Chemistry:Evodiamine
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
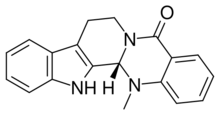
| Formula | C19H17N3O |
| Molar mass | 303.365 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Evodiamine is a chemical compound extracted from the plant genus Tetradium, which has been shown to reduce fat uptake in mouse studies. It is suspected that its mechanism of action is similar to that of capsaicin.[1] As such, it has been included in some dietary supplements. Neither its fat-burning effects in humans nor any potential side effects have been empirically established.
Evodiamine acts primarily as a thermogenic and stimulant.[2]
Evodiamine may also act by increasing the number of serotonin transporters available in the brain, enhancing the reuptake of serotonin.[3]
References
- ↑ "Capsaicin-like anti-obese activities of evodiamine from fruits of Evodia rutaecarpa, a vanilloid receptor agonist". Planta Medica 67 (7): 628–33. October 2001. doi:10.1055/s-2001-17353. PMID 11582540.
- ↑ "Evodiamine improves diet-induced obesity in a uncoupling protein-1-independent manner: involvement of antiadipogenic mechanism and extracellularly regulated kinase/mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling". Endocrinology 149 (1): 358–66. January 2008. doi:10.1210/en.2007-0467. PMID 17884939.
- ↑ "Berberine and evodiamine influence serotonin transporter (5-HTT) expression via the 5-HTT-linked polymorphic region". The Pharmacogenomics Journal 12 (5): 372–8. October 2012. doi:10.1038/tpj.2011.24. PMID 21647174.
 |

