Chemistry:Cefiderocol
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Fetroja, Fetcroja |
| Other names | RSC-649266 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a620008 |
| License data | |
| Routes of administration | Intravenous infusion |
| Drug class | Siderophore cephalosporins |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 56–58%[4] |
| Elimination half-life | 2.8 hours |
| Excretion | mainly kidney (60–70% unchanged) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
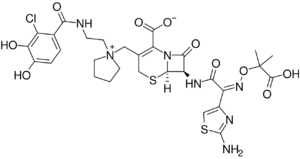
| Formula | C30H34ClN7O10S2 |
| Molar mass | 752.21 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Cefiderocol, sold under the brand name Fetroja among others, is an antibiotic used to treat complicated urinary tract infections when no other options are available.[5] It is indicated for the treatment of multi-drug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria including Pseudomonas aeruginosa.[6][7][8] It is given by injection into a vein.[1]
Common side effects include diarrhea, infusion site reactions, constipation and rash.[9]
Cefiderocol is in the cephalosporin family of medications.[5][10] It was approved for medical use in the United States in November 2019, and in the European Union in April 2020.[5][11][2] In September 2020, cefiderocol (Fetroja) received FDA approval[12] as supplemental New Drug Application (sNDA) for treatment of hospital-acquired bacterial pneumonia (HABP) and ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia (VABP) when caused by Gram-negative bacteria resistant to other antibiotics. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[13]
Medical uses
Cefiderocol is used to treat adults with complicated urinary tract infections, including kidney infections caused by susceptible Gram-negative microorganisms, who have limited or no alternative treatment options.[5][10]
In the United States, cefiderocol is indicated in adults 18 years of age or older who have limited or no alternative treatment options for the treatment of complicated urinary tract infections (cUTIs), including pyelonephritis caused by the following susceptible Gram-negative microorganisms: Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Enterobacter cloacae complex.[1]
For the treatment of severe pneumonia (HABP and VABP), it is indicated in patients 18 years of age and older whose pneumonia is not responding to other, more commonly used antibiotics and is confirmed to be caused by one of the following Gram-negative organisms:
- Acinetobacter baumannii complex
- Escherichia coli
- Enterobacter cloacae complex
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Serratia marcescens
This indication is supported by a study in which cefiderocol was not inferior to meropenem in treating nosocomial pneumonia caused by Gram-negative bacteria. The primary endpoint of the study was mortality due to any cause at day 14, where both antibiotics were shown to be equally effective.[14]
As of 2020, cefiderocol is indicated in the European Union for the treatment of infections due to aerobic Gram-negative bacteria in adults with limited treatment options.[2]
Adverse effects
Cefiderocol may cause serious and life-threatening allergic reactions, severe diarrhea caused by C. difficile and seizures.[9]
An increased rate of mortality was observed in people treated with cefiderocol as compared to other antibiotics in a separate clinical trial in critically ill people with multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections.[5][9] The higher rate was observed in people treated for hospital-acquired/ventilator-associated pneumonia (i.e., nosocomial pneumonia), bloodstream infections, or sepsis. The cause of death has not been established, but some of the deaths were a result of worsening or complications of infection, or underlying co-morbidities.[5] The safety and efficacy of cefiderocol has not been established for the treatment of these types of infections.[5] Hence, cefiderocol label includes a warning regarding the higher all-cause mortality rate.[5]
In 2021, the first cases of antibiotic resistance were reported,[15] and as of 2022 alarming proportions of up to 50% of resistance in some cohorts have been reported. In September 2022, the German RKI reported victims of the Ukraine War with cefiderocol resistant surgical infections (Klebsiella species and Acinetobacter baumannii) who had been treated in Germany.[16]
Pharmacology
Its structure is similar to cefepime and ceftazidime, but a chlorocatechol group at the end of the C-3 side chain further enhances its β-lactamase stability and renders it a siderophore.[17]
This means it enters into bacterial cells by binding to iron, which is actively transported into the bacterial cells.[1][18][19][20][21] It was the first siderophore antibiotic to be approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).[22] It bypasses the bacterial porin channels by using the bacteria's own iron-transport system for being transported in.[23] Once within the periplasmic space, cefiderocol dissociates from the iron and binds to PBPs, inhibiting peptidoglycan cell wall synthesis.[24]
