Chemistry:Europium(II) iodide
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Europium(II) iodide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| EuI2 | |
| Molar mass | 405.77 g/mol |
| Appearance | Tea yellow powder |
| Melting point | 510 °C (950 °F; 783 K) |
| Boiling point | 1,120 °C (2,050 °F; 1,390 K) |
| Soluble in THF | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Europium(II) iodide is the iodide salt of divalent europium cation.
Preparation
Europium(II) iodide can be prepared in a handful of ways, including:
Reduction of europium(III) iodide with hydrogen gas at 350 °C:[1]
- 2 EuI
3 + H
2 → 2 EuI
2 + 2 HI
Thermal decomposition of europium(III) iodide at 200 °C:[1]
- 2 EuI
3 → 2 EuI
2 + 2 I
2
Reaction of europium with mercury(II) iodide:[1]
- Eu + HgI
2 → Eu I
2 + Hg
Reaction of europium with ammonium iodide:[1]
- Eu + 2 NH
4I → EuI
2 + 2 NH
3 + H
2
Structure
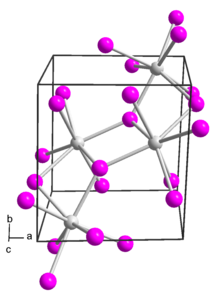
Europium(II) iodide has several polymorphs.[2] It adopts a monoclinic crystal structure in space group P 21/c (no. 14).[3][4]
It also adopts an orthorhombic polymorph in space group Pbca (no. 61). This form is isostructural with strontium iodide.[5]
A third polymorph of europium(II) iodide is formed if it is prepared from europium and ammonium iodide at low temperatures (200 K) in liquid ammonia. This low-temperature phase is orthorhombic and in space group Pnma (no. 62). This is the same structure as modification IV of strontium iodide.[6]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Brauer, Georg (1975). Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry. ISBN 3-432-02328-6.
- ↑ Wells, A. F. (1984). Structural Inorganic Chemistry (5th ed.). Oxford University Press. pp. 415–416. ISBN 978-0-19-965763-6.
- ↑ Bärnighausen, H.; Beck, H.; Grueninger, H. W.; Rietschel, E. T.; Schultz, N. (1969). "Neue AB2-strukturtypen mit siebenfach koordiniertem kation". Z. Kristallogr. 128: 430.
- ↑ Bärnighausen, H.; Schulz, N. (1969). "Die Kristallstruktur der monoklinen Form von Europium(II)-jodid EuJ2". Acta Crystallogr. B 25: 1104–1110. doi:10.1107/S0567740869003591.
- ↑ Bärnighausen, H.; Beck, H. P.; Grueninger, H. W. (1971). "Search Results - Access Structures". Rare Earths Mod. Sci. Technol. 9: 74–. https://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/structures/Search?Ccdcid=1621024&DatabaseToSearch=Published.
- ↑ Krings, M.; Wessel, M.; Dronskowski, R. (2009). "EuI2, a low-temperature europium(II) iodide phase". Acta Crystallogr. C 65: i66–i68. doi:10.1107/S0108270109038542.
| HI | He | ||||||||||||||||
| LiI | BeI2 | BI3 | CI4 | NI3 | I2O4, I2O5, I4O9 |
IF, IF3, IF5, IF7 |
Ne | ||||||||||
| NaI | MgI2 | AlI3 | SiI4 | PI3, P2I4 |
S | ICl, ICl3 |
Ar | ||||||||||
| KI | CaI2 | Sc | TiI4 | VI3 | CrI3 | MnI2 | FeI2 | CoI2 | NiI2 | CuI | ZnI2 | Ga2I6 | GeI2, GeI4 |
AsI3 | Se | IBr | Kr |
| RbI | SrI2 | YI3 | ZrI4 | NbI5 | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | AgI | CdI2 | InI3 | SnI4, SnI2 |
SbI3 | TeI4 | I | Xe |
| CsI | BaI2 | HfI4 | TaI5 | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | AuI | Hg2I2, HgI2 |
TlI | PbI2 | BiI3 | Po | AtI | Rn | |
| Fr | RaI2 | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | |
| ↓ | |||||||||||||||||
| La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | SmI2 | Eu | Gd | TbI3 | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |||
| Ac | ThI4 | Pa | UI3, UI4 |
Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | EsI3 | Fm | Md | No | Lr | |||
 |

