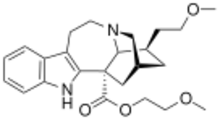
Chemistry:2-Methoxyethyl-18-methoxycoronaridinate
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C24H32N2O4 |
| Molar mass | 412.530 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
(−)-2-Methoxyethyl-18-methoxycoronaridinate (ME-18-MC) is a second generation synthetic derivative of ibogaine developed by the research team led by the pharmacologist Stanley D. Glick from the Albany Medical College and the chemist Martin E. Kuehne from the University of Vermont.[1] In animal studies it has shown similar efficacy to the related compound 18-methoxycoronaridine (18-MC) at reducing self-administration of morphine and methamphetamine but with higher potency by weight, showing anti-addictive effects at the equivalent of half the minimum effective dose of 18-MC. Similarly to 18-MC itself, ME-18-MC acts primarily as a selective α3β4 nicotinic acetylcholine antagonist, although it has a slightly stronger effect than 18-MC as an NMDA antagonist, and its effects on opioid receptors are weaker than those of 18-MC at all except the kappa opioid receptor, at which it has slightly higher affinity than 18-MC.[2][3]
See also
References
- ↑ Glick SD, Kuehne ME, "Ibogamine congeners", US patent 6211360, issued 3 April 2001, assigned to University of Vermont
- ↑ "Synthesis and biological evaluation of 18-methoxycoronaridine congeners. Potential antiaddiction agents". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 46 (13): 2716–30. June 2003. doi:10.1021/jm020562o. PMID 12801235.
- ↑ "Novel iboga alkaloid congeners block nicotinic receptors and reduce drug self-administration". European Journal of Pharmacology 492 (2–3): 159–67. May 2004. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2004.03.062. PMID 15178360.
 |