Cefiderocol shows high stability against β-lactamases, with a broad spectrum of activity against all classes of carbapenemases, including serine-carbapenemases (class A such as KPC and class D such as OXA-48) and metallo-β-lactamases (class B such as VIM, NDM, and IMP).[25]
History
Cefiderocol received a Qualified Infectious Disease Product designation from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and was granted priority review.[5] In November 2019, the FDA granted approval of cefiderocol to Shionogi & Co. as an antibacterial drug for treatment of adults 18 years of age or older with complicated urinary tract infections (cUTI), including kidney infections caused by susceptible Gram-negative microorganisms, who have limited or no alternative treatment options.[5][11][1]
The safety and effectiveness of cefiderocol was demonstrated in a study (NCT02321800) of 448 participants with cUTIs.[5][9] Of the participants who were administered cefiderocol, 72.6% had resolution of symptoms and eradication of the bacteria approximately seven days after completing treatment, compared with 54.6% in participants who received an alternative antibiotic.[5] The clinical response rates were similar between the two treatment groups.[5] The trial included participants from Europe, United States and Mexico.[9]
In the clinical trial, participants with cUTI were chosen at random to receive cefiderocol, or another antibacterial drug called imipenem/cilastatin.[9] Both treatments were given intravenously for 7–14 days and neither the participants nor the health care professionals knew which drugs were given until after the trial was complete.[9] Participants could not be switched to an oral antibacterial drug to complete the treatment for cUTI.[9]
The benefit of cefiderocol was measured by the proportion of participants who achieved cure or improvement in their symptoms related to cUTI and a negative urine culture test in comparison to imipenem/cilastatin.[9]
In April 2020, Cefiderocol was approved for medical use in the European Union .[2]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 "Fetroja- cefiderocol sulfate tosylate injection, powder, for solution". 19 November 2019. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=75c0c785-38e0-4049-a6fb-b77581f5b35c.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 "Fetcroja EPAR". 24 February 2020. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/fetcroja.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ "Fetcroja Product information". https://ec.europa.eu/health/documents/community-register/html/h1434.htm.
- ↑ "Cefiderocol, a Siderophore Cephalosporin for Gram-Negative Bacterial Infections: Pharmacokinetics and Safety in Subjects With Renal Impairment". Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 57 (5): 584–591. May 2017. doi:10.1002/jcph.841. PMID 27874971.
- ↑ 5.00 5.01 5.02 5.03 5.04 5.05 5.06 5.07 5.08 5.09 5.10 5.11 5.12 "FDA approves new antibacterial drug to treat complicated urinary tract infections as part of ongoing efforts to address antimicrobial resistance". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 14 November 2019. Archived from the original on 16 November 2019. Retrieved 15 November 2019.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ "Cefiderocol: a novel siderophore cephalosporin". Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs 27 (2): 193–197. February 2018. doi:10.1080/13543784.2018.1426745. PMID 29318906.
- ↑ "Cefiderocol (S-649266), A new siderophore cephalosporin exhibiting potent activities against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other gram-negative pathogens including multi-drug resistant bacteria: Structure activity relationship". European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 155: 847–868. July 2018. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.06.014. PMID 29960205.
- ↑ "Cefiderocol versus imipenem-cilastatin for the treatment of complicated urinary tract infections caused by Gram-negative uropathogens: a phase 2, randomised, double-blind, non-inferiority trial". The Lancet. Infectious Diseases 18 (12): 1319–1328. December 2018. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30554-1. PMID 30509675.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 9.6 9.7 9.8 "Drug Trials Snapshot: Fetroja". 14 November 2019. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-approvals-and-databases/drug-trials-snapshot-fetroja.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 "Cefiderocol: A Siderophore Cephalosporin with Activity Against Carbapenem-Resistant and Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacilli". Drugs 79 (3): 271–289. February 2019. doi:10.1007/s40265-019-1055-2. PMID 30712199.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 "Drug Approval Package: Fetroja (cefiderocol)". 19 December 2019. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2019/209445Orig1s000TOC.cfm.
- ↑ "FDA Approves Fetroja (cefiderocol) for the Treatment of Hospital-acquired Bacterial Pneumonia and Ventilator-associated Bacterial Pneumonia" (in en). https://www.drugs.com/newdrugs/fda-approves-fetroja-cefiderocol-hospital-acquired-bacterial-pneumonia-ventilator-associated-5352.html.
- ↑ World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 22nd list (2021). Geneva: World Health Organization. 2021. WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2021.02.
