal of Family Practice 55 (2): 106–12. PMID 16451776. http://www.jfponline.com/Pages.asp?AID=3850.
- ↑ "5.1.2 Cephalosporins and other beta-lactams". British National Formulary (56 ed.). London: BMJ Publishing Group Ltd and Royal Pharmaceutical Society Publishing. September 2008. pp. 295. ISBN 978-0-85369-778-7. https://archive.org/details/britishnationalf0000unse_k4e9/page/295.
- ↑ Campagna, JD; Bond, MC; Schabelman, E; Hayes, BD (May 2012). "The use of cephalosporins in penicillin-allergic patients: a literature review.". The Journal of Emergency Medicine 42 (5): 612–20. doi:10.1016/j.jemermed.2011.05.035. PMID 21742459.
- ↑ Kitson, Trevor M. (May 1987). "The effect of cephalosporin antibiotics on alcohol metabolism: A review". Alcohol 4 (3): 143–148. doi:10.1016/0741-8329(87)90035-8. PMID 3593530.
- ↑ Shearer, M. J.; Bechtold, H.; Andrassy, K.; Koderisch, J.; McCarthy, P. T.; Trenk, D.; Jähnchen, E.; Ritz, E. (January 1988). "Mechanism of Cephalosporin-induced Hypoprothrombinemia: Relation to Cephalosporin Side Chain, Vitamin K Metabolism, and Vitamin K Status". The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 28 (1): 88–95. doi:10.1002/j.1552-4604.1988.tb03106.x. PMID 3350995.
- ↑ Stork CM (2006). "Antibiotics, antifungals, and antivirals". Goldfrank's toxicologic emergencies. New York: McGraw-Hill. pp. 847. ISBN 978-0-07-143763-9. https://books.google.com/books?id=cvJuLqBxGUcC&pg=PA847.
- ↑ Ren, Shiyan; Cao, Yuxia; Zhang, Xiuwei; Jiao, Shichen; Qian, Songyi; Liu, Peng (2014). "Cephalosporin Induced Disulfiram-Like Reaction: A Retrospective Review of 78 Cases". International Surgery 99 (2): 142–146. doi:10.9738/INTSURG-D-13-00086.1. ISSN 0020-8868. PMID 24670024.
- ↑ Mergenhagen, Kari A.; Wattengel, Bethany A.; Skelly, Megan K.; Clark, Collin M.; Russo, Thomas A. (21 February 2020). "Fact versus Fiction: a Review of the Evidence behind Alcohol and Antibiotic Interactions". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 64 (3): e02167-19. doi:10.1128/aac.02167-19. PMID 31871085.
- ↑ Tipper, D J; Strominger, J L (October 1965). "Mechanism of action of penicillins: a proposal based on their structural similarity to acyl-D-alanyl-D-alanine.". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 54 (4): 1133–1141. doi:10.1073/pnas.54.4.1133. ISSN 0027-8424. PMID 5219821. Bibcode: 1965PNAS...54.1133T.
- ↑ "Cephalosporin spectrum of resistance". http://antibiotics.toku-e.com/m/?w=cephalosporin.
- ↑ Sutaria, Dhruvitkumar S.; Moya, Bartolome; Green, Kari B.; Kim, Tae Hwan; Tao, Xun; Jiao, Yuanyuan; Louie, Arnold; Drusano, George L. et al. (25 May 2018). "First Penicillin-Binding Protein Occupancy Patterns of β-Lactams and β-Lactamase Inhibitors in Klebsiella pneumoniae". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 62 (6): e00282-18. doi:10.1128/AAC.00282-18. PMID 29712652.
- ↑ "Cephalosporins – Infectious Diseases – Merck Manuals Professional Edition" (in en-US). Merck Manuals Professional Edition. https://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/infectious-diseases/bacteria-and-antibacterial-drugs/cephalosporins.
- ↑ Narisada, Masayuki; Tsuji, Teruji (1990). "1-Oxacephem Antibiotics". Recent Progress in the Chemical Synthesis of Antibiotics. pp. 705–725. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-75617-7_19. ISBN 978-3-642-75619-1.
