Chemistry:Hassium tetroxide
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Hassium tetraoxide | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Tetraoxohassium | |
| Other names
Hassium(VIII) oxide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
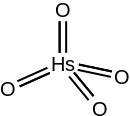
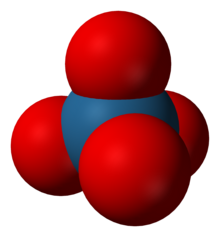
| HsO4 | |
| Molar mass | 334 g·mol−1 |
| Structure[1] | |
| tetrahedral (predicted) | |
| Related compounds | |
Other cations
|
Osmium(VIII) oxide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Hassium tetroxide (also hassium(VIII) oxide) is the inorganic compound with the formula HsO4. It is the highest oxide of hassium, a transactinide transition metal. It has little use outside of scientific interest, where it is often studied in comparison to osmium tetroxide and ruthenium tetroxide, its lighter octavalent group 8 element analogs.
Physical properties
Because of the extreme cost and difficulty of producing hassium, hassium tetroxide has never been obtained in macroscopic amounts, as only a few molecules have ever been synthesized. As a result, many of its physical properties are experimentally uncharacterized and unknown. However, most research available generally shows hassium tetroxide to behave like a typical congener to osmium tetroxide. Hassium tetroxide is less volatile than osmium tetroxide.[2][3][4]
Synthesis
Hassium tetroxide can be obtained by reacting atomic hassium with oxygen at 600 °C.[3][2]
- Hs + 2 O
2 → HsO
4
- Hs + 2 O
Reactions
Hassium tetroxide can be combined with sodium hydroxide in an acid-base reaction, in which case it acts like the acid, to form sodium hassate(VIII):[5]
- HsO
4 + 2 NaOH → Na
2[HsO
4(OH)
2]
- HsO
References
- ↑ Gulzari, Malli L. (2002). "Dramatic relativistic effects in atomization energy and volatility of the superheavy Hassium tetroxide and OsO4.". Journal of Chemical Physics 117 (23): 10441–10443. doi:10.1063/1.1527057. Bibcode: 2002JChPh.11710441M.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Chemistry of Hassium". Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung. 2002. http://www.gsi.de/documents/DOC-2003-Jun-29-2.pdf.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Düllmann, Ch. E.; Brüchle, W.; Dressler, R. et al. (August 2002). "Chemical investigation of hassium (element 108)". Nature 418 (6900): 859–862. doi:10.1038/nature00980. PMID 12192405. Bibcode: 2002Natur.418..859D.
- ↑ Hoffman, Lee & Pershina 2006, pp. 1714–1715.
- ↑ von Zweidorf, A.Expression error: Unrecognized word "et". (2003). "Final result of the CALLISTO-experiment: Formation of sodium hassate(VIII)". Advances in Nuclear and Radiochemistry. 3. Forschungszentrum Jülich. pp. 141–143. ISBN 978-3-89336-362-9. https://download.uni-mainz.de/fb09-kernchemie/jb2003/a2.pdf. Retrieved 2023-07-11.
Sources
- Hoffman, D. C.; Lee, D. M.; Pershina, V. (2006). "Transactinides and the future elements". in Morss, L. R.; Edelstein, N. M.; Fuger, J.. The Chemistry of the Actinide and Transactinide Elements. 3 (3rd ed.). Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Springer. pp. 1652–1752. ISBN 1-4020-3555-1. https://archive.org/details/chemistryactinid00katz.
 |