- ↑ "Cefiderocol (S-649266) for Nosocomial Pneumonia Caused by Gram-Negative Pathogens: Study Design of APEKS-NP, a Phase 3 Double-Blind Parallel-Group Randomized Clinical Trial". American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. May 2018. doi:10.1164/ajrccm-conference.2018.197.1_MeetingAbstracts.A3290. https://www.atsjournals.org/doi/abs/10.1164/ajrccm-conference.2018.197.1_MeetingAbstracts.A3290. Retrieved 20 September 2020.
- ↑ Choby JE, Ozturk T, Satola SW, et al. Widespread cefiderocol heteroresistance in carbapenem- resistant Gram-negative pathogens. Lancet Infect Dis 2021; 21: 597-598
- ↑ "Infektionsmedizinische und chirurgische Herausforderungen durch Carbapenem-resistente bakterielle Erreger bei der Versorgung Kriegsverletzter aus der Ukraine". Epidemiologisches Bulletin 36/2022. 2022-09-08. https://www.rki.de/DE/Content/Infekt/EpidBull/Archiv/2022/Ausgaben/36_22.pdf.
- ↑ "Cefiderocol: Systematic Review of Mechanisms of Resistance, Heteroresistance and In Vivo Emergence of Resistance". Antibiotics 11 (6): 723. May 2022. doi:10.3390/antibiotics11060723. PMID 35740130.
- ↑ "Cefiderocol: Discovery, Chemistry, and In Vivo Profiles of a Novel Siderophore Cephalosporin". Clinical Infectious Diseases 69 (Suppl 7): S538–S543. November 2019. doi:10.1093/cid/ciz826. PMID 31724047.
- ↑ "Antibiotic 'Trojan horse' could defeat superbugs causing global medical crisis, trial finds". The Independent. 2018-10-26. https://www.independent.co.uk/news/health/antibiotic-resistance-bacteria-infection-superbug-ecoli-uti-symptoms-lancet-a8601641.html.
- ↑ "New 'Trojan horse' drug proves effective against antibiotic resistant bacteria". The Telegraph. 2018-10-26. ISSN 0307-1235. https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/2018/10/26/new-trojan-horse-drug-proves-effective-against-antibiotic-resistant/.
- ↑ "Antimicrobial Metallodrugs". Inorganic and Organometallic Transition Metal Complexes with Biological Molecules and Living Cells. Elsevier. 2017. ISBN 978-0-12-803887-1. https://www.elsevier.com/books/inorganic-and-organometallic-transition-metal-complexes-with-biological-molecules-and-living-cells/lo/978-0-12-803814-7.
- ↑ "Pharmacokinetics, Safety, and Tolerability of Cefiderocol, a Novel Siderophore Cephalosporin for Gram-Negative Bacteria, in Healthy Subjects". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 62 (3): 1–12. March 2018. doi:10.1128/AAC.02163-17. PMID 29311072.
- ↑ "Siderophore Cephalosporin Cefiderocol Utilizes Ferric Iron Transporter Systems for Antibacterial Activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 60 (12): 7396–7401. December 2016. doi:10.1128/AAC.01405-16. PMID 27736756.
- ↑ "Microbiological, Clinical, and PK/PD Features of the New Anti-Gram-Negative Antibiotics: β-Lactam/β-Lactamase Inhibitors in Combination and Cefiderocol-An All-Inclusive Guide for Clinicians". Pharmaceuticals 15 (4): 463. April 2022. doi:10.3390/ph15040463. PMID 35455461.
- ↑ "Cefiderocol: A Siderophore Cephalosporin". The Annals of Pharmacotherapy 54 (12): 1215–1231. December 2020. doi:10.1177/1060028020929988. PMID 32522005.
Further reading
- "Fetcroja: EPAR - Public assessment report". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 27 February 2020. https://www.ema.europa.eu/documents/assessment-report/fetcroja-epar-public-assessment-report_en.pdf.
External links
- "Cefiderocol". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://druginfo.nlm.nih.gov/drugportal/name/cefiderocol.
- "Cefiderocol sulfate tosylate". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://druginfo.nlm.nih.gov/drugportal/rn/2009350-94-9.
- Clinical trial number NCT02321800 for "A Study of Efficacy and Safety of Intravenous Cefiderocol (S-649266) Versus Imipenem/Cilastatin in Complicated Urinary Tract Infections (APEKS-cUTI)" at ClinicalTrials.gov
 |