- ↑ "Case Based Pediatrics Chapter". http://www.hawaii.edu/medicine/pediatrics/pedtext/s06c05.html.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 Bui, Toai; Preuss, Charles V. (2023), "Cephalosporins", StatPearls (Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing), PMID 31855361, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551517/, retrieved 2023-06-02
- ↑ Duplessis, C.; Crum-Cianflone, N. F. (2011). "Ceftaroline: A New Cephalosporin with Activity against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)". Clinical Medicine Reviews in Therapeutics 3: a2466. doi:10.4137/CMRT.S1637. PMID 21785568.
- ↑ Jędrzejczyk, Tadeusz. "Internetowa Encyklopedia Leków". leki.med.pl. http://www.leki.med.pl/lek.phtml?id=428&idnlek=2682&menu=4.
- ↑ Scholar, Eric M.; Scholar, Eric Michael; Pratt, William B. (2000). The Antimicrobial Drugs. Oxford University Press. p. 108. ISBN 978-0-19-512528-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=ZQ6KNRLWHLQC&pg=PA108.
- ↑ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (10 August 2012). "Update to CDC's Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, 2010: oral cephalosporins no longer a recommended treatment for gonococcal infections". Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report 61 (31): 590–594. PMID 22874837. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm6131a3.htm.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 Arumugham, VB; Gujarathi, R; Cascella, M (January 2021). Third Generation Cephalosporins. PMID 31751071.
- ↑ Richard L Sweet; Ronald S. Gibbs (1 March 2009). Infectious Diseases of the Female Genital Tract. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 403–. ISBN 978-0-7817-7815-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=wuR_ngItU5oC&pg=PA403. Retrieved 8 September 2010.
- ↑ "CHEBI:140376 – cefiderocol". EMBL-EBI. https://www.ebi.ac.uk/chebi/searchId.do?chebiId=CHEBI:140376.
- ↑ Widmer AF (March 2008). "Ceftobiprole: a new option for treatment of skin and soft-tissue infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus". Clin. Infect. Dis. 46 (5): 656–658. doi:10.1086/526528. PMID 18225983.
- ↑ Kosinski, Mark A.; Joseph, Warren S. (July 2007). "Update on the Treatment of Diabetic Foot Infections". Clinics in Podiatric Medicine and Surgery 24 (3): 383–396. doi:10.1016/j.cpm.2007.03.009. PMID 17613382.
- ↑ Kollef MH (December 2009). "New antimicrobial agents for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus". Crit Care Resusc 11 (4): 282–6. PMID 20001879.
- ↑ Takeda, S; Nakai, T; Wakai, Y; Ikeda, F; Hatano, K (2007). "In vitro and in vivo activities of a new cephalosporin, FR264205, against Pseudomonas aeruginosa". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 51 (3): 826–30. doi:10.1128/AAC.00860-06. PMID 17145788.
- ↑ Toda, A; Ohki, H; Yamanaka, T; Murano, K; Okuda, S; Kawabata, K; Hatano, K; Matsuda, K et al. (2008). "Synthesis and SAR of novel parenteral anti-pseudomonal cephalosporins: Discovery of FR264205". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 18 (17): 4849–52. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2008.07.085. PMID 18701284.
- ↑ Sader, H. S.; Rhomberg, P. R.; Farrell, D. J.; Jones, R. N. (2011). "Antimicrobial activity of CXA-101, a novel cephalosporin tested in combination with tazobactam against Enterobacteriaceae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Bacteroides fragilis strains having various resistance phenotypes". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 55 (5): 2390–4. doi:10.1128/AAC.01737-10. PMID 21321149.
- ↑ Craig, W. A.; Andes, D. R. (2013). "In vivo activities of ceftolozane, a new cephalosporin, with and without tazobactam against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Enterobacteriaceae, including strains with extended-spectrum β-lactamases, in the thighs of neutropenic mice". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 57 (4): 1577–82. doi:10.1128/AAC.01590-12. PMID 23274659.
- ↑ Zhanel, G. G.; Chung, P; Adam, H; Zelenitsky, S; Denisuik, A; Schweizer, F; Lagacé-Wiens, P. R.; Rubinstein, E et al. (2014). "Ceftolozane/tazobactam: A novel cephalosporin/β-lactamase inhibitor combination with activity against multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacilli". Drugs 74 (1): 31–51. doi:10.1007/s40265-013-0168-2. PMID 24352909.
- ↑ Podolsky, Daniel K. (1998). Cures out of Chaos. CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-4822-2973-8.[page needed]
External links
 |