Chemistry:Pozanicline
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H16N2O |
| Molar mass | 192.262 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
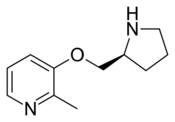
Pozanicline (INN,[1] codenamed ABT-089) is a drug developed by Abbott, that has nootropic and neuroprotective effects.[2][3][4] Animal studies suggested it useful for the treatment of ADHD[5] and subsequent human trials have shown ABT-089 to be effective for this application.[6] It binds with high affinity subtype-selective to the α4β2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and has partial agonism to the α6β2 subtype,[7][8] but not the α7 and α3β4 subtypes familiar to nicotine. It has particularly low tendency to cause side effects compared to other drugs in the class.[9][10]
Synthesis
Pozanicline is synthesized from 2-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine and Boc-L-Prolinol through a dehydration reaction followed by deprotection of the nitrogen atom of prolinol[11]
References
- ↑ "International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN). Recommended International Nonproprietary Names: List 62". World Health Organization. p. 257. https://www.who.int/medicines/publications/druginformation/innlists/RL62.pdf.
- ↑ "Structure-activity studies on 2-methyl-3-(2(S)-pyrrolidinylmethoxy) pyridine (ABT-089): an orally bioavailable 3-pyridyl ether nicotinic acetylcholine receptor ligand with cognition-enhancing properties". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 40 (3): 385–90. January 1997. doi:10.1021/jm960233u. PMID 9022806.
- ↑ "ABT-089 [2-methyl-3-(2-(S)-pyrrolidinylmethoxy)pyridine]: I. A potent and selective cholinergic channel modulator with neuroprotective properties". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 283 (1): 235–46. October 1997. PMID 9336329.
- ↑ "ABT-089 [2-methyl-3-(2-(S)-pyrrolidinylmethoxy)pyridine dihydrochloride]: II. A novel cholinergic channel modulator with effects on cognitive performance in rats and monkeys". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 283 (1): 247–58. October 1997. PMID 9336330.
- ↑ "Central nicotinic receptor agonists ABT-418, ABT-089, and (-)-nicotine reduce distractibility in adult monkeys". Psychopharmacology 136 (1): 50–8. March 1998. doi:10.1007/s002130050538. PMID 9537682.
- ↑ "ABT-089, a neuronal nicotinic receptor partial agonist, for the treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in adults: results of a pilot study". Biological Psychiatry 59 (11): 1065–70. June 2006. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2005.10.029. PMID 16499880.
- ↑ "Selectivity of ABT-089 for alpha4beta2* and alpha6beta2* nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in brain". Biochemical Pharmacology 78 (7): 795–802. October 2009. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2009.05.022. PMID 19481067.
- ↑ "Stimulation of dopamine release by nicotinic acetylcholine receptor ligands in rat brain slices correlates with the profile of high, but not low, sensitivity alpha4beta2 subunit combination". Biochemical Pharmacology 78 (7): 844–51. October 2009. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2009.06.024. PMID 19555668.
- ↑ "ABT-089: pharmacological properties of a neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist for the potential treatment of cognitive disorders". CNS Drug Reviews 10 (2): 167–82. 2004. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3458.2004.tb00011.x. PMID 15179445.
- ↑ "Neuronal nicotinic receptor agonists for the treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: focus on cognition". Biochemical Pharmacology 74 (8): 1212–23. October 2007. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2007.07.002. PMID 17689498.
- ↑ "ABT-089: pharmacological properties of a neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist for the potential treatment of cognitive disorders". CNS Drug Reviews 10 (2): 167–82. 2006. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3458.2004.tb00011.x. PMID 15179445.
 |
