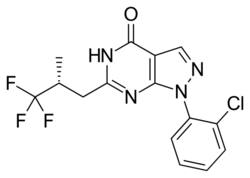
Chemistry:BAY 73-6691
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H12ClF3N4O |
| Molar mass | 356.73 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
BAY 73-6691 is a drug developed by Bayer for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. It was the first compound developed that acts as a phosphodiesterase inhibitor selective for the PDE9A subtype. The PDE9A enzyme is expressed primarily in the brain, with high concentrations in the cerebellum, neocortex, striatum, and hippocampus, and acts to limit the cGMP-mediated signal transduction which occurs following glutamate binding to NMDA receptors. Consequently, selective PDE9A inhibitors were predicted to prolong intracellular responses to glutamate and enhance glutamate signalling, and since this process is known to be involved in learning and memory, PDE9A inhibitors should have a nootropic effect and may be useful in the treatment of Alzheimer's.[1]
Animal studies have confirmed these expectations, and BAY 73-6691 has been shown to improve learning and memory in rats.[2] As the first selective PDE9A inhibitor to be developed, it is also widely used in research into the function of this enzyme subtype. However pre-clinical research is at an early stage and it is not yet known whether BAY 73-6691 will prove suitable to progress to human trials, or if it will remain merely a laboratory research tool.
References
- ↑ "Characterization of the first potent and selective PDE9 inhibitor using a cGMP reporter cell line". Molecular Pharmacology 68 (6): 1775–81. December 2005. doi:10.1124/mol.105.017608. PMID 16150925.
- ↑ "The novel selective PDE9 inhibitor BAY 73-6691 improves learning and memory in rodents". Neuropharmacology 55 (5): 908–18. October 2008. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2008.07.005. PMID 18674549.
 |

