Chemistry:Titanium(II) iodide
From HandWiki
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| TiI2 | |
| Appearance | black solid |
| Density | 5.2 g/cm3 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
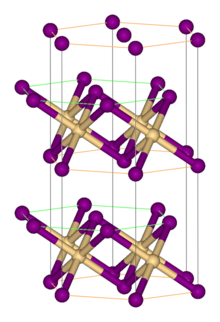
Titanium(II) iodide is the inorganic compound with the formula TiI2. It is a black micaceous solid. It adopts the cadmium iodide structure, featuring octahedral Ti(II) centers. It arises via the reaction of the elements:[1]
- Ti + I2 → TiI2
As such, it is an implied intermediate in the van Arkel–de Boer process for the purification of titanium metal.
References
- ↑ Klemm, Wilhelm; Grimm, Ludwig (1942). "Zur Kenntnis der Dihalogenide des Titans und Vanadins". Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie 249 (2): 198–208. doi:10.1002/zaac.19422490204.
| HI | He | ||||||||||||||||
| LiI | BeI2 | BI3 | CI4 | NI3 | I2O4, I2O5, I4O9 |
IF, IF3, IF5, IF7 |
Ne | ||||||||||
| NaI | MgI2 | AlI3 | SiI4 | PI3, P2I4 |
S | ICl, ICl3 |
Ar | ||||||||||
| KI | CaI2 | Sc | TiI4 | VI3 | CrI3 | MnI2 | FeI2 | CoI2 | NiI2 | CuI | ZnI2 | Ga2I6 | GeI2, GeI4 |
AsI3 | Se | IBr | Kr |
| RbI | SrI2 | YI3 | ZrI4 | NbI5 | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | AgI | CdI2 | InI3 | SnI4, SnI2 |
SbI3 | TeI4 | I | Xe |
| CsI | BaI2 | HfI4 | TaI5 | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | AuI | Hg2I2, HgI2 |
TlI | PbI2 | BiI3 | Po | AtI | Rn | |
| Fr | RaI2 | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | |
| ↓ | |||||||||||||||||
| La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | SmI2 | Eu | Gd | TbI3 | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |||
| Ac | ThI4 | Pa | UI3, UI4 |
Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | EsI3 | Fm | Md | No | Lr | |||
 |

